Analyzing Environments
advertisement

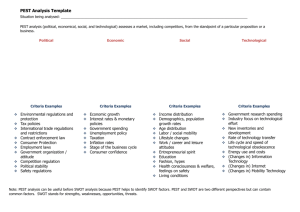
Chapter 4 Analyzing Environments © David O’Sullivan 4-1 Case > Riversimple Car http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iAfhDB0CDr4 http://www.gizmag.com 4-2 Reflections Outline a process for defining innovation goals Use techniques for conducting environmental analysis Understand the importance of benchmarking in innovation Explain how to develop statements such as mission and vision statements Identify stakeholders and their requirements Describe the process of strategic planning Outline the process of creating performance indicators 4-3 Activities [Discussion of selected student ‘Activities’ from previous chapter] 4-4 Learning Targets Outline the process of defining goals for an organization Understand the five-forces model used in business analysis Explain the difference between rational and incremental goal definition Explain the benchmarking process Understand the PEST process for environmental analysis Develop SWOT statements for innovation Begin the process of codifying critical data for innovation 4-5 Goal Planning 4-6 Perspectives of Goal Definition Rational perspective views goal definition as a conscious effort to structure the development of an organization toward a planned future Incremental perspective views goal definition as an ongoing stream of decisions regarding the development of the organization that eventually determines an organization’s future 4-7 Environment Analysis 4-8 PEST Analysis 4-9 PEST Analysis 4-10 Porter’s Five Force Model 4-11 Benchmarking 4-12 SWOT Statements (Sun Hotel) Strengths Family tradition Many years of experience and culture of hospitality among staff Multicultural staff Old infrastructure Weak marketing Aging (retiring) management Lack of experience in international cooperation City plans new annual festival to increase tourist market. City has great tourist potential. Government is expected to launch business expansion tax incentives. New hotels and hotel chains in city More demanding business travelers Health and safety legislation Weaknesses Opportunities Threats 4-13 Other Statements Statements is to communicate key messages and beliefs across the organization that will guide the behavior of all members Examples include Mission Vision Safety Quality 4-14 Core Competencies Core competencies can be viewed as the integrated set of abilities that distinguish an organization in the marketplace Organization’s can perform these core competencies better than competitors and add value to the customer 4-15 Strengths/Core Competencies Workforce Facilities Market Understanding Financial Know How Technology 4-16 Mission Purpose: Why the organisation exists Strategy: The competitive position and distinctive competence Values: What the organisation believes in Behaviour Standards: The policies and behaviour patterns that underpin the distinctive competence and value system 4-17 Ashridge Mission Model First Hanson Hewlett Packard Purpose The shareholder is king. Think of the pensioner living off her investments. Be respected by our customers, our people and society. Strategy Better financial discipline Knowledge of cash cows Skill at buying up and breaking up poor performing groups Better operators Better people, better motivated Engineering excellence New product development Better after sales service Values Individual responsibility Autonomy and accountability Efficiency is good Victorian work ethic Good people need space Informality is good Creativity is a human being’s ultimate purpose Caring is good Borrowing is weak Behaviour Standards Budgets must be met Managers work hard Keep businesses simple Decentralise Focus on short term financial performance Management by objectives MBWA (Management By Walking Around) Open door Team work Communication No Borrowing 4-18 Summary Outline the process of defining goals for an organization Understand the five-forces model used in business analysis Explain the difference between rational and incremental goal definition Explain the benchmarking process Understand the PEST process for environmental analysis Develop SWOT statements for innovation Begin the process of codifying critical data for innovation 4-19 Activities 4-20 Search Online http://mitworld.mit.edu/ The Art of Engineering (J. Dyson) Innovation Through Design Thinking (T. Brown) The World is Flat (T.L. Friedman) 4-21