Physiology and behavior: Localization of function
advertisement

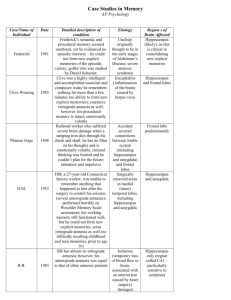
The Brain Physiology and behavior: Localization of function • Explain one study related to localization of function in the brain. Explain one study related to localization of function in the brain. Studies • Scoville and Milner • Maguire et al. Terms • Phrenology • Tan • Broca’s Area • Broca’s Aphasia • HM • Wernicke’s Aphasia • Hippocamous Early investigation of localization of function Phrenology • The attempt to make inferences about ones personality and intelligence by examining skull formation. • Done by manually searching for bumps and indentations. Franz Joseph Gall In general…. • If there is a bump or protrusion in that area it indicates MORE of that ability or trait. • If there is an indentation it indicates a deficiency of that ability or trait. Phrenology? • Do you think it is a valid science? • Work was picked up by Cesare Lombroso • These ideas, although dangerous, are still the basis behind modern day criminal profiling. Case studies of people with naturally occurring brain damage Phineas Gage Paul Broca • Worked with a patient he called “Tan” • “Tan” could only say the word “Tan” • “Tan” died Broca’s Area • In post-mortem autopsy, Broca found damage in the left frontal area of Tan’s brain. • Broca discovered the area of our brain that is responsible for making our mouth move during speech. Broca’s Aphasia • Aphasia means damage to a speech area of our brain. • Very common in TBI or stroke patients. Sarah Scott Studies of individuals who have undergone brain surgery Damage to the hippocampus and memory (The HM Study) Scoville and Milner (1957) • HM fell off his bicycle when he was 7, injuring his head. • He began having epileptic seizures when he was 10. • By the time he was 27 he had so many seizures he could not live a normal life. The HM Study Scoville and Milner (1957) • Scoville performed experimental surgery on HM to stop the seizures. • Seizures did stop, but HM had amnesia for the rest of his life. • We learned a whole lot from HM’s issues. HM • They removed parts of his temporal lobe. • They took out a little too much and removed part of his hippocampus. • Experienced both Retrograde and Anterograde Amnesia. Memories and the Hippocampus Retrograde Amnesia • Forget past. • It can be time period, event or select person. Anterograde Amnesia • Cannot form new memories. HM’s Memory • He could not transfer new episodic or semantic memories (explicit memories) into his LTM. • He COULD form new long-term procedural memories (implicit memories). • He could carry on a normal conversation (working memory) but would forget it almost immediately. OK…what actually happened to HM’s brain? • Corkin (1997) gave an old HM an MRI • He found missing parts of the temporal lobes and hippocampus and surrounding areas. • These areas tend to be pathways for memory (highways for ACH). What can be learned about the relationship between brain and memory with HM? • Our memory system is specialized and complex. • The hippocampus plays a critical role in converting memories of experience from STM to LTM. • HM retained some memories, so hippocampus does not store the memories, but processes them. Maguire et al. (2000) • Aim: To investigate whether or not the hippocampus plays a role in human spatial memory Maguire et al. (2000) Method: • London taxi drivers with a range of age and experience were the participants because their work requires the extensive use of spatial navigational skills • Matched pairs design: participants were age and gender matched with a control group • Two different types of MRI scanning were used to assess how the brains of the taxi drivers differed from the control group • Quasi experiment Maguire et al. (2000) • showed significantly more grey matter in both left and right hippocampi of the taxi drivers compared to the control group Maguire et al. (2000) Evaluation: • No ethical implications • Only observed males • Only observed 16 matched pairs • Nature vs. Nurture debate: did the driving influence the change in the hippocampus, or did their larger than average hippocampus lead them to become taxi drivers?