ratio analysis
advertisement

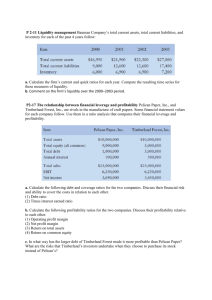
Business Analysis Types of Business Analysis Credit Analysis Equity Analysis Business Environment and strategy Analysis Financial Analysis Prospective Valuation Analysis Business Analysis Business Environment Analysis – Company’s economic & industry circumstances, SWOT Analysis , industry analysis Business strategy Analysis – Company’s business decisions leading to a competitive advantage, its product mix, cost structure Company profile and significant events Company shareholding pattern Roadmap to Financial Analysis Company Analysis Financial performance Revenues Profitability Asset Utilisation Cash flows Working capital Management Stock performance RATIO ANALYSIS A. Short term solvency Current ratio Liquid ratio Absolute liquid ratio Cash ratio Cash burn ratio B. Long term solvency Long term debt to equity Total debt to equity Total debt to total capital ratio Fixed assets to equity capital ratio Net tangible assets to long debt Financial leverage Interest coverage Cash interest coverage Debt service coverage Cashflow adequacy C. Profitability I.Overall profitability – Net Profit / Total invts IIComponents of profitability – Net profit / Sales / total investments III. Gross margin / Operating ratio / Net margin / Working capital T.o / Fixed Assets T.o Iv. Expenses / T.o , CA / CL /T.o Terms Capital employed = Equity shareholders funds + Preference share capital + Long term borrowed funds Net worth = Equity shareholders funds +/Deferred tax = Equity share capital + Reserves & surplus – Miscellaneous Expenditure not written off + Deferred tax Turnover = Sales ROI ratios 1. ROI = NP before tax and interest Total capital employed This ratio indicates the return earned by the company on its total investment. This is very important to shareholders and other stake holders as it is the ultimate measure of the company’s overall performance. This ratio when compared with industry average gives an indication about the financial performance of the company. 2. RONW = PAT – Preference dividend * 100 Net worth ( ESHs Fund ) This ratio indicates the return earned by equity shareholders. High ratio means high dividend , better growth prospects and high valuation in capital market. 3. EPS = PAT – Preference dividend Number of equity shares This ratio gives the return earned on each share. It is an important measure of profitability for the investors. This ratio is the basis for valuation of companies in the event of mergers etc, strategic investments by owners. Higher ratio shows company in a positive light. Higher ratio indicates higher returns Comparative Standards / Benchmarking Industry leader Industry average WACC Cost of borrowings Influencing factors Sales Cost economies Optimum capital structure Structural ratios / Gearing ratios / Long term solvency ratios 1. Debt equity ratio = Long term Debt Total net worth ( ESHs Funds + PC ) This ratio helps in assessing whether the company is relying on own funds or borrowed funds. Higher the debt more fixed liabilities by way of interest. FI s generally look for a D/E of 1.5 :1 while financing projects. This ratio also indicates whether the company has a optimum capital structure to improve the returns available to equity shareholders. 2. Debt service coverage ratio = NPBIT Interest + Loan repayment This ratio indicates the profits available to service the debts. This ratio is very important for lenders. Higher the ratio higher is the ability of the company to finance the debt and less risk of default. 3. Interest coverage ratio = NPBIT Interest Comparative Standards / Benchmarking Industry average NAV of industry leader / laggard Institutional norms Growth / Decline over the previous years Influencing factors ROI & EPS Dividend policy Liquidity ratios 1. Current ratio = Current Assets, loans & Advances Current liabilities & Provisions 2. Quick ratio = Current Assets, loans & Adv – inventories – prepaid Exp Current liabilities & Provisions– Bank overdraft These 2 ratios helps in analyzing the current assets and current liabilities of the company and its ability to discharge its day to day obligations Quick ratio is more realistic. It indicates the extent to which the company has current assets to meet its current liabilities. Higher the ratio higher is the solvency level of the company and less risk of default. Comparative Standards / Benchmarking Institutional norms Effective asset utilisation Cost economies Proportion of non cash charges in expense structure Influencing factors Proper asset liability management Credit period availed and credit period allowed Inventory management / Supply chain management/ level of obsolescence Efficiency ratios 1.Fixed assets turnover ratio = assets Net sales Net block of fixed Fixed assets are income generating assets for any company. This ratio indicates the efficiency with which the fixed assets are used to generate revenue. Higher the ratio better is the utilization of assets for generating sales. 2. Net worth turnover ratio = Net sales Net worth This ratio indicates the overall financial and operational efficiency of the company It is an indication about the optimum capital structure and production efficiencies of the company. 3. Debtors Turnover ratio = Net Sales Avg. Debtors This ratio indicates the number of times the debtors are converted into cash. 4. Average debt collection period = Avg. Debtors * 360 days Sales 5.Inventory Turnover ratio = COGS Avg. inventories This ratio shows the number of times a company’s inventory is turned into sales. 6. Avg. Inventory holding period = Avg inventories * 360 COGS Comparative Standards / Benchmarking Industry average Industry leader Trend over a period of time Influencing factors Production efficiencies Investment in relevant technologies Price and quality of products Profitability ratios 1.GP ratio = GP*100 Sales 2. Net profit ratio = PAT * 100 Sales These ratios study the profitability in relation to sales. It helps to assess the business performance starting from Gross Profit. Multi level profitability ratios helps to understand the levels at which there is pressure on margin ( profit ) Comparative Standards / Benchmarking Trend over a period of time Industry average Industry leader / laggard WACC Influencing factors Qualitative and quantitative growth in sales Age of fixed assets ( depn ) Cost of borrowing Efficient tax planning Valuation ratios 1. P/E ratio = Market price of equity share EPS This ratio is the most popular ratio for valuation of a company by the investors. This ratio indicates market confidence in the company and its future prospects. 2. Book value per share ( Net Asset Value ) = Net worth No. of equity shares This ratio measure the net worth per equity share. This ratio indicates the efficiency of the company’s management in building up reserves and its prudent financial practices. Comparative Standards / Benchmarking Industry average Leaders & laggards in industry Trend over a period of time Influencing factors Dividend policy Size of the company Market conditions NAV Analysts should take the following precautions Analysis of trends over a long period of time Interpretation of observation against industry bench mark Analysis of core ratios only Inter firm comparison for variations in accounting policies In case of conglomerates comparative performance of different lines of business