4C Physics of Work and Machines
advertisement

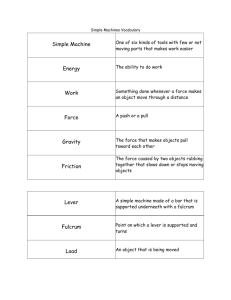
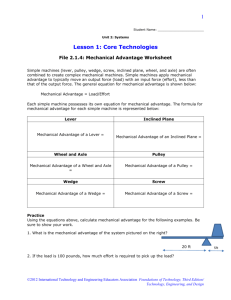
NOTE: This presentation was not made for public use. Please do not use this presentation without my permission and the permission of each of the authors of the photographs, quotes, and other materials that they contain. Thank you, Vicki Hughes Labs and Activities for this Presentation: (none) Work and Machines WORK Work = the use of force to move an object. Not all force that is used to move an object does work. For work to be done, the force must be applied in the same direction that the object moves. WORK Force If a force is applied in a different direction than the object moves, no work is done. NOT WORK direction Force Work, Force, and Distance Work is directly related to both the force applied and the distance moved. Work = Force x Distance Who is doing more work (pretend the weights are the same)? Arnold Sylvester http://www.schooltube.com/video/85de91bb7097c101fbda/Eureka-Episode-8-Work. Practice Problem #1 Work = Force x Distance Who is doing more work (weights are different)? Balloons = 0.5 N Height = 2.5 meters Work = 0.5 N x 2.5 m = 1.25 Nm Steel balls = 500 N Height = 2.5 meters Work = 500 N x 2.5 m = 1250 Nm Work, Force, and Distance Example: Todd pushed a 500 N box 4 meters across the floor. How much work did he do? Work = Force x Distance Work = 500 N x 4 meters = 2000 Nm Newton meters can also be called Joules (J). So… Work = 500 N x 4 meters = 2000 J Machines A simple machine is any device that makes work easier by changing the size or direction of a force. Machines • Machines that increase force (Examples: doorknobs, ramps, nutcrackers) • Machines that increase the distance over which a force is applied (Examples: paddles and hammers) • Machines that change only the direction of force (Examples: Rope systems on flagpoles) Machines An inclined plane is a sloped surface and changes the direction of the force. Wedge Screw Ramp Machines A lever is a bar that pivots on a point (fulcrum) changes the direction of the force. Bottle Opener Scissors Crowbar Seesaw Machines A pulley is grooved wheel that holds a rope or cable and multiplies force over distance. Fixed Pulley Moveable Pulley Machines A wheel and axle is a wheel on a fixed point that multiplies force over distance. Steering Wheel Door Knob Screwdriver Machines Input force = force that you apply to a machine. Output force = force that the machine applies to an object. Machines Mechanical Advantage of Machines Mechanical Advantage = Output Force Input Force Ideal Mechanical Advantage (IMA) = multiplication of input force that would be achieved in the absence of friction. IMA = Input Distance Output Distance Machines In the illustration below, a man pushes a heavy box up a ramp. Calculate the IMA. IMA = Input Distance = 6 m = 3 Output Distance 2 m This means that the output force is 3 times that of the input force. Practice Problem #2 A man uses a force of 30 N to push a 300-N box up a long ramp. What is the mechanical advantage of the ramp? MA = Fout = 300 N = 10 Fin 30 N ACT 23 Practice Problem #3 A woman uses a lever to move a load weighing 100 N over a distance of 0.1 m from the fulcrum. The woman applies a force of 20 N. How far from the fulcrum does she need to apply the input force? (ignore friction) Force due to load x distance from fulcrum = input force x distance from fulcrum Load = Output F1 x d1 = F2 x d2 d2 = F1 x d1 F2 d2 = 100 N x 0.1 m 20 N d2 = 0.5 m Air Pressure and Fluids Pressure is the result of force acting on a given area. Buoyancy is the force a fluid exerts on an object pushing it up. Archimedes’ Principle = size of the buoyant force of an object is equal to the amount of fluid it displaces. The buoyant force of this rock is 3 ml. 23 ml – 20 ml = 3 ml Oceanic and Atmospheric Pressure Fluids exert more pressure at greater depths due to all of the fluid above pressing down. Lower pressure Higher pressure Oceanic and Atmospheric Pressure Divers must ascend slowly with frequent pauses to allow their bodies to adjust to the decrease in pressure. What would happen to the diver’s body cells if he ascended to quickly? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LfCOnGHheok Oceanic and Atmospheric Pressure Air in the atmosphere acts as a fluid and exerts pressure that increases with depth. Why do people sometimes get headaches when traveling up a http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3bNI8TNkltQ high mountain? Pascal’s Law Pascal’s Law states that a change in pressure at any point in an enclosed fluid is transmitted equally throughout the fluid. pressure released pressure applied pressure transmitted Bernoulli’s Principle Bernoulli’s principle states that whenever the speed of flow increases, the fluid’s pressure increases. ACT 24 Buoyancy and the Titanic http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dnU3_GKSoxc Any Questions?