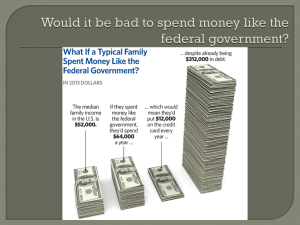
MyPoliSciLab Chapter 14 PRE-TEST QUESTIONS A budget deficit
advertisement

MyPoliSciLab Chapter 14 PRE-TEST QUESTIONS 1. A budget deficit occurs when a. Republicans control congress. b. Democrats control congress. c. The U.S. economy goes into recession. d. Expenditures exceed revenues in a fiscal year. e. Government programs are under-funded. Page reference: 442 2. When it comes to the federal budget, the American public wants a. A balanced budget. b. Keeping taxes low. c. Increased spending on most policies. d. All of the above. e. None of the above. Page reference: 443 3. Some critics of tax expenditures prefer to call them a. Give-aways. b. Fraud. c. Tax evasion. d. Tax loopholes. e. All of the above. Page reference: 447 4. What name is given to a tax, if everyone is taxed at the same rate? a. Progressive. b. Flat. c. Regressive. d. Sales. e. Tariff. Page reference: 444 5. The budget for national defense a. Decreased in the 1990s. b. Constitutes the bulk of the ‘uncontrollable’ expenditures of the United States budget. c. Constitutes over half of all federal expenditures. d. Is the driving force in the expansion of the federal budget. e. All of the above. Page reference: 453 6. The largest social policy of the federal government is in the area of a. Social Security. b. Health care. c. Education. d. Job training. e. Housing. Page reference: 454 7. When it comes to federal expenditures liberals prefer all of the following EXCEPT a. Spending for social programs, rather than military weapons. b. Using federal funds to support programs that assist individuals and groups in society. c. Using federal funds to provide food subsidies to the poor. d. Using federal funds to support drug rehabilitation programs. e. Investing the social security trust fund in the stock market. Page reference: 455 8. Budget items mandated by law or by a previous obligation are known as a. Uncontrollable expenditures. b. Increments. c. Fiscal mandates. d. Unfunded mandates. e. Procurements. Page reference: 457 9. Budget battles are highly political because they involve conflict between a. Political interest groups. b. Political ideologies. c. Government agencies. d. Programmatic interests. e. All of the above. Page reference: 457-458 10. What government agency has been established to carry out the budgeting decisions and tasks on the president’s behalf? a. The Internal Revenue Service b. The Congressional Budget Office c. The Treasury Department d. The Office of Management and Budget e. The Commerce Department Page reference: 458 11. By 2002, the budget deficit had increased again due to a. Decreased tax revenues. b. Income tax cuts in 2001. c. The war in Iraq. d. All of the above. e. None of the above. Page reference: 464 12. When was the last time the United States had a balanced budget? a. 2000 b. 1990 c. 1980 d. 1970 e. 1960 Page reference: 463 13. Some economists argue that less affluent voters will always use their votes to support policies that a. Cut all tax rates. b. Redistribute benefits from the rich to the poor. c. Favor large defense budgets. d. Keep taxes low. e. Increase spending on foreign aid. Page reference: 465 14. Support for redistribution of wealth, which fuels federal spending comes from a. The working class. b. Corporations. c. Interest groups like the agricultural lobby. d. Average citizens. e. All of the above. Page reference: 465 15. _______ are not unwilling victims of the big government and its big taxes in a democracy, they are at least its coconspirators. a. Citizens b. Members of Congress c. Presidents d. Bureaucrats e. Political parties Page reference: 466 16. Research has found that the public sector expands principally a. As a result of liberal politicians controlling the government. b. As a result of Federal Reserve Board monetary policies influencing interest rates and currency reserves. c. As a function of increased international economic competition. d. In response to changes in economic and social conditions that affect the public’s preferences for government activity. e. In response to the perceived need for increased defense expenditures. Page reference: 451 POST-TEST QUESTIONS 1. An excise tax is a. A tax on personal income. b. A tax on foreign goods. c. A tax on corporate profits. d. A tax on the manufacture, transportation, sale, or consumption of a good. e. A tax on property. Page reference: 443 2. How much income tax revenue comes from taxpayers with the top 10 percent of taxable incomes? a. ½ b. ¾ c. 2/3 d. 4/5 e. ¼ Page reference: 444 3. The ability of businessmen to deduct the cost of a “three-martini” lunch was an example of a a. Tax loophole. b. Social welfare tax. c. Tax reduction. d. Tax reform. e. Tax expenditure. Page reference: 447 4. Which of the following statements is closest to George W. Bush’s views on the deficit? a. The deficit must be reduced