Minerals: Functions & Sources - Animal & Vegan
advertisement
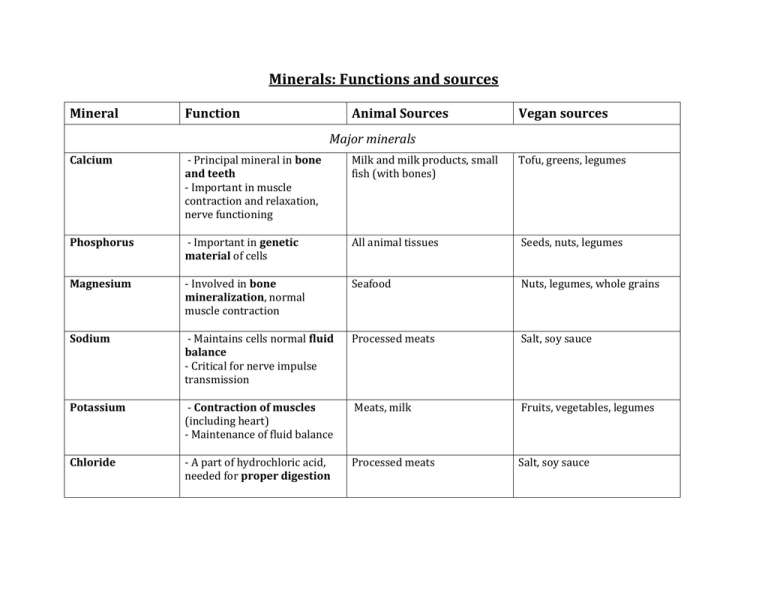
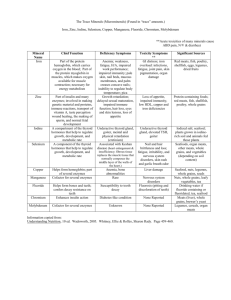
Minerals: Functions and sources Mineral Function Animal Sources Vegan sources Major minerals Calcium - Principal mineral in bone and teeth - Important in muscle contraction and relaxation, nerve functioning Milk and milk products, small fish (with bones) Tofu, greens, legumes Phosphorus - Important in genetic material of cells All animal tissues Seeds, nuts, legumes Magnesium - Involved in bone mineralization, normal muscle contraction Seafood Nuts, legumes, whole grains Sodium - Maintains cells normal fluid balance - Critical for nerve impulse transmission Processed meats Salt, soy sauce Potassium - Contraction of muscles (including heart) - Maintenance of fluid balance Meats, milk Fruits, vegetables, legumes Chloride - A part of hydrochloric acid, needed for proper digestion Processed meats Salt, soy sauce Trace minerals Iron - Part of hemoglobin (carries oxygen in blood) - Makes oxygen available to muscles Meat, fish, poultry Legumes, dried fruit Copper - Helps form hemoglobin - Part of several enzymes Organ meats, seafood Nuts, seeds, whole grains Zinc - Part of insulin and many enzymes - Necessary in sperm development and normal fetal development Protein containing foods: meats, fish, poultry Protein containing foods: grains, vegetables Iodine - A component of thyroid hormone (thyroxine), which helps to regulate growth, development and metabolic rate Seafood, animals that have been feed plants grown in the country Iodized salt, most plants grown in the country Fluoride - Helps form bones and teeth Seafood Tea Chromium - Associated with insulin, needed for energy release from glucose Meat Unrefined grains, vegetable oils Selenium - Assists a group of enzymes that defends against oxidation Seafood, organ meats Whole grains and vegetables depending on soil content