Notes for Chemistry of Life
advertisement

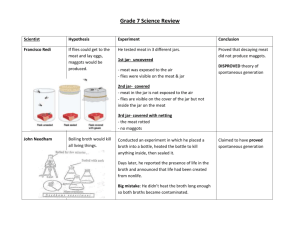
Notes for Chemistry of Life - Completed Dead – Living organisms that were once alive but are no longer Non-living – Not able to do all of the 8 functions nor were ever alive Living – Plant, animal or other life that performs ALL 8 FUNCTIONS (Nutrition, Respiration, Reproduction, Excretion, Growth, Response to Environment, Movement, Secretion) As it rains, we tend to see a lot more earthworms come out onto the sidewalks and pavements. Where did people long ago believe earthworms came from? Spontaneous Generation – The thought that living things came from non-living things. Francesco Redi – Italian doctor who challenged the theory of spontaneous generation. Draw a picture of Redi’s experiment and label each drawing Open – maggots appeared Netting – maggots formed on top of netting Closed – no maggots appeared What did Redi disprove? Spontaneous Generation What else did he discover by doing this experiment? Life cycle of fly Where do flies actually come from? maggots Louis Pasteur: A French chemist and microbiologist who also disproved the idea that microbes grew from organic matter, including things like juice. Here is the experiment: 3 S-shaped jars were used to figure out why broth was spoiling. Put broth in each jar, boiled, and after a few days, found no microbes living in broth (broth did not spoil). Noticed dust in S-shape neck – when broken, the broth became spoiled. Helped to discover Pasteurization. The 8 functions of Life 1. Nutrition: Take in food and water for energy and growth Example: eating and drinking 2. Respiration: Exchange and use of gases especially oxygen and carbon dioxide. This is what helps release energy from food. Example: Breathing 3. Reproduction: Producing more of it’s own kind. Survival of the species depends on it. 4. Excretion: Removal of wastes Example: urinating, crying, sweating, exhaling 5. Growth: Development and aging of organisms over time Example: trees grow taller, a wound heals 6. Response to environment: React to changes in its surroundings Example: Seedling bending towards the sun, geese migrating south, pupils dilating to dim light 7. Movement: Organism may move and materials inside also move Example: tree branches blowing and water flowing through the tree, we walk and run and our blood flows through our body 8. Secretion: Useful chemicals are made and given off Examples: saliva helps digest and swallow food, poison ivy secretes an oil that protects it from animals, hormones Basic Needs of Life: “MAWS” Minerals Air Water Sun **All living things need to interact with non-living things to survive!