Cell Structure & Function
advertisement

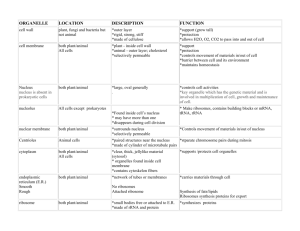
Cell Structure & Function Cell Theory • All living things are made up of cells. • Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things. • All cells are produced from other cells. Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. Two Types of Cells •Prokaryotic •Eukaryotic Prokaryotic “An organism whose cells lack a nucleus and some other cell structures.” • Do not have structures surrounded by membranes • Few internal structures • One-celled organisms, Bacteria Eukaryotic “An organism whose cells contain nuclei.” • Contain organelles surrounded by membranes • Most living organisms Plant Animal “Typical” Animal Cell “Typical” Plant Cell Cell Parts Organelles Cell Membrane • Outside cell boundaries that controls which substances can enter or leave the cell. • Double layer Cell Wall • A rigid layer of nonliving material that surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms. • Supports & protects cells • Surrounds cell membrane Inside the Cell Nucleus • The control center of a eukaryotic cell that directs the cell’s activities and contains the information that determines the cell’s form and function. • Separated from cytoplasm by nuclear membrane • Contains genetic material - DNA Nuclear Membrane • Surrounds nucleus • Made of two layers • Openings allow material to enter and leave nucleus Chromosomes • In nucleus • Made of DNA • Contain instructions for traits & characteristics • A doubled rod of condensed chromatin Nucleolus • Inside nucleus • Contains RNA to build proteins Cytoplasm • Gel-like mixture • Surrounded by cell membrane • Contains hereditary material Endoplasmic Reticulum • A cell structure that forms passageways in which proteins and other materials are carried through the cell. • Smooth type: lacks ribosomes • Rough type (pictured): ribosomes embedded in surface Ribosomes • Grain-like • Makes proteins • Some attach to endoplasmic reticulum; others float in the cytoplasm Mitochondria • Rod-shaped cell structures that convert energy in food molecules to energy the cell can use to carry out its functions. • Produces energy through chemical reactions – breaking down fats & carbohydrates • Controls level of water and other materials in cell • Recycles and decomposes proteins, fats, and carbohydrates Golgi Bodies • Protein 'packaging plant‘ • Move materials within the cell • Move materials out of the cell Lysosome • Small, round structures containing chemicals that break down certain materials. • Digestive 'plant' for proteins, fats, and carbohydrates • Transports undigested material to cell membrane for removal Vacuoles • Membrane-bound sacs for storage, digestion, and waste removal • Contains water solution • Help plants maintain shape Chloroplast • Usually found in plant cells • Contains green chlorophyll • Where photosynthesis takes place Compare and Contrast Plant and Animal Cells Animal Cells *Cell membrane *Cytoplasm *Vacuoles *Nucleus Plant Cells *Cell Wall *Cell Membrane *Cytoplasm *Vacuoles *Chloroplasts *Nucleus