Key Terms for Chapter 3
advertisement

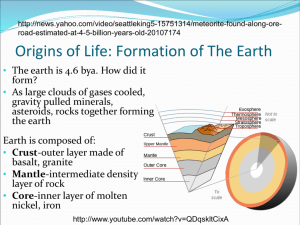
NVCC - Nesbitt Key Terms for Bio 101 - Chapters 19 and 20 biological species (Mayr) – defined by sexual repro between population members speciation modes – allopatric (physical separation); sympatric (no PS); parapatric repro isolation: prezygotic by mechanical, temporal, behavioral, ecological postzygotic by gamette mortality - ex. hybrid zygote dies or sterile (as mule) plant polyploidy (autopolyploids and allopolyploids) – no problems as in animals evolution models: gradual and punctuated (distinct spin-offs) evolutionary lines extinction – 98 percent of all species now extinct even though over 2M species Carl von Linne – father of taxonomy (organizing life by naming representatives) Linne’s binomial system, specific epithet for each using Latin names (kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species) Animala, Chordata, Mammalia, Carnivora, Canidae, Canis familiaris Animala, Chordata, Mammalia, Primates, Hominidae, Homo sapiens Major Kingdoms: Bacteria, Archaea, Protista, Plantae, Fungi, Animalia gymnosperms, angiosperms, dinosaurs, reptiles, etc. are the life forms prokaryotic, eukaryotic, eubacteria, archaebacteria - defined by nucleus endosymbiosis is thought to have resulted in the mitachondria and chloroplast earliest atmosphere: H2, N2, CO, CO2, no H2O; no O2 until after photosynthesis Some Milestones in Evolutionary History: 65 MYA – K/T dinosaurs go extinct; mammal begin adaptive radiation 250 MYA – 95 percent of all species lost in mass dieoff 900 MYA – all major lineages of life developed and diversity is underway 1.2 BYA – mitochondria deveop as do later chloroplasts, both symbionts 2.5 BYA – O2 release pathway develops that allows aerobic respiration 3.2 BYA – living cells begin to use cyclic path photosynthesis 3.8 BYA – first prokaryotes develop and use anaerobic pathways 4.6 BYA – start of a basis for life with cell precursor chemicals/compounds 12-15 BYA – the “big bang” that gave start to our universe