The Human Body Systems
advertisement

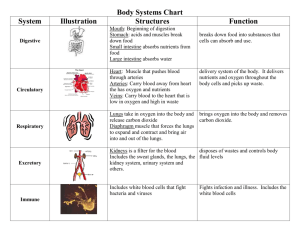
THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS MS. BROWNE GRADE 5 HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS UNIT SKELETAL SYSTEM Function • Support • Movement • Protection • Blood Cell Production Consists of: • Bones – 206 in adults • Joints – where bones meet • Tendons – attaches muscles to bones • Ligaments - attaches bones to other bones MUSCULAR SYSTEM Function • Movement of the body parts things within the body • Protection Consists of: • Muscles Smooth - inside organs Cardiac - heart/pumps blood Skeletal - controlled consciously RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Function • Breathing in oxygen and expelling carbon dioxide Consists of: • Mouth/Nose • Trachea – tube that • • Lungs – gives oxygen to blood and takes out CO2 allows air to pass through • Diaphragm – it contracts the neck in order to expand the lungs to breath in. Bronchi – carries air to the lungs from the trachea CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Function • Transportation system of blood throughout the body to deliver: Oxygen Nutrients Consists of: • Heart – muscle that pumps blood • Blood Vesicles – carry blood throughout body • Blood - consisting of red (carry oxygen) and white (fight infections) blood cells DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Function • Breakdown of food in order to receive energy for the body Consists of: • Mouth • Pharynx • Epiglottis • Esophagus • Stomach • Small Intestine • Pancreas • Large Intestine • Liver • Gall Bladder NERVOUS SYSTEM Function • Control center of all systems • Thinking Consists of: • Brain • Spinal cord • Nerves – receptor, motor, and afferent, efferent SKELETAL & MUSCULAR SYSTEM SKELETAL SYSTEM Function • Support • Movement • Protection • Blood Cell Production Consists of: • Bones – 206 in adults • Joints – where bones meet • Tendons – attaches muscles to bones • Ligaments - attaches bones to other bones SKELETAL SYSTEM Function: Support - provides the framework which supports the body and maintains its shape. *Draw a picture of what you think we would look like without our bones Movement – muscles connect to our bones in order to move our body Protection • Skull protects our brain • Ribs protect our lungs and other organs • Spine protects out spinal cord Blood Cell Production – Bone marrow that’s inside of our bones helps produce our red (carry oxygen) and white (fight infections) blood cells. See any system connections yet? SKELETAL SYSTEM An adult has 206 bones are in the body. We can keep them strong by making sure we digest lots of calcium for them. SKELETAL SYSTEM Joints Where bones meet SKELETAL SYSTEM Movable Joints - Forward and Backwards movement - Most movement - Bones glide against each other - Side to side movement SKELETAL SYSTEM Movable Joints - Elbows - Knees - Shoulders - Hips - Wrists - Ankles - Neck SKELETAL SYSTEM What Joints Are Being Used? • Wave to your friends • Sit down and stand up • Hula Hoop • Pitch a ball • Look before you cross the street • Do a dance • Push open a door SKELETAL SYSTEM Immovable Joints Fixed Joint - where segments of bone are fused together in the skull. MUSCULAR SYSTEM Function • Movement of the body parts things within the body • Protection Consists of: • Muscles Smooth - inside organs Cardiac - heart/pumps blood Skeletal - controlled consciously MUSCULAR SYSTEM Function Movement of the body parts like you arms and legs. Muscles are attacked to you bones in order to move them. things within the body such as the heart muscles pumping blood through your veins Protect your organ MUSCULAR SYSTEM Types of Muscles Voluntary Involuntary - Cardiac Muscles - Skeletal Muscles - Smooth Muscles MUSCULAR SYSTEM Think of a situation where you would use a voluntary muscle? How about an involuntary muscle? Can you think of a situation that would require both? MUSCULAR SYSTEM To allow movement, skeletal muscles work in pairs. While one muscle contracts, the other goes to its normal size. This is because muscles cannot extend. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Function • Breakdown of food in order to receive energy for the body Consists of: • Mouth • Pharynx • Epiglottis • Esophagus • Stomach • Small Intestine • Pancreas • Large Intestine • Liver • Gallbladder DIGESTIVE SYSTEM After the stomach, can you remember where the food goes next? DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Small Intestine After the stomach, food travels into the small intestine. The first part of the small intestine works with juices from the live, gallbladder, and pancreas to continue to break down our food. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Small Intestine The second part is where the food’s nutrients gets absorbed. Nutrients goes through the intestine walls and into the blood stream. The blood works to distribute these nutrients to the rest of the body. (What system does the digestive system work with here?) This nutrients from the food provides our body with energy, vitamins, and minerals that it needs in order to function and grow. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Large Intestine The last stage is the large intestine. Any food that the body doesn't need or can't use is sent to the large intestine where it water is absorbed from it. Later the food matter leaves the body as waste through the rectum.