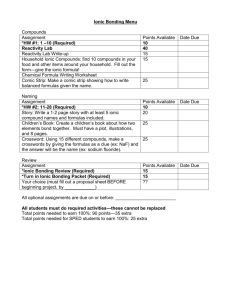
Chapter 7- part II
Ionic Compounds and Naming of Ionic compounds
Resources: Class powerpoint presentation
Textbook sections 7.2 and sections 9.1,9.2,9.5 (naming)
Simulations – Atoms and ions
http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulations/category/chemistry/general
Samples of Ionic compound and conductivity sticks
Chapter 7 reading and study guide
Prentice Hall review workbook – parts of Units 2 & 6
POGIL: Chemical formulas and Names of Ionic Compounds
Practice problems
Regents ref. Tables E, S and the Periodic Table
7.2
Ionic Bonds and Ionic Compounds
In many coastal countries
that have warm, relatively
dry climates, salt is
produced by the
evaporation of seawater.
You will learn how cations
and anions combine to
form stable compounds
such as sodium chloride.
Slide
2 of 25
© Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
End Show
7.2
Ionic Bonds and Ionic
Compounds
Formation of Ionic
Compounds
> Formation of Ionic Compounds
Compounds
composed of cations
and anions are called
ionic compounds.
What is the
electrical charge
of an ionic
compound?
Slide
3 of 25
© Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
End Show
7.2
Ionic Bonds and Ionic
Compounds
Formation of Ionic
Compounds
> Formation of Ionic Compounds
Compounds
composed of cations
and anions are called
ionic compounds.
What is the
electrical charge
of an ionic
compound?
Although they
are composed of ions,
ionic compounds are
electrically neutral.
Slide
4 of 25
© Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
End Show
7.2
Ionic Bonds and Ionic
Compounds
> Formation of Ionic Compounds
Aluminum metal and
the nonmetal bromine
react to form an ionic
solid, aluminum
bromide.
Slide
5 of 25
© Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
End Show
7.2
Ionic Bonds and Ionic
Compounds
> Formation of Ionic Compounds
Ionic Bonds
The electrostatic forces that hold ions together in
ionic compounds are called ionic bonds.
Slide
6 of 25
© Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
End Show
7.2
Ionic Bonds and Ionic
Compounds
> Formation of Ionic Compounds
Formula Units
• A chemical formula shows the kinds and
numbers of atoms in the smallest
representative unit of a substance.
• A formula unit is the lowest whole-number
ratio of ions in an ionic compound.
Slide
7 of 25
© Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
End Show
7.2
Ionic Bonds and Ionic
Compounds
> Formation of Ionic Compounds
NaCl is the chemical formula for sodium
chloride.
Slide
8 of 25
© Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
End Show
Conceptual Problem 7.2
Slide
9 of 25
© Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
End Show
Conceptual Problem 7.2
Slide
10 of 25
© Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
End Show
Conceptual Problem 7.2
Slide
11 of 25
© Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
End Show
Conceptual Problem 7.2
Slide
12 of 25
© Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
End Show
Practice Problems for Conceptual Problem 7.2
Slide
13 of 25
© Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
End Show
7.2
Ionic Bonds and Ionic
Compounds
> Properties of Ionic Compounds
Properties of Ionic Compounds
What are three properties of ionic
compounds?
Slide
14 of 25
© Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
End Show
7.2
Ionic Bonds and Ionic
Compounds
> Properties of Ionic Compounds
Most ionic compounds are crystalline
solids at room temperature.
Ionic compounds generally have high
melting points.
Slide
15 of 25
© Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
End Show
7.2
Ionic Bonds and Ionic
Compounds
> Properties of Ionic Compounds
The orderly arrangement of component ions
produces the beauty of crystalline solids.
Slide
16 of 25
© Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
End Show
7.2
Ionic Bonds and Ionic
Compounds
> Properties of Ionic Compounds
Ionic compounds can conduct an electric
current when melted or dissolved in water.
Slide
17 of 25
© Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
End Show