Memory - Barrington 220
advertisement

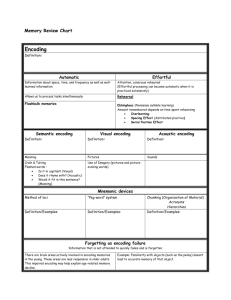
Memory The Phenomenon of Memory What is memory? Memory persistence of learning over time via the storage and retrieval of information • Flashbulb memories a clear memory of an emotionally significant moment or event The Structure of Memory • Information Processing Model • Memory involves • Encoding • Storage • Retrieval • A memory is not stored as one object Information Processing Encoding the processing of information into the memory system Storage the retention of encoded information over time Retrieval process of getting information out of memory Three types of memory Sensory Memory the immediate, initial recording of sensory information in the memory system Short-Term Memory activated memory that holds a few items briefly Long-Term Memory the relatively permanent and limitless storehouse of the memory system Sensory Memory • The initial recording of sensory information in the memory system • Iconic Memory • A fleeting photographic memory • Lasts only a few tenths of a second A Model of Memory Sensory input Attention to important or novel information Encoding External events Sensory memory Short-term memory Encoding Long-term memory Retrieving Memory Encoding: Getting Information In How We Encode Encoding Effortful Automatic How We Encode Automatic Processing unconscious encoding of incidental information space time frequency well-learned information word meanings we can learn automatic processing reading backwards How we encode • .citamotua emoceb nac gnissecorp luftroffE • Effortful processing can become automatic. • .ecitcarp elttil a sekat tsuj tI • It just takes a little practice. • .siht ta retteb gnitteg era ouy that ees ydaerla nac ouY • You can already see that you are getting better at this. How We Encode Effortful Processing requires attention and conscious effort Rehearsal conscious repetition of information to maintain it in consciousness to encode it for storage Effortful Processing • Studied by Hermann Ebbinghaus • Principles of effortful processing • The amount remembered depends on the time spent learning • Spacing effect • Serial position effect What We Encode • We encode meaning • We encode imagery • We encode organization Encoding Meaning • Semantic Encoding encoding of meaning including meaning of words Acoustic Encoding encoding of sound especially sound of words Visual Encoding encoding of picture images Encoding Meaning Encoding Meaning • Aoccdrnig to a rscheearch at Cmabrigde Uinervtisy, it deosn't mttaer in waht oredr the ltteers in a wrod are, the olny iprmoetnt tihng is taht the frist and lsat ltteer be at the rghit pclae. The rset can be a toatl mses and you can sitll raed it wouthit porbelm. Tihs is bcuseae the huamn mnid deos not raed ervey lteter by istlef, but the wrod as a wlohe. Encoding Imagery Imagery mental pictures a powerful aid to effortful processing, especially when combined with semantic encoding Mnemonics memory aids especially those techniques that use vivid imagery and organizational devices • Mnemonics • Method of Loci • Peg word • Chunking Organizing Information Chunking organizing items into familiar, manageable units like horizontal organization 1776149218121941 (1776) (1492) (1812) (1941) often occurs automatically use of acronyms HOMES--Huron, Ontario, Michigan, Erie, Superior ARITHMETIC--A Rat In Tom’s House Might Eat Tom’s Ice Cream Encoding: Chunking Organized information is more easily recalled Encoding: Hierarchies Hierarchies: complex information broken down into broad concepts and further subdivided into categories and subcategories Encoding (automatic or effortful) Meaning (semantic Encoding) Imagery (visual Encoding) Chunks Organization Hierarchies