Implementation Planning (PPT 1.41 Mb)
advertisement

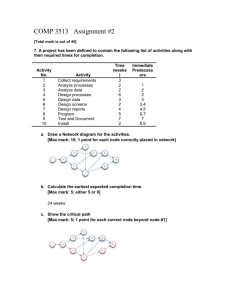
Action Implementation and Evaluation Planning • Whist the intervention plan describes how the population nutrition problem for a particular target group will be addressed (what type questions) • The implementation plan details the specific tasks of the intervention identifying who is responsible for each task, the resources required and the timeline within which the task should be completed (how, who, when and with what type questions) • Evaluation planning should occur in parallel with implementation planning to ensure the two processes are linked Implementation and Evaluation Planning Implementation and Evaluation Planning Planning for Implementation • Implementation planning starts with the strategy mix and systematically works through a process of: • Deconstructing strategies into activities Considering the time and resources required for this work Scheduling the sequence of work Assigning who is responsible for each piece of work An implementation plan is a core project management tool and provides a hierarchical breakdown of the work to be done for the intervention Implementation and Evaluation Planning Planning for Implementation • A possible process for identifying activities and tasks for each intervention strategy includes : Writing down each strategy (output) Breaking each output into sequential units of work; activities Break each activity into sequential smaller units of work called tasks confirm the activities and tasks are appropriately grouped and classified each completion of each set of tasks will result in achievement of the activity Move activities and tasks around as necessary give each item on the list a unique identifier to use as a reference → this information can be entered into a table for consultation Implementation and Evaluation Planning Developing Work Package Plans • • • • After identifying the activities and tasks required for achieving each output, work package plans for each output can be detailed – one for each strategy Developing work packages for intervention outputs allows transparency activities and identification of key milestones for each work package Each work package should be developed by the intervention player responsible for implementing the activities and tasks Work packages can be illustrated in various forms and usually include specific reference to the sequence and duration of activities Simple table format Gantt chart Implementation and Evaluation Planning Work package schedule – example simple table format Work package ID Description Who Scheduled start Scheduled finish 2.1 Indentify nutrition expertise + develop session curriculum Project manager 05 Feb 2009 18 Feb 2009 2.1.4 2.1.5 2.1.6 Develop, consult and pilot curriculum Nutritionist 20 Feb 2009 30 March 2009 2.2 Identify and book venue +catering Project officer 20 Feb 2009 05 March 2009 Predecessor WP 2 Implementation and Evaluation Planning 2.1 Work package schedule – example Gantt chart Implementation and Evaluation Planning Developing a Gantt Chart • A Gantt chart is a horizontal bar chart that shows intervention activities and tasks in sequential order where bars represent the time estimates • A Gantt chart is a flexible document that should be regularly updated through the life of the intervention • A Gantt chart can be used for day-to-day management, planning and reporting • A Gantt chart is useful to clarify planning estimates, work requirements and timelines with senior management Implementation and Evaluation Planning Developing a Gantt Chart • The process to complete a Gantt chart follows: List the work/work packages of the intervention – list each output in a separate cell in the first column Identify resources – list resources required for each activity in the next column Identify who is responsible – in the third column list who is responsible for delivering the activity Estimate timeframes – create a timeline for the project in the remaining columns Identify milestones – mark each significant event that acts as a progress marker (e.g. a black diamond) – add a milestone description Implementation and Evaluation Planning Developing Intervention Budgets • Budgeting is the determination of costs associated with the defined activities of the intervention • Developing an intervention budget involves calculating the cost of the activities of the intervention • A costing table can be developed for each strategy and then collapsed into a total intervention budget table Example cost titles include: • Personnel/staff Catering/ venue hire Travel Design/ publishing/ printing Implementation and Evaluation Planning Example - intervention costing table Personnel / Staff Catering/ Venue Hire Travel Design/ Publishing Phone/ Postal Activity 1.1 Activity 1.2 Activity 1.3 Activity 2.1 Activity 2.2 etc Implementation and Evaluation Planning Income TOTAL Developing Intervention Budgets • A costing table should include both direct and indirect costs • • Direct costs = resources that are actually expended on the project activities Indirect costs are ‘in-kind’ expenses the partnering organisations are going to contribute to support the intervention • A costing table should include a brief description of the items and calculation methodology • Estimating intervention costs may involve: Calling for quotes Estimating the staff time an activity will require seeking standard formulas for estimating on-costs and overheads Applying standard government and consultancy rates for staff/consultants Implementation and Evaluation Planning • Being able to accurately predict the resources needed to implement an intervention and justify this resource allocation is an important part of the grantsmanship process. • A submission that fails to explain and justify how each item of funding (eg. Salaries, travel costs, equipment) relate to the activities outlined in the plan is likely to be considered high and will generally not be funded. • Remember to show ‘in kind’ costs funding agencies like to see the organisation they are funding are also contributing to the intervention. Writing Action Statements Evaluation Planning • Intervention evaluation is the systematic collection of data to enable critical appraisal of an intervention’s activities and outcomes to produce sensible conclusions and useful proposals that improve intervention efficiency, effectiveness or adequacy In simple terms: • • Evaluation assesses whether the intervention objectives were met methods used were appropriate and well-organised Evaluation findings are fed back into planning process to improve the next phase of the intervention and future interventions Implementation and Evaluation Planning Evaluation Planning • Evaluation starts at the planning stages of an intervention and continues throughout the life of the intervention • It is important to plan evaluation strategies in parallel with implementation planning to: Ensure the two processes are linked and inform each other Inform stakeholders of the importance of evaluation Assure stakeholders of the internal validity of the intervention Increase participation in evaluation strategies Implementation and Evaluation Planning Levels of Evaluation • There are several different levels of evaluation in PHN practice: 1. Formative Evaluation - data collected prior to intervention implementation which is used to inform intervention design and assess capacity 2. Process Evaluation – assessed the intervention strategies and capacity building strategies 3. Impact Evaluation – measures whether the intervention objectives have been met 4. Outcome Evaluation – measures whether the intervention goal has been met 5. Economic Evaluation – measures cost-effectiveness of the intervention or intervention strategies Implementation and Evaluation Planning Action Statements and Evaluation Levels Relationship of goals and objectives to evaluation Problem reflected in Goal measured by Outcome evaluation Determinants reflected in Objective measured by Impact evaluation Strategies reflected in Strategy Activities measured by Process evaluation Implementation and Evaluation Planning Developing Evaluation Indicators • Planning for evaluation involves considering two fundamental elements of evaluation: 1. Identifying a criterion of good performance (indicator) 2. Gathering the necessary data through observation and measurement too make an assessment • • Indicators are specific measures that signify the point at which goals and objectives have been achieved and are used as the criteria in intervention evaluation Each objective and strategy should have at least one clearly defined indicator of success – with the data source clearly stated Implementation and Evaluation Planning • Evaluation planning should be heavily dependent and integrated with determinant analysis and related logic modelling. • Evaluation needs to answer the questions: – – – Has the intervention changed determinants? By how much? How and why? (or just as important questions such as why not?) Writing Action Statements