The History of Life
advertisement

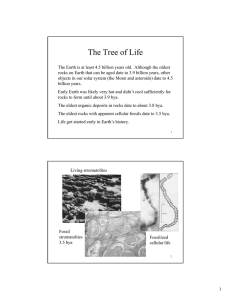
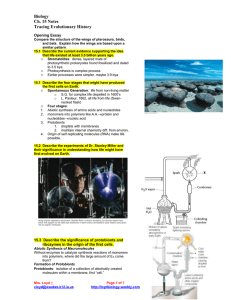
The History of Life An Introduction to Biological Diversity Early history of life Solar system~ 12 billion years ago (bya) Earth~ 4.5 bya Life~ 3.5 to 4.0 bya Prokaryotes~ 3.5 to 2.0 bya stromatolites Oxygen accumulation~ 2.7 bya photosynthetic cyanobacteria Eukaryotic life~ 2.1 bya Multicelluar eukaryotes~ 1.2 bya Animal diversity~ 543 mya Land colonization~ 500 mya The Origin of Life Spontaneous generation vs. biogenesis (Pasteur) The 4-stage Origin of life Hypothesis: – Abiotic synthesis of organic monomers – Polymer formation – Origin of Self-replicating molecules – Molecule packaging (“protobionts”) Synthesis of Organic Compounds Oparin /Haldane hypothesis: – Conditions of primitive earth – “Primordial Soup” – Volcanic vapors (reducing atmosphere) + lightning +UV radiation = complex molecule formation (no O2) Miller/Urey experiment: – Tested Oparin hypothesis – Heated “primordial soup”; added sparks and condensed – Produced some amino acids and other organic compounds – Some modern evidence suggests that this would not have been possible Other Possible Sources of Life Synthesis of organic compounds in deep sea vents (sulfur, iron, and no oxygen) Organic compounds arrived on meteorites from space Intelligent Design ??? Macromolecule Formation Amino acid polypeptides (proteinoids) – formed from amino acid solutions dripped on hot sand, clay or rock Protobionts (coacervates) – Abiotic macromolecules surrounded by a membrane-like structure – Could be the precursors to the first living cells The “RNA World” First genetic material was probably RNA (Cech/Altman) The first protobionts contained selfreplicating ribozymes Natural selection was able to occur due to base-pair mutations Geologic History of Earth Fossil record led to the creation of a geologic record of Earth’s history 3 Eons, further divided into Eras and Periods – Eras marked by mass extinctions of organisms Earth’s “History Clock” The First Prokaryotes First fossils= stromatolites – Rocklike structures composed of layers of bacteria Electron Transport Systems and ATP production Photosynthesis – Produced great levels of oxygen so that cellular respiration, etc. could occur Eukaryotes by Endosymbiosis First eukaryotes arose from the symbiosis of small prokaryotes inside of larger ones Multicellular Organisms Eukaryotes organized into colonies Cells became specialized so that they could not exist independently The “Cambrian Explosion” The sudden appearance of most major animal phyla within the first 20 million years of the Cambrian period – Sponges and cnidarians appeared earlier “Land, Ho!” Plants, fungi, and animals gradually colonized land Developed adaptations that allowed them to venture out of the water Continental Drift Earth’s crust is made up of ever-moving plates All of Earth’s landmasses were once joined in “Pangaea” The Evolution of Taxonomy 2-kingdom system (Aristotle, Linnaeus) 5-kingdom system (Whittaker, 1969) 6-kingdom system Three domain system