Greenhouse Simulation
advertisement
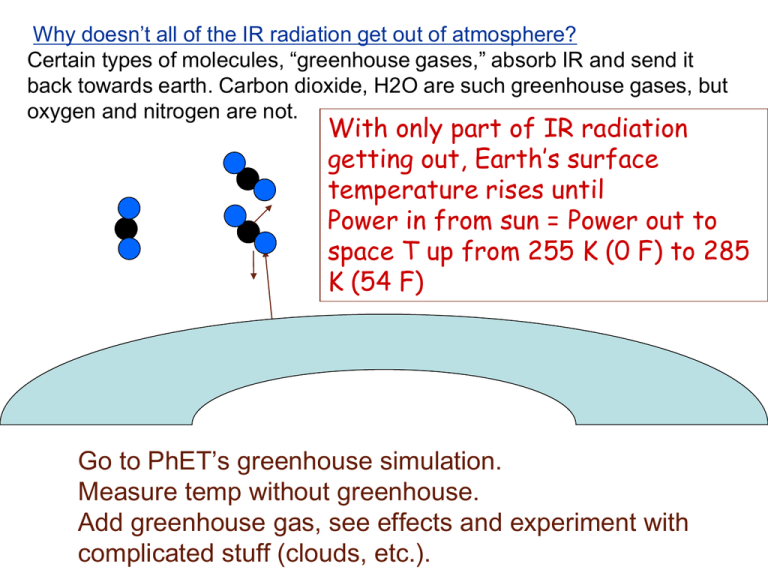
Why doesn’t all of the IR radiation get out of atmosphere? Certain types of molecules, “greenhouse gases,” absorb IR and send it back towards earth. Carbon dioxide, H2O are such greenhouse gases, but oxygen and nitrogen are not. With only part of IR radiation getting out, Earth’s surface temperature rises until Power in from sun = Power out to space T up from 255 K (0 F) to 285 K (54 F) Go to PhET’s greenhouse simulation. Measure temp without greenhouse. Add greenhouse gas, see effects and experiment with complicated stuff (clouds, etc.). How to calculate temperature when greenhouse effect? Powerin = solar power/m2 at earth * area of sunlight intersected by earth * fraction of sunlight absorbed by earth = 1380 W/m2 * πR2earth * 0.7 = = 1.22 x 1017 Watts(!) Temperature of surface of earth has to be a certain value so that Power out to space = Power in from sun Stefan-Boltzmann Law says Power out to space = 2.89 * 107 W/K4 * T4 * fraction of IR escaping If greenhouse gases absorb and emit IR such that only 61% of power radiated by earth’s surface gets into space, Pout = 0.61 * 2.89 * 107 W/K4 * T4. To conserve energy Pin = Pout, which means T is higher than before. 1.22 * 1017 W = 0.61 * 2.89 * 107 W/K4 * T4, solving for T, get T = (6.92 * 109)1/4 = sqrt (sqrt(6.92 * 109)) = 288 K. When the concentration of greenhouse gases goes up, the total power emitted by earth into space a. goes up. b. goes down. c. stays the same. Answer: c. stays the same. The atmosphere always has to just balance the amount coming in from sun or earth will rapidly heat up. The effect of greenhouse gases is to block some of the radiation going from the ground to space, so more leaving ground would be necessary to maintain the same amount leaving into space. power in = power out Add clouds to the simulation. What is the effect? a. Clouds decrease global temperature because they reflect part of sunlight back to space. b. Clouds increase global temperature because they absorb IR radiation from earth. c. Clouds increase global temperature because reflected sunlight is then absorbed by the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. d. b and c e. None of the above accurately describe the effect of clouds in the atmosphere.








