Byzantine Empire and Orthodox Christianity
advertisement

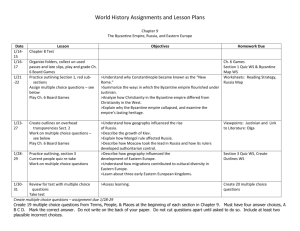
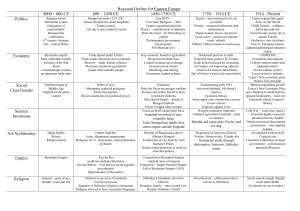
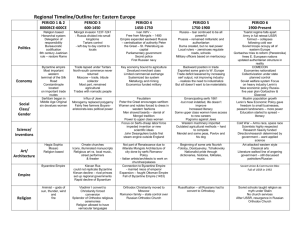
Byzantine Empire and Orthodox Christianity Europe During PostClassical Period Following fall of Roman Empire, 2 Christian societies emerged in Europe Western Europe: Roman Catholicism Eastern Europe: Orthodox Christianity The religion and culture of Eastern Europe was largely shaped by the Byzantine Empire. Map of Byzantine Empire http://guide-martine.com/images/history_byzantine3.jpg Origins of the Byzantine Empire Late in the Classical Period, Rome established an eastern capital at Constantinople (formerly Byzantium) Attempt to keep empire from collapsing Roman Empire eventually split into eastern and western halves East began to thrive, west experienced decline Byzantine Empire Both empires were hit hard by foreign invasion and disease in the late-classical period. BUT, Byzantine Empire survived, the Roman Empire did not Why was the Byzantine Empire stronger than that of Rome???? Thrived on trade Trade with Rome in decline Military derived from Middle Eastern provinces Rome hired foreign mercenaries Strong political and religious leadership in form of the Byzantine Emperor Roman Emperor and Pope competed for power Emperor Justinian Byzantine Empire flourished under Justinian’s rule Art, architecture, construction projects Hagia Sophia- church with world’s largest dome (at the time) Engineering marvel Created standardized system of law codes (Justinian Law Code) Maintain stability, unity, consistency Under Justinian, the Byzantine Empire extended its influence 533: Emperor Justinian attempted to reunite eastern and western halves of the old Roman Empire Failed Gained territory in N. Africa and Italy However, the Muslim empires will later conquer about half of the territory once controlled by the Byzantine Empire Mosaic of Emperor Justinian http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ima ge:Meister_von_San_Vitale_in _Ravenna_004.jpg Byzantine Society Emperor was ordained by God to be head of Church and state Patriarchal rule, but some women were able to hold throne temporarily In early days, women enjoyed some freedom, but became more restricted as time passed Practiced veiling and confinement of women Muslims later adopt these practices Religion in Byzantine Empire Initially, the Byzantines were under the authority of the Pope Over time, conflict arose between the Pope in Rome and the Byzantine Emperor in Constantinople Began to develop differences in religious practices 1054: Great Schism Official split in Church Roman Catholicism and Eastern Orthodox Government Under Byzantine Empire Complex centralized bureaucracy Mostly aristocrats in power positions Possible for other social classes to hold office Bureaucrats had to be well educated Most positions that were closest to the Emperor were held by eunuchs Provincial governors and spy network to maintain order Close tie between church and state Government Under the Byzantine Empire Focus on military Recruited local troops Exchanged military service for land that could be passed on to children Military helped fend off foreign invasions Regulation of the economy Controlled food prices Adopted silk making from China, allowing them to compete in luxury markets Government Sponsored trade with Europe, Asia, Arab Muslims, India Role of merchant class was diminished due to govt. involvement in trade Art and Architecture Strong Hellenistic Influence Domed buildings (adopted from Rome) Mosaics: use of small, colored pieces of glass, tile, stone to create an image Icon Painting: paintings of religious figures Often used rich colors such as blue and gold to signify the purity and brilliance of heaven http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Byzantine_Architecture Mosaic of Christ from Hagia Sophia http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Byzantine_art Hagia Sophia http://www.wayfaring.info/wp-content/uploads/2006/11/copy-of-hagia-sophia-west-view.jpg http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Hagia_Sophia_interior_March_2008.jpg Decline of Byzantine Empire Long decline Muslim Invasions Turkish Troops seized territory in Asia Slavic peoples rebelled and created independent kingdoms in Balkan Peninsula Crusaders 1453: Turkish Sultan and his army attacked Constantinople and seized the city Established the Ottoman Empire under Muslim control STOP PREPARE FOR QUIZ !!!!!!!!! Legacy of the Byzantine Empire Although the Byzantine Empire fell to Muslims in 1453, it left behind a cultural legacy in Eastern Europe Sent missionaries into Eastern Europe Conversions to Eastern Orthodox Christianity Taught the Slavic peoples a written language called Cyrillic Still used by many cultures of Eastern Europe Russia 6th-7th Centuries: ppl. From Scandinavia navigated the rivers of Russia on their way to trade with the Byzantine Empire Known as Varangians Established cities along major rivers Most important city was Kiev Legend states it became a monarchy in 855 First ruler was Viking named Rurik Became ruler of kingdom known as Keivan Rus Kievan Rus Kiev maintained close ties to the Byzantine Empire Adopted many cultural practices from the Byzantines Adopted use of Cyrillic alphabet (created by Byzantine Missionaries) 988: Vladimir I converted to Orthodox Christianity Most Russians were polytheistic before this conversion Went from polygamy to monogamy Began to model their art & architecture after those of Byzantine Empire Used wood rather than stone in most buildings Government in Kievan Rus Series of independent, rival kingdoms Local, decentralized rule Most people lived on communes, very little private ownership of land Created strong sense of community Kiev most powerful city, but did not create a centralized bureaucracy to unite all of Russia Close tie between church and state after the conversion to Orthodox Christianity Kievan Rus Religion became the center of life for people of Kievan Rus King of Kiev played major role in church Church was center of life in Russian towns and villages Scientific thought was overshadowed by the teachings of religious leaders Art was centered around religious figures Decline of Kievan Rus Over time, Kievan Rus went into decline Rivalry among various kingdoms Decline of Byzantine Empire affected the Russians 1240: Kiev and Russia fell under Mongol rule Russia forced to take orders from and pay tribute to the Mongol rulers (known as the Golden Horde) Mongols maintained rule until mid-1400’s Ivan the Great Under the rule of Ivan III, Moscow began campaign to end Mongol rule in Russia Quit paying tributes in mid-1400’s Conquests in Russia to unite major cities under Muscovite rule Mongol rule over by end of 1400’s More on Russia in next unit!