The Parts of Speech
advertisement

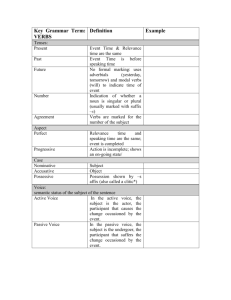
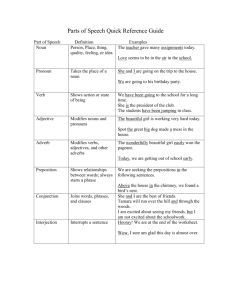
The Parts of Speech An Overview The Noun A word or word group that names a person, a place, a thing, or an idea. The Noun Names a person – Secretary – Mrs. Kathy The Noun Names a place – School bus – Pembroke Middle The Noun Names things – Pencils – desks The Noun Names ideas – Love – freedom The Noun There are 6 types of nouns The Noun 1. common nouns – Names any one of a group of persons, places, things, or ideas – Not capitalized Examples: – – – – – – scientist woman city building continent day The Noun 2. proper nouns – Names a particular person, place, thing, or idea – Is capitalized . Examples – – – – – – Marie Curie Coretta Scott King Cairo Eiffel Tower North America Monday The Noun 3. concrete noun – Names a person, place or thing that can be seen, heard, tasted, touched, or smelt – Examples Cloud Poison Ivy Thunder Silk Yogurt Sarah The Noun 4. Abstract noun 1. Names an idea, a feeling, a quality, or a characteristic 2. Cannot be seen, heard, touched, tasted, or smelt physically 3. is mental 4. Examples 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Freedom Well-being Beauty Kindness Buddhism The Noun 5. compound noun – Consists of two or more words used together as a single noun – Examples One word: firefighter, Iceland, newspaper Separate words: prime minister, Red River Dam, fire drill, race car driver Hyphenated words: sister-in-law, Port-auPrince, pull-up The Noun 6. collective noun – A word that names a group – Examples People: audience, chorus, committee, crew Animals: brood, flock, gaggle, herd Things: assortment, batch, bundle, cluster The Pronoun A word that is used in place of one or more nouns or pronouns Example: – Stan bought a suit and an overcoat. He will wear them. The Pronoun There are 6 types of pronouns. The Pronoun 1. Personal pronouns – Refers to the one speaking (1st person), the one spoken to (2nd person), or the one spoken about (3rd person). Pronouns- Personal – 1st person personal pronouns (the one speaking) I Me My Mine We Us Our ours Pronouns- Personal - 2nd person pronouns (the one spoken to) – You – Your – yours Pronouns- Personal - 3rd person pronouns (the one spoken about) – – – – – – – – – – – – He Him His She Her Hers It its They Them Their theirs Prounouns 2. Reflexive and Intensive – Reflexive pronouns refer to the subject of a sentence – Intensive pronouns emphasize its antecedent. – Examples: 1st person: myself, ourselves 2nd person: yourself, yourselves 3rd person: himself, herself, itself, themselves Prounouns 3. Demonstrative – Demonstrative pronouns are used to point out a specific person, place, thing, or idea. – Examples: This That These those Prounouns 4. Interrogative – Interrogative pronouns introduce a question Examples: – – – – – Who Whom Which What Whose Prounouns 5. Relative – Relative pronouns introduce a subordinate clause (a group of words that is not a complete sentence, even though it has a subject and a verb) Examples: – – – – – That Which Who Whom Whose Prounouns 6. Indefinite – Indefinite pronouns refer to one or more persons, places, ideas or things that may or may not be specifically named. – Refer to chart on page 381 Examples: – – – – – – – All Anybody Both Few Many Nobody Somebody Pronouns Antecedents – The word that a pronoun stands for or refers to – Example: Why did Oscar give his camera to the film school? Adjectives An adjective is a word that is used to modify a noun or a pronoun. The word modify means “to describe”. Adjectives Adjectives answer three questions about the word it modifies. – 1. What kind? – 2. Which one? – 3. How many? Adjectives What kind? Example: gray skies Adjectives Which one? Example: last chance Adjectives How many? Example: five fingers Adjectives Adjectives usually come BEFORE the noun or pronoun it modifies. Example: Ms. Barbara tells all students that good workers will be given special privileges. Adjectives Some words can be used as either adjectives or pronouns. Examples: this, that, these, those These words, as you may recall, are demonstrative pronouns. However, they can also be used as adjectives when they describe a noun or a pronoun. Example: Did Jennifer draw this picture or that one? That is my favorite. Adjectives Some words can be used as either adjectives or nouns. You must look at the way the word is used in the sentence to determine its part of speech. Example: I love cheese. I would like a cheese sandwich. Adjectives Proper adjectives are formed from proper nouns. Examples: Texas coast Picasso painting Adjectives The most frequently used adjectives are the ARTICLES. Articles