Byzantine Art and Architecture

The Byzantine Empire
The capital of the
Eastern Roman empire was changed to
Byzantium to provide political, economic and military advantages.
It was then renamed
Constantinople by
Constantine.
What military advantages do you see with this location?
Constantinople
Location of Constantinople
• Protection of the eastern frontier
• Distance from Germanic invasions in the Western Empire
• Crossroads of trade
• Easily fortified site on a peninsula bordered by natural harbors
Its location was a crossroads for trade connecting Europe with Asia and the Black
Sea with the Mediterranean Sea.
Role of Constantinople
•Seat of the Byzantine
Empire until Ottoman
(Muslim) conquest
•Preserved classical
Greco-Roman culture
•Center of trade
Istanbul Market
Greco-Roman Traditions
Byzantine families continued to educate their children in Roman and Greek grammar and literature through monasteries and private tutors, preserving Greco-Roman culture.
Meanwhile, in the west, Rome had been conquered by Germanic tribes that had no written language. As civilization declined in the west, it continued to flourish as the New Rome in
Constantinople.
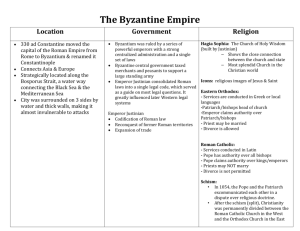
Justinian came to power in 527 AD as an absolute ruler
•As the first to codify Roman law,
Justinian provided the basis for the law codes of Western
Europe. Became known as
Justinian’s Code.
•Under Justinian, the Byzantine
Empire reached its height in culture and prosperity.
•Reconquest of former Roman territories in an effort to restore
New Rome to earlier glory
•Expansion of trade
Greek Orthodox Christianity and imperial patronage enabled the Byzantine Empire to develop a unique style of art and architecture.
Greek and Roman traditions were preserved in the Byzantine Empire.
What is imperial patronage? It means that the emperor supported and paid for beautiful pieces of art and the construction of buildings.
The Byzantines used domes and columns in their architecture. Christianity was the theme of
Byzantine art and mosaics were used to show religious ceremonies.
Mosaic of Constantine looking over his city
Byzantine Art and Architecture
•Inspiration provided by Christian religion and imperial power
•Icons (religious images)
•Mosaics in public and religions structures
•Hagia Sophia (a
Byzantine domed church)
Can you think of 5 adjectives to describe this artwork?
Icon
Hagia Sophia What elements of Roman Architecture do you see?
Byzantine Culture
•Continued flourishing of
Greco-Roman traditions
•Greek language
(as contrasted with
Latin in the West)
•Greek Orthodox
Christianity
•Greek and Roman knowledge preserved in
Byzantine libraries
Basilica Cistern
Valens Aqueduct
The cultural and political differences between the eastern (Byzantine) and western Roman
Empires weakened the unity of the Christian
Church and led to its division in 1054.
Western Church
Eastern Church
•Centered in Rome
•Farther from the seat of power after Constantinople
Became the capital
•Use of Latin Language in liturgy
•Authority of the Pope accepted
•Practices such as celibacy accepted
• Centered in Constantinople
• Close to the seat of power after
Constantinople became capital
• Use of Greek language in the liturgy
• Authority of the Patriarch accepted
• Icons prohibited – Iconoclasts destroyed images
Byzantine civilization influenced
Russian and Eastern
European civilizations through its religion, culture and trade.
Why?
Kievan Rus around 1050 CE http://www.drshirley.org/geog/map30c_rus.gif
Traders from Kiev (present day Ukraine) traveled down the Dnieper River to trade in the city of Constantinople. These traders were Vikings and Slavs (people of the region north of the Black Sea). The name “Slav” comes from Slave as many were sold in Constantinople as slaves.
Kiev would be one of Russia’s earliest civilizations
Dnieper
River
Constantinople which is
Istanbul today
Influence of Byzantine Culture on Eastern Europe and
Russia
•Trade routes between the
Black Sea and Baltic Sea
•Adoption of Orthodox
Christianity by Russia and much of Eastern Europe
•Adoption of Greek alphabet for the Slavic languages by St. Cyril
(Cyrillic Alphabet)
•Church architecture and religious art
Baltic and Black Sea Trade Routes http://www2.warwick.ac.uk/fac/arts/history/undergraduate/modules/hi127/programme/western/late_medieval_trade_routes.jpg
Cyril and his brother Methodius developed a new alphabet while trying to teach the
Bible to the Slavs.
The Slavs had no written language so
Cyril and Methodius worked to give them an alphabet.
The Cyrillic alphabet is still used today.
The Cyrillic Alphabet http://www.pbs.org/weta/faceofrussia/reference/img/cyrillicalphabet.gif
http://www.davidgoodwin.net/albums/album30/DSCF1565.sized.jpg
The use of Domes in church architecture was adopted from the Byzantines and were modified –
Russian domes are onion-shaped.
Constantinople
Role
Location
___________________________________
______________________________
______________________________
___________________________________
______________________________
___________________________________
______________________________
___________________________________
Justinian
Greco-Roman traditions
___________________________________
•As the first to codify Roman law, Justinian provided the basis for the law codes of Western
Europe. Became known as Justinian’s Code.
___________________________________
•Under Justinian, the Byzantine Empire reached its height in culture and prosperity.
___________________________________
•Re-conquest of former Roman territories in an effort to restore New Rome to earlier glory.
•Expansion of trade.
What was Imperial Patronage: _____________________________________________
Byzantine Art and Architecture
_________________________________
_________________________________
Influence of Byzantine
Culture on Eastern
Europe and Russia
_________________________________
_________________________________
The Great Schism (Split of the Christian Church)
West East
•Trade routes between the
Black Sea and Baltic Sea
•Adoption of Orthodox
Christianity by Russia and much of Eastern Europe
•Adoption of Greek alphabet for the Slavic languages by St.
Cyril (Cyrillic Alphabet)
•Church architecture and religious art