Work and Power
advertisement

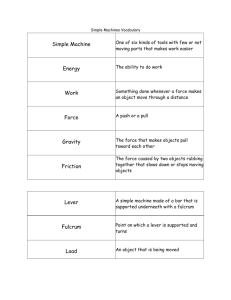
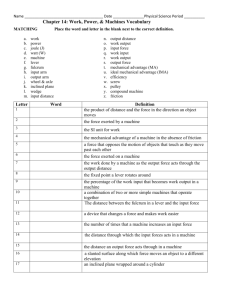
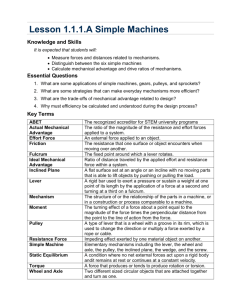
Chapter 14 Work, Power, and Simple Machines Work • Force acting through a distance • Must be movement • Work = force x distance Joule Newton meters Work • If the direction of the movement is Not the same as the force… NO work is done! applied force Motion Motion Applied force Is Work Done? SI unit of Work Joule = Newton x meter (J) = N x m A weight lifter lifts a 1600 newton barbell over his head. The barbell is lifted to a height of 2.0 meters. Calculate the work done. Work = Force x Distance A student rows a boat across a still pond with a force of 72 newtons. The student travels a distance of 13 meters Calculate the work done. Work = Force x Distance •Involves time Power • How fast is work done? • Power = Work / time Watts Joules seconds • Large amounts of power are measured in kilowatts Doing work faster requires more power. You can increase the amount of work done in a given time. OR You can do a given amount of work in less time. SI unit of Power Watt = Joule second (W) = J/s A truck pulls a trailer at a constant velocity for 100 m while exerting a force of 480 N for 1 minute (60 s). Calculate the work done and the power. Work = Force x Distance Power = Work time Complete the Math Practice on page 415 Horse- • equal to 750 watts power • 1 strong horse can move a 750 N object 1 meter in 1 second • 1 hp = small electric motor • family car = 100 hp • diesel train = 10,000 hp Energy, Work, Power, and Energy Worksheet Answers Part 1: Work and Power 1. Amy uses 20-N of force to push a lawn mower 10meters. How much work does she do? Part 1: Work and Power 2. Frank does 2400-J of work in climbing a set of stairs. If he does the work in 6 seconds, what is his power output? Part 1: Work and Power 3. A girl weighing 420 Newtons takes 55 seconds to climb a flight of stairs 18 meters high. What is her power output vertically? Part 1: Work and Power 4. How much work does an elephant do while moving a circus wagon 20 meters with a pulling force of 200-N? Part 1: Work and Power 5. A 40 N force is used to push a 2.00 kg cart a distance of 5 meters. What is the work done on the cart? Part 1: Work and Power 6. A 900-N mountain climber scales a 100 meter cliff. How much work is done by the mountain climber? Part 1: Work and Power 7. A small motor does applies a 200N force over 10m in 20 seconds. What is the power of the motor in watts? Section 14:2 WORK AND MACHINES Yes…machines do work Machine Work Input • makes work easier increase force increase distance change the direction • Work applied to the machine by you Work • Work done by the machine Output Work Input = Input Force x Input Distance Work Output = Output Force x Output Distance 14:3 Mechanical Advantage Number of times a machine multiplies the force applied Ex. Cracking Pecans Actual Mechanical Advantage The mechanical advantage determined by measuring the actual forces acting on a machine. Actual Mechanical Advantage = Output Force Input Force http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lo_BxRD WyRE Ideal Mechanical Advantage The mechanical advantage in the absence of friction. Ideal Mechanical Advantage = Input Distance Output Distance http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=E59b5D SJRvo A woman drives her car onto wheel ramps to perform some repairs. If she drives a distance of 1.8 meters along the ramp to raise the car 0.3 meter, what is the ideal mechanical advantage (IMA) of the wheel ramps? IMA = Input Distance Output Distance Complete the Math Practice on Page 425. 1. 6 2. 10 3. 2.5 m Part 2: Machines and Mechanical Advantage 1. 2. 3. Part 3: Torque The drawing above represents a wrench. The left end of the wrench is attached to a bolt. Four equal forces of 100N are applied as indicated in the drawing. A. A 100N force would cause the most torque if it was placed at which letter above? (Why) B. What is the torque at A C. What is the torque at C 4. What is the boy weight in order for the seesaw to be in equilibrium? 5. How far is the boy from the fulcrum in the see-saw in equilibrium below? Efficiency • How much work input is used to create work output • Eff. = Work output x 100% Work input Ex. Gas mileage = Miles driven Gallons of gas Complete the Math Practice on Page 426. 14:4Simple Machines Does Six work with one movement Types: √ Lever √ Inclined Plane √ Screw √ Wheel & Axle √ Wedge √ Pulley Lever http://www.neok12.com/video/SimpleMachines/zX7d4d664c41666974425163.htm • bar that is free to pivot around a fixed point called a fulcrum ________. •Classified in 3 categories fulcrum is 1st class: The _______ effort located between the ______ resistance and the _________. Output Force Input Force Fulcrum Ex. Seesaw, crowbar 2nd class: The ________ resistance is fulcrum located between the ______ effort and the _______. Input Force Output Force Fulcrum Ex. Wheelbarrow, hole punch effort 3rd class: The ________ is fulcrum located between the ______ resistance and the __________. fulcrum Input Force Ex. Baseball bat, rake Output Force Wheel and Axle Different sized wheels •_______ rotating together. • Ex: door knob, tires, can opener Inclined Plane http://www.neok12.com/Simple-Machines.htm • Sloping surfa ••ce Ex: ramp, slide •IMA = length/height 4 4 Wedge An inclined plane that moves Ex. Axe, sledgehammer Screw http://www.neok12.com/video/SimpleMachines/zX4b56517b586556415a5a45.htm An inclined plane wrapped around a cylinder Ex. lids Light bulb, bolts, Let’s make our own screw Take out a sheet of paper. Fold it at an angle. Tear along the crease. Slowly wrap it around your pen or pencil. Turn your pen/pencil. PULLEYS http://www.neok12.com/video/SimpleMachines/zX5c757c52524a4e59434f02.htm Cylinder with a rope, •_______ chain, or cable. •Three different types Fixed Pulley •A wheel is attached in a fixed location. •Rotate in place. •Ex. flagpole Movable Pulley •Attached to the moving object. •Ex. Sails Pulley System •Combines fixed and movable pulleys •Ex. Crane http://www.neok12.com/vid eo/SimpleMachines/zX7a7d457d065b 790405707f.htm Compound Machines Combination of two or more simple machines that operate together. Ex. Car, watch, washing machine