even if that means raising taxes. b. Tax cuts designed to stimulate economic growth are more important than worries over a growing deficit. c. Deficit spending is necessary during economic downturns in order to stimulate economic growth. d. Deficit spending is not a significant problem. e. Deficits are a useful way to shrink the size of government. Page reference: 449 5. In order of decreasing amounts, federal expenditures include: a. National defense, interest on the national debt, and direct payments to individuals. b. Interest on the national debt, national defense, and direct payments to individuals. c. National defense, direct payments to individuals, and interest on the national debt. d. Direct payments to individuals, national defense, and interest on the national debt. e. Direct payments to individuals, interest on the national debt, and national defense. Page reference: 451 6. The Social Security Act was adopted in order to a. Provide universal health care to elderly Americans. b. Provide compensation to unemployed workers during the Great Depression. c. Provide a minimal level of subsistence to older Americans. d. Provide emergency relief for needy families. e. Provide a social safety net for families with dependent children. Page reference: 454 7. The idea that last year’s budget plus a little more is the best predictor this year’s budget is known as a. Pay as you go. b. Expenditures. c. Appropriations. d. Incrementalism. e. Uncontrollable expenditures. Page reference: 456 8. An ‘uncontrollable’ expenditure in the federal budget is defined as a. Expenditures exceeding revenues so as to require borrowing to cover the difference. b. An expenditure that is required by current law or a previous government obligation to people automatically eligible for some benefit. c. An annual incremental increase in the cost of a program. d. One in which more money must be appropriated to handle a national crisis. e. The government’s allowance for meeting budget requests. Page reference: 456 9. The Senate committee charged that shares the responsibility of writing the tax codes is a. The Senate Finance Committee. b. The Senate Ways and Means Committee. c. The Senate Commerce Committee. d. The Senate Revenue Committee e. The Senate Banking Committee Page reference: 458 10. According to the Constitution, federal appropriations must be authorized by a. The General Accounting Office. b. The Office of Management and Budget. c. The President. d. Congress. e. The Secretary of the Treasury. Page reference: 460 11. A congressional process through which program authorizations are revised to achieve required savings is known as a. Appropriations. b. Reconciliation. c. Entitlement restructuring. d. Resolution. e. Controlling expenditures. Page reference: 462 12. According to the Gramm-Rudman-Hollings Act, spending that exceeded mandated limits would trigger a. Automatic budget cuts of entitlement programs. b. Automatic budget cuts of defense programs. c. Automatic budget cuts of international spending. d. Automatic budget cuts of both domestic and defense programs. e. Automatic increases in taxes. Page reference: 463 13. Economists Allen Meltzer and Scott Richard argue that the cost of government grows because a. Democracy works best at the federal level. b. Big government is necessary for the maintenance of a capitalists system. c. Democracy is by nature an expensive form of government to operate. d. People in a democracy use the government to secure benefits. e. Iron triangles pressure the government to expand their favored programs. Page reference: 465 14. When economists Allen Meltzer and Scott Richard say that government grows in a democracy because of the equality of suffrage, what do they mean? a. The larger number of poorer voters will always use their votes to support public policies that redistribute benefits from rich to poor. b. As voters age, the more need there will be for social security benefits. c. It is impossible to make the government smaller when there is a war on terrorism, which a large part of the population supports. d. Poor people only vote on issues regarding the government’s size. e. The smaller number of wealthy individuals will always vote against a larger government. Page reference: 465 15. Compared to other democracies, the United States has a ______ tax burden. a. Light b. Heavy c. Fairer d. More progressive e. Less complicated Page reference: 466 16. When it comes to big government and its big taxes, a. The redistributive attitudes of the poor are to blame. b. Democrats are to blame. c. Ronald Reagan’s defense initiatives are to blame. d. Major corporations that seek government bailouts are to blame. e. All citizens and interests of all kinds share in the blame. Page reference: 466 CHAPTER EXAM QUESTIONS 1. Supreme Court Justice Oliver Wendell Holmes, Jr. once said of taxes: a. “No taxation without representation.” b. “Taxes are what we pay for civilization.” c. “There is nothing in life more certain that taxes and death.” d. “I hate to pay taxes.” e. “Taxes are undemocratic.” Page reference: 443 2. Which of the following statements about the national debt is NOT true? a. Every dollar borrowed today will cost taxpayers many more dollars in interest in the future. b. Paying the interest on the national debt is optional. c. Nine percent of all federal expenditures go to paying interest on the national debt. d. All of the above are true. e. None of the above is true. Page reference: 446-447 3. To deal with deficits that some say resulted from the Reagan tax cuts of 1981, President Clinton sought to raise income taxes on a. The top 2 % of income earners. b. The top 5 % of income earners. c. The top 10% of income earners. d. The top 25% of income earners. e. Everyone equally. Page reference: 448-449 4. Which of the following was NOT a result of the Tax Reform Act of 1986? a. Several million low-income individuals were removed from the tax rolls. b. The number of tax brackets was greatly reduced. c. The value of many tax deductions were eliminated or reduced. d. None of these things resulted from the bill. e. All of these things resulted from the bill. Page reference: 450 5. Liberals argue that defense spending a. Is critical, as national defense is the first priority of government. b. Is insufficient to meet the mounting threats to national security. c. Shortchanges the poor while lining the pockets of defense contractors. d. Ought to be increased in order to create jobs in the defense industry. e. Is more important than spending on social programs. Page reference: 452 6. The main reason for decreased defense expenditures in the 1990s was a. Total U.S. dominance in the military technology. b. The election of George H.W. Bush. c. The breaking apart of the military industrial complex. d. Globalization and lower labor costs. e. Declining tensions with the end of the Cold War. Page reference: 453 7. The conservative view on social programs see them as a. Essential assistance for individuals and groups. b. More important than spending on new military technology. c. Worthy of increased taxes or increased borrowing. d. A drain on the federal treasury. e. A necessary evil. Page reference: 455 8. All of the following are features of incremental budgeting, EXCEPT a. The budget for any given agency tends to stay the same from year to year. b. Agencies can safely assume they will get at least the budget they had the previous year. c. Most of the debate and most of the attention in the budgetary process tends to focus on proposed increments of budgetary increases. d. Policymakers focus little attention on the budgetary base—the amounts agencies have had over the previous years. e. All of these are features of incremental budgeting. Page reference: 456 9. Social Security payments are an example of a(n) a. Increment. b. Index. c. Apportionment. d. Controllable expenditure. e. Entitlement. Page reference: 457 10. The Director of the Office of Management and Budget a. Is a career official. b. Is elected by the Council of Economic Advisors. c. Is a congressional appointee. d. Is a presidential appointee requiring approval of the Senate. e. Is appointed by the Senate Finance Committee. Page reference: 458 11. What is the legal deadline by which the president must submit a budget to Congress? a. The first Tuesday after the First Monday in November. b. The first of the calendar year. c. The first day of the new fiscal year. d. The first Monday in February. e. The fifteenth of April. Page reference: 461 12. Sequestrations are a. Joint meetings between members of the House and Senate designed to hammer out budget deals. b. Across the board spending cuts. c. Money allocated to specific programs within the budget. d. Money allocated to specific executive agencies within the budget. e. Money withheld to presidential initiatives by members of Congress. Page reference: 463 13. Cutting spending on Medicaid in order to increase Medicare benefits would be an example of a. Deficit spending. b. Pay as you go. c. Borrowing from Peter to pay Paul. d. Pork barrel spending. e. Sequestration. Page reference: 463-464 14. In 1990, Congress split discretionary spending into three categories: a. Domestic, defense, and international b. Social security, military, and debt relief c. Health care, environment, and defense d. Homeland security, national defense, and domestic e. Welfare, defense, and foreign aid Page reference: 463 15. Ironically, the very size of the federal budget means a. We more on social programs in the U.S. than any other country. b. Scarcity of fund helps to reign in spending and prevent significant government expansion. c. The American president is the most powerful businessman in the world. d. All of the above. e. None of the above. Page reference: 466