Road to Secession
advertisement

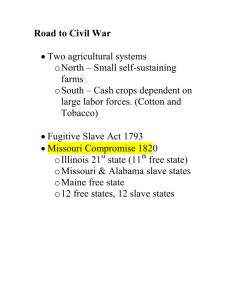
THE ROAD TO SECESSION US History Mrs. Lacks Causes of Civil War Civil war: war between two or more groups within one country The issue of slavery was one of many causes of civil war, as is the idea of states’ rights vs. rights of the federal government There are political, cultural, & economic causes Causes of Civil War Missouri Compromise Kansas-Nebraska Act/ Tariff of Abominations Bleeding Kansas Abolitionist Movement Dred Scott v. Sanford Wilmot Proviso Compromise of 1850 Uncle Tom’s Cabin Lincoln-Douglass Debates Harper’s Ferry, Va (WV) Election of 1860 Missouri Compromise Split the country politically into 2 parts: north & south Missouri enters union as slave state Maine enters union as free state Slavery banned in the Louisiana Territory north of the 36 30' line Wilmot Proviso Proposed by PA representative David Wilmot Said no slavery in Mexican Cession idea of “free soil” - allow slavery to exist where it already was but not spread into new territory constitutional issues - constitution protects property • slaves = property in south • Congress has no right to limit slavery in territories • would upset the balance bill failed!! Compromise of 1850 The Issues • California applied for statehood as a free state (does not fall under Missouri Compromise - not part of Louisiana Terr.) • northerners demand abolition of slavery in DC • south wanted north to enforce Fugitive Slave Act of 1793 Compromise of 1850 Very controversial How it passed: • President Taylor was dragging his heels – Senate feared he would veto the bill • July 1850 - Taylor died suddenly - succeeded by Millard Fillmore who supported the Compromise • September 1850 - Compromise passed COMPROMISE OF 1850 Political Par ties in 1840s Democrats (started with A. Jackson) Whigs (anti-Jacksonians) New parties forming: • Free-Soilers • Know-Nothings (Northern anti-immigrant (esp Irish), anti-Catholic, anti-free African) 1852 PRESIDENTIAL ELECTION √ Franklin Pierce Democrat Gen. Winfield Scott Whig John Parker Hale Free Soil Uncle Tom’s Cabin 1852 Sold 300,000 copies in the first year. 2 million in a decade! Harriet Beecher Stowe So this is the lady who started this big war. -- Abraham Lincoln K ansas-Nebraska Act divided Nebraska Territory into Nebraska and Kansas allowed them to decide slavery issue by popular sovereignty (let the people decide) did away with the 36 30' line of the Missouri Comp. "Death of the Missouri Compromise" K ansas-Nebraska Act Major results of Kansas-Nebraska Act • birth of the Republican Party • split Democratic party and destroyed already badly divided Whigs • Led to “Bleeding Kansas” Bleeding K ansas People rushed in to Kansas to vote for or against slavery when time came to hold elections, 1000s of “border ruffians” from neighboring Missouri (slave) came it and voted illegally Kansas became a slave state Bleeding K ansas Anti-slavery voters did not want to accept this Two capitals were established • Lecompton: proslavery • Topeka: anti-slavery Civil war erupted in Kansas when proslavery people attacked antislavery people “Bleeding Kansas” Border “Ruffians” (pro-slavery Missourians) Bleeding K ansas John Brown • Religious fanatic (thought he was God’s instrument) • Very antislavery • Started a massacre that led to the deaths of 200 proslavery citizens Sumner-Brooks Affair Senator Charles Sumner gave a speech denouncing slavery advocates, including Sen. Andrew Butler from SC 2 days after speech, Sen. Preston Brooks (SC and nephew of Butler) approached Sumner to confront him about his speech Brooks beat Sumner with his cane on the Senate floor Southerners cheered him and sent him new canes “The Crime Against Kansas” Sen. Charles Sumner (R-MA) Con. Preston Brooks (D-SC) “Bleeding Sumner” BIRTH OF THE REPUBLICAN PARTY, 1854 ß Northern Whigs. (anti-slavery) ß Northern Democrats. (anti-slavery) ß Free-Soilers. (anti-slavery) ß Know-Nothings. (restrictions on immigration) ß Other miscellaneous opponents of the KansasNebraska Act. 1856 PRESIDENTIAL ELECTION √ James Buchanan Democrat John C. Frémont Republican Millard Fillmore Whig 1856 Election Results Tariff of Abominations Still in tact since the 1820s Made South trade with North almost exclusively Southerners lost what could be made in Europe Led to the Panic of 1857 Increases Southern anger at North South Carolina tries to secede in 1858, but stays in Dred Scott v. Sanford, 1857 Dred Scott v. Sanford Dred Scott was a slave belonging to an officer in the US army taken from Missouri (slave) to Illinois (free) then to Wisconsin Terr. (Free by Missouri Comp) and back to Missouri after master died, Scott sued new master for freedom, claiming that since he had lived on free soil then he was free case went to Supreme Court - took 3 years to decide Dred Scott v. Sanford Chief Justice Roger B. Taney along with majority decided • Scott was still a slave, not a citizen, therefore had no right to sue in federal court • Congress had no power to prohibit slavery in the territories, therefore the Missouri Compromise was unconstitutional The Lincoln-Douglas (Illinois Senate) Debates, 1858 A House divided against itself, cannot stand. Lincoln-Douglass Debates Illinois Senate seat Incumbent: Stephen Douglass Challenger: Abraham Lincoln First series of open discussions/debates about slavery Lincoln-Douglass Debates Douglass: Popular Sovereignty Lincoln: let slavery stay in the South, but not extend to new territories in the west Lincoln lost, Douglass kept his Senate seat John Brown’s Raid on Harper’s Ferry, 1859 Harper’s Fer r y, Va John Brown led a band of men into Harpers Ferry in order to seize the federal arsenal and lead a slave rebellion (aka “army of emancipation”) they took 60 hostages and held out against the local militia finally surrendered to Marines under Robert E. Lee Brown wounded and taken prisoner convicted by Commonwealth of Va of treason, murder, and inciting slave rebellion 1860 PRESID John Bell √ Abraham Lincoln Republican ENTIALConstitutional Union ELECTI ON Stephen A. Douglas Northern Democrat John C. Breckinridge Southern Democrat 1860 Election Results Secession!: SC Dec. 20, 1860