Tissue - Cloudfront.net
advertisement

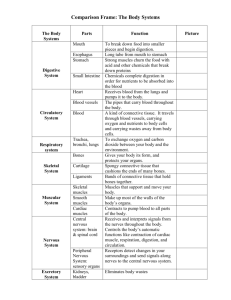
Miss Van Heuven There are many different types of cells in the human body. None of these cells would function well on their own, they are part of the larger organism that is called --- you. Cells group together to form tissues A collection of similar cells Join together to perform a specific function Tissues are 60-99% water with various dissolved substances This water is slightly salty in nature and is called “tissue fluid” Dehydration= when there is an insufficient amount of tissue fluid Edema= when there is an excess amount of tissue fluid Dehydration consequences: Deterioration of health Decrease in sports performance Depletion of energy Bad Mood! Quick Test: How fast does your skin bounce back? When you don’t get enough water, the effects can be devastating and even fatal! VIDEOS: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=e1L1jK2N 7OA http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=z8HlsY6T Ugk Take the following online quiz and see how you do! http://sportsmedicine.about.com/library/qui z/blquiz2_q1.htm 4 primary types of tissue in the human body: Epithelial Connective Muscle Nerve Covers the surface of the body and is main tissue in the skin Forms the lining of the intestinal, respiratory, circulatory, and urinary tracts Adds support and structure to the body 2 main classifications: Soft Hard Type 1: Adipose (fatty) tissue Stores fat as a food reserve or source of energy Insulates the body Fills empty areas and acts as padding Type 2: Fibrous tissue Ligaments and tendons Help hold body structures together Many sports require protective padding Where is our body’s natural protective padding? Cartilage and bone Cartilage = tough, elastic material that is found in between bones Cartilage acts as a shock absorber (padding) and allows for flexibility Why is bone considered “connective tissue”? Feel and compare the following: Jaw vs. Ear Cheek Points vs. Nose Special tissue that can contract and relax Produces power and action by movement of muscle fibers There are 3 main types: Skeletal (muscles attached to bones for body movement) Cardiac (muscles causing the heart to beat) Smooth (muscles in the walls of respiratory, digestive, urinary tract, and blood vessels) Controls and coordinates the body by transmitting messages (electrical signals) throughout the body Made of special cells called neurons The nerves, brains, and spinal cord are composed of nerve tissue Walk around the room…when teacher says “stop” extend your arms and grab 2 shoulders (on different people) Now let’s see if we can send a message through the entire chain like neurons! Messages to send: “Don’t mess this up (last person in line’s name)” “Only 5 weeks until Thanksgiving break!” You accidentally place your hand on the hot eye of the stove top: Nerve Tissue: sends message to brain that hand must be quickly removed Muscle Tissue: contracts to make hand move away from stove Soft Connective Tissue: acts as padding and prevents deeper damage Epithelial Tissue: damaged skin cells by extreme heat Answer the questions by holding up the correct/corresponding number with your fingers 1.) Epithelial Tissue 2.) Connective Tissue 3.) Muscle Tissue 4.) Nerve Tissue Ask the following questions to the class: The lining of your kidney The skin you are touching when you apply lotion Flexing your huge biceps How messages get sent throughout the body How your heart beats The bendable part of your ear Your shin bone Organ = structure containing at least 2 types of tissue working together for a common purpose Largest organ in the human body = SKIN! 3 layers of skin: Epidermis ▪ (Barrier between us and outside world) Dermis ▪ (Has blood vessels and nerves so we can feel things) Subcutaneous ▪ (Cushions the skin and protects us from the cold) A Body System is composed of organs working to accomplish something more complex than what a single organ can do on its own Body System = multiple organs connected to accomplish a goal together 11 Major Body Systems: Integumentary Muscular Skeletal Nervous Endocrine Circulatory Immune Lymphatic Respiratory Digestive Urinary Reproductive Consists of: Your SKIN! Helps protect your body from invasion Helps regulate your body temperature (sweating, shivering, hair growth, etc.) Produces movement Protects internal organs and bones Produces body heat Maintains posture Consists of: Skeletal muscles Smooth muscles Cardiac Muscles Voluntary vs. Involuntary Muscles Voluntary = we control ▪ Skeletal Muscles ▪ Our brain sends messages via our Nervous System Involuntary = we do not consciously control ▪ Cardiac and Smooth Muscles Wiggle your toes and fingers Kick your legs Squeeze your gluteus muscles 5 times Wiggle your lungs Wiggle your ears Make your heart stop beating Pat your head while rubbing your belly in a clockwise motion Reverse it! How do our muscles move??? 1.) Muscles are connected to bones by tendons 2.) Convert chemical energy into tension 3.) Produce movement simply by shortening (contraction) and then lengthening (relaxation) 4.) Muscles pull, but they cannot push! This is the body’s frame Bones, ligaments, cartilage, tendons Provides support and structure Helps to protect organs (ex: brain) Stores calcium, phosphorus, and produces blood cells 2 parts of Skeletal System: Axial Skeleton ▪ Skull, vertebral column, rib cage ▪ Protects organs, brain, nervous system Appendicular Skeleton ▪ Upper limbs, lower limbs, pelvic girdle ▪ Makes motion possible The Skeletal System: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8dRBe8JBVs **(Pause after 1:20)** What we would look like if we had no bones: http://www.imdb.com/video/hulu/vi11862023 93/ Coordinates and controls body activities Sends electrical signals through body Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Connects the CNS to the rest of the body ▪ Allows for motion and sensation Activity: 2 volunteers 1 student will be the “dummy” Teacher = Central Nervous System (creating messages to be delivered) Other student = Peripheral Nervous System (receiving messages and carrying them out in the body) (Student) wakes up in the morning and starts to walk to school (Student) looks at his/her watch and realizes he/she is late! So they he/she starts to run (Student) hears his/her favorite song playing from Miss V’s Jeep….so he/she starts to dance (Student) starts to eat his/her cali burrito while dancing (Student) see a hot boy/girl passing and gives him/her his/her sexy pose VIDEOS School House Rock!: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ivk_irrH1 WY Short Lecture: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x4PPZCL nVkA Produces and secretes hormones to regulate body processes Glands = group of cells that secrete (give off) chemicals Hormones: Regulate mood, growth, and development Allow reproductive processes Control metabolism Major parts: Hypothalamus Pineal Body Pituitary Thyroid and Parathyroid Pancreas Adrenal Reproductive (Testes or Ovaries) Go to the following website: http://kidshealth.org/teen/your_body/body_b asics/endocrine.html# 1.) List each part of the Endocrine System 2.) Define where it is found in the body 3.) Describe it’s function (Ex: Hypothalamus = Found in the lower central part of the brain, this portion of the Endocrine System is responsible for….) A.K.A: Cardiovascular System Consists of: Heart and blood vessels (Includes arteries and veins) A pumping heart forces blood to move in a circle throughout the system Blood: About 55% plasma ▪ (fluid containing water, proteins, sugar, hormones, etc.) Carries oxygen and nutrients to entire body Carries waste products away from cells Helps produce cells to fight infection Has clotting agents Our bodies actually have 2 Circulatory Systems: Systemic ▪ Carries oxygenated blood from heart to the rest of the body ▪ Returns deoxygenated blood back to heart Pulmonary ▪ Carries deoxygenated blood from heart to the lungs ▪ Returns oxygen-rich blood to the heart Let’s exercise our Circulatory System! Resting Heart Rate Heart Rate after 30 sec. of light exercise What a difference! (Lecture Clip) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oE8tGkP 5_tc Best Song Ever! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LqhvmU EdOYY **We will cover anatomy of the heart and circulatory system in our next unit** Breathes in oxygen Eliminates carbon dioxide Primary function = supply blood with oxygen that will be delivered to all parts of body Consists of: Nose and mouth Trachea/Throat Bronchi Alveoli Lungs Paper ball race Each side of the room will pick one person to represent their team The 2 elected representatives will race to blow a paper ball from one end of the table to the other **We will go over the Respiratory System more in the next lessons ** Video: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hc1YtXc_ 84A Song that will get stuck in your head! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p4zOXO M6wgE Go to the following website: http://www.lung.org/your-lungs/how-lungswork/ Click on each part of the Respiratory System Record each part in your notebooks and it’s role in the Respiratory System Consists of: Lymph nodes Lymph vessels Bone marrow Spleen Thymus Filters lymph Lymph = white watery fluid that is removed from blood during “cleaning process” Collects and transfers fluids and plasma back into bloodstream Assists with fighting infection Example: Doing the dishes Video: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KhXdNnTZUo http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qTXTDqv PnRk Works with Lymphatic System Our body’s defense system against disease and infection 3 types of responses to danger (in the order they occur): Anatomic response ▪ Physically prevents substances from entering body ▪ Ex: skin, stomach acid, membrane around organs, etc. Inflammatory system ▪ Pushes the invaders out of your body ▪ Ex: sneeze, cough, runny nose, fever, swelling Immune response ▪ White blood cells fight infection ▪ Works with Lymphatic System to filter out bacteria/infection Leukocytes (White blood cells) = our soldiers that fight the “bad guys” White blood cells made by bone marrow 1 volunteer will fight off invading bacteria Then 5/more volunteers will join powers to fight off that same bacteria The system is strong: white blood cells, anatomic response, inflammatory response, etc. Artistic Tutorial https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Nw27_j MWw10 Child cartoon https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WJEc2G DEfz8 Digests food (physically and chemically) Transports food Absorbs nutrients and converts to energy Eliminates waste Food’s path: Saliva and teeth slightly break down food Esophagus = stretchy 10 inch pipe connecting back of throat to stomach Epiglottis = flap that covers your windpipe Stomach = shaped like letter “J” stores and breaks food down into liquid And the path continues: Small Intestine: NOT SMALL! (Adult = 22 ft when stretched out) Extracts good stuff from food with help from Liver, Pancreas, and Gall Bladder Nutrients then go to Liver and are mixed into blood Waste moves on to Large Intestine And continues…. Large Intestine is fatter, but not longer than the small intestine Appendix = at the end, but no real function Colon = last chance to absorb nutrients (including H20) So material becomes hard… i.e: poop! Exits via the Rectum and finally the Anus Video: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=s1q2srfU U0g http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Z7xKYNz 9AS0 Filters blood to maintain fluid and electrolyte balance in the body Produces and eliminates urine You drink…you pee… but it is more complex than that: **Kidneys: filter waste from blood and produce urine Ureters = 2 thin tubes that take urine from kidneys to Bladder Bladder = a sac that holds urine until it is time to go Urethra = a tube that carries urine out of the body http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lfGYd1wr TgE Provides for reproduction Different for males and females Main male parts: Testes (where sperm are produced) and Penis Vas deferens (tube) carries semen (fluid containing sperm) into abdominal cavity and then out of the ejaculatory duct Main female parts: Vagina, uterus (receptacle for semen), and ovaries (produce the ova) Vagina is attached to uterus by cervix Uterus is attached to ovaries by fallopian tubes Fertilization = 2 types of sex cells (gametes) meet in the female reproductive organ: Sperm (male) and Egg/Ovum (female) Sperm combines with egg cell Characteristics passed onto offspring through genes