Unit 1 Notes
advertisement

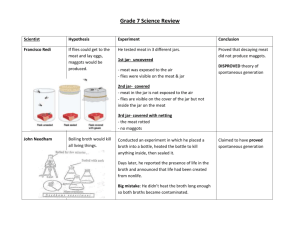
Unit 1: What is Biology I. What is Biology? A. Biology – study of life, of all living things 1. Many branches: biochemistry, cell biology, genetics, evolutionary theory, microbiology, botany, zoology, et. B. Six (6) Major Themes in Biology 1. Cell Structure & Function a) Unicellular – organisms made of one cell b) Multicellular – organisms made of more than one cell 2. Stability & Homeostasis a) Homeostasis – a level of stable internal environment in cells/living things 3. Reproduction & Inheritance a) Sexual Reproduction – DNA from 2 parts or 2 organisms is combined b) Asexual Reproduction – DNA is not combined, rather an organism copies its DNA and splits 4. Evolution a) Evolution – how organisms change and come to exist b) Natural Selection – “survival of the fittest”; drives evolution 5. Interdependence of Organisms 6. Matter, Energy, & Organization a) Organisms obtain, use, & transfer energy & matter b) Autotrophs – organisms that can make their own food to obtain energy c) Heterotrophs – orgnanisms that cannot make their own food, but must take it in for energy C. Characteristics of Life 1. Made of units called cells. • • Prokaryote Cell – cell that lacks a true nucleus and true organelles Eukaryote Cell – cell that has a true nucleus and true organelles 2. Reproduce 3. Based on a universal genetic code 4. Grow & develop 5. Obtain and use materials, and energy • Metabolism (Energy use) – sum of all chemical reactions in an organism 6. Respond to external environment 7. Homeostasis – maintain a stable internal environment 8. As a group, living things change over time II. Spontaneous Generation vs. Biogenesis A. Spontaneous Generation – early theory that nonliving material could give rise to living organisms B. Francesco Redi - In 1668, tested the theory of spontaneous generation, specifically that maggots come from rotting meat. Control Group - Placed raw meat in an open jar - In a few weeks, maggots were on the meat - Flies layed eggs on meat, maggots are fly larva Experimental Group - placed meat in a jar covered with netting - in a few weeks, maggots were on the netting - flies could smell meat, but only lay eggs on netting 3rd Experiment by Redi - Placed meat in a sealed jar - Maggots never appeared - Flies could not smell the meat Redi’s Experiment C. Lazzaro Spallanzani – 1768, microscopes have been invented & microorganisms are known to exist; tests the spontaneous generation of microorganisms. Control Group Experimental Group - Boiled broth to sterilize - boiled broth - Left flask open to air - sealed flask immediately - in several days, broth - in several days, broth remains was cloudy clear Spallanzani’s Experiment D. Louis Pasteur – 1862 1. Many refused to give up their belief in spontaneous generation. They argued that life required a “vital force”, and that Spallanzani killed this force and prevented it from entering by sealing the flask. 2. Pasteur completely disproved spontaneous generation and the idea of a “vital force”. Pasteur cont. 3. Pasteur boiled broth in a flask with a curved neck. This allowed him to sterilize the broth and leave in open for the “vital force”. After 1 year, the broth remained clear and sterile. FSGPT – Discuss and write down similarities and differences between the three scientists experiments. E. Biogenesis – current, accepted theory that living organisms can only arise from preexisting living organisms. III. Scientific Method Steps: A.Observing & Asking Questions 1. Observation – act of noting or perceiving objects or events by using the senses B. Formulating a Hypothesis 1. Hypothesis – possible explanation that can be tested by observation or experimentation. C. Perform an Experiment 1. Experiment – carried out under controlled conditions to test a hypothesis. A. Control Group – group used as a comparison; results are known B. Experimental Group – identical to control group except for one factor, making the outcome unknown. i. Independent Variable – the factor that is different in the experimental group ii. Dependent Variable – During the experiment, this is what is being observed or measured 2. Example: FSGPT Hypothesis – adding food coloring to a white flower’s water will change the flower’s color Control Group Experimental Group Independent Variable Dependent Variable - D. Analyzing Results – complete calculations, plot data, summarize observations, etc. E. Draw Conclusions & Verify Results 1. Draw conclusions that explain experimental results. 2. Verify conclusions by repeating experiments & checking other scientists results. F. Scientific Theories – highly tested, generally accepted principle that explains a vast number of observations and experimental data – Hypothesis = specific, testable prediction for a limited set of conditions – Theory = general explanation for a broad range of data