Osmosis and Diffusion - MMakris-Grade7
advertisement

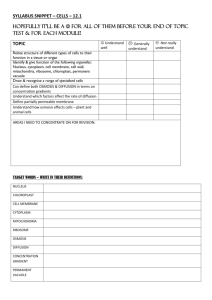
OSMOSIS AND DIFFUSION By: Raelee Robinson and Chantal Jabbour INTRODUCTION TO OSMOSIS AND DIFFUSION Diffusion Osmosis All living things have certain requirements they must satisfy in order to stay alive A cell membrane allows some substances to leave or enter the cell. Diffusion plays a part in moving substances into and out of a cell Concentration determines the direction that a substance takes through the cell membrane Particles move from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration until there is a balance – “equilibrium” The diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane is LESSON SEQUENCE Diffusion The movement of a substance from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration Diffusion is a passive process where substances move across a concentration gradient from high to low The process of diffusion creates equilibrium Molecules are in constant motion Lesson Sequence Osmosis A special type of diffusion Occurs when water molecules move across a partially permeable membrane (like a cell membrane) from a lower concentrated solution of a higher concentrated solution Solute particles are too large to pass through the membrane, so the water moves Lesson Sequence Diffusion and Osmosis in plant and animal cells Cell membranes are selectively permeable Solutions can be classified as hypotonic, hypertonic, and isotonic relative to their solute concentrations Water potential describes the tendency of water to leave one area in favour of another, it is affected by 2 factors: pressure and amount of solute (use examples of this in red blood cells, as well as potato cells) CURRICULUM EXPECTATIONS Grade 8: Understanding Life Systems: Cells Overall Expectations: 2. investigate functions and processes of plant and animal cells; 3. demonstrate an understanding of the basic structure and function of plant and animal cells and cell processes. Specific Expectations: 3.3 compare the structure and function of plant and animal cells 3.4 explain the processes of diffusion and osmosis and their roles within a cell TEACHING APPROACH Video demonstration on Diffusion and Osmosis TEACHING APPROACH Gizmo activity on diffusion. Students explore the motion of particles as they bounce across the screen and through an adjustable gap. Temperature, mass and initial number of particles can be altered. Lab Activity Investigation of Diffusion and Osmosis Using Eggs Prior to the lab, the teacher will dissolve the shells of 4 eggs using vinegar so that only the membrane remains on the egg to create a simulation of a cell. Materials: Eggs (see above) Water Water coloured with blue food colouring Molasses Corn syrup 4 beakers Toothpicks Procedure: Students will determine the mass of the eggs and record it in a table They should pour 150 ml of each substance into it’s own beaker, and then add an egg to each beaker and store in the fridge for 24 hours After 24 students remove the eggs from their beakers and record their observations. Students should record the volume of liquid in the beaker as well as the mass of the egg After recording their observations, students should use a toothpick to pop the egg membrane and record their observations Safety Students should wear safety goggles while popping the egg membrane with a toothpick The lab floor area should be cleared of all backpacks, stools etc The teacher should ask students if there are any allergies to the materials being used in the lab See teacher notes below, taken from sciencespot.net POTENTIAL STUDENT DIFFICULTIES Difficulty understanding the abstract concept of molecules and how they permeate a cell membrane Visuals including the Gizmo activity, web video animations, and lab activity may help the students to conceptualize the membrane’s qualities Difficulty with the concept of solutions’ “desire” to reach equilibrium The teacher can demonstrate this by using simple familiar demonstrations such as food colouring in water Difficulty applying and using vocabulary such as hypotonic vs. hypertonic, solute, solvent, concentration gradient etc correctly Students will have plenty of exposure to the correct use of vocabulary through the Gizmo, and multimedia introduced. They will practice their vocabulary and knowledge during the lab activity to identify the hypertonic and hypotonic solutions A Word Wall with the words and their definitions can be used REAL WORLD APPLICATIONS Diffusion How odours travel through air Pollution and air quality Mixing of substances Osmosis Water passing through plants from their roots Cooking with water Osmosis in medicine (red blood cell, kidneys) Preservation of fruits and meets Water Filters DIFFERENTIATED ASSESSMENT Students will work in partners and choose one of the following activities for their final assessment Interpersonal: Find someone who uses diffusion or osmosis in their career and conduct an interview asking them questions related to osmosis or diffusion and their job Spatial: Create a 2D or 3D display depicting the processes of diffusion and osmosis. Be sure to show both as separate processes. Spatial: Create a 2D or 3D display depicting the processes of diffusion and osmosis. Be sure to show both as separate processes. Linguistic: Write a diary or journal entry of a water molecule going through osmosis and diffusion. The entry should describe the process, and Logical: the differences thethe two. The studentsbetween will use computer in some way to create a demonstration of diffusion and osmosis. They can use any program the teacher approves. A summary chart must be included highlighting the similarities and differences of the two processes. Linguistic: Create a poem or mind map describing osmosis and diffusion, be sure to use as much unit vocabulary as possible.