Grade 7 Science Review Scientist Hypothesis Experiment
advertisement
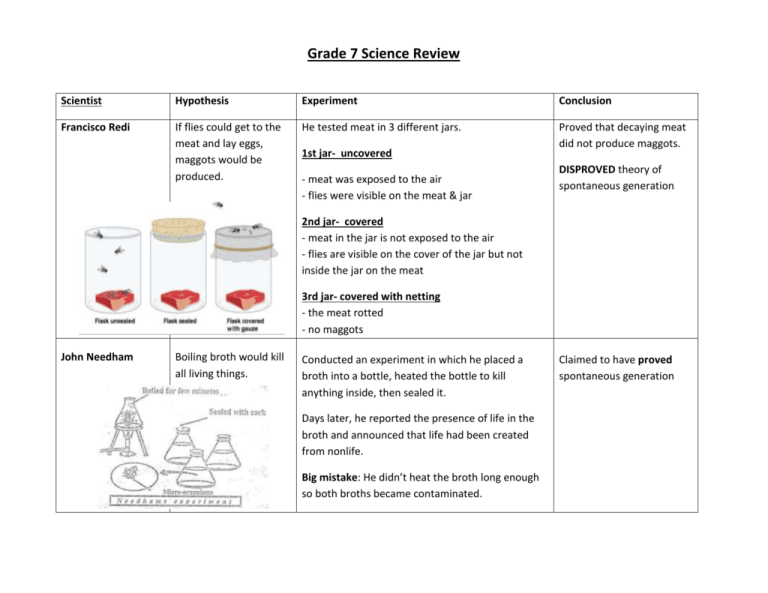
Grade 7 Science Review Scientist Hypothesis Experiment Conclusion Francisco Redi If flies could get to the meat and lay eggs, maggots would be produced. He tested meat in 3 different jars. Proved that decaying meat did not produce maggots. 1st jar- uncovered - meat was exposed to the air - flies were visible on the meat & jar DISPROVED theory of spontaneous generation 2nd jar- covered - meat in the jar is not exposed to the air - flies are visible on the cover of the jar but not inside the jar on the meat 3rd jar- covered with netting - the meat rotted - no maggots John Needham Boiling broth would kill all living things. Conducted an experiment in which he placed a broth into a bottle, heated the bottle to kill anything inside, then sealed it. Days later, he reported the presence of life in the broth and announced that life had been created from nonlife. Big mistake: He didn’t heat the broth long enough so both broths became contaminated. Claimed to have proved spontaneous generation Lazzaro Spallanzani Microbes come from the air. Boiling will kill microorganisms. Placed broth in two separate bottles, boiled broth in both bottles, then sealed one bottle and left the other open. Days later, the unsealed bottle contained small living things. The sealed bottle showed no signs of life. Boiling did NOT damage broth’s ability to support life, growth depended on the SEAL only. He put broth into several S-shaped flasks. Each flask was boiled and placed at various locations. He observed no life in the jar for one year. He then broke off the top of the flask, exposing it to the air, and noted life-forms in the broth within days. He reasoned that the contamination came from life-forms in the air. Disproved spontaneous 2 corrections he made: 1. boiled the broth and flask generation longer 2. sealed both flasks so no air could enter Louis Pasteur Microbes come from cells of organisms on dust particles in the air; not the air itself. Disproved spontaneous generation Definitions Spontaneous generation The idea that living things can come from non-living things Controlled experiment Very structured, always contains the independent variable and dependent variable Biogenesis The theory that living things come from only other living things Who discovered the microscope? Anton van Leeuwenhoek Theory A full explanation of an event in nature; subject to change Microorganism/Microbe Microscopic organism Pasteurization Sterilizing milk Sterile Free from bacteria, totally clean Other Concepts to Know 1. What are variables in an experiment? Factors to be tested 2. How many variables should an experiment test at one time? 1 3. What is a controlled experiment? Experimenter controls the variable to be tested; you control the IV 4. How a theory can be replaced or written – by interpreting existing data in new ways and including those views with new results 5. Identify the IV, DV & constant variables in an experiment. 6. Why did scientists in the 1800s use direct observation?