The Big Bang Theory All matter in the universe condensed into a
advertisement

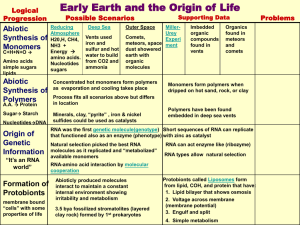
I. The Big Bang Theory A. All matter in the universe condensed into a singularity Singularity – a large mass (in the context of the Big Bang) B. Singularity makes up the universe and continues to expand II. The Solar System and the Sun A. Formation of the Sun 1. Cloud of interstellar dust and gases condensed 2. Dust and gas contracted under its own gravity, condensed, and heated until thermonuclear reactions formed the sun 3. Perfect size for sustaining life 4. Not too big to burn itself out; not too small to not have enough fuel to burn B. The Planets 1. Disk-shaped cloud of dust, gases, and other smaller pieces condensed to form planets 2. Occurred 4.6-4.5 billion years ago (BYA) Early Earth A. Temperature intense heat B. Weather 1. Intense lightning + volcanic activities 2. Violent meteor storms C. Atmosphere 1. Lack of ozone + O2 (leading to severe UV radiation to pass through) 2. Composed of H2O, CO2, CO, N2, CH4, and NH3 Early Life A. Organic monomers synthesized from inorganic substances B. Organic polymers and genetic material 1. Formed from existing monomers 2. Believed that hot sand or finely divided clay served as catalysts for synthesis C. Non-living clumps 1. Non-living clumps from organic polymers formed 2. Exhibited some properties of life but NOT ALIVE D. Prokaryotes 1. (Estimated) 4.1 – 3.5 BYA – first prokaryotes came into existence 2. Prokaryotes diversified into 6 kingdoms of life we recognize today (through Theory of Evolution) III. IV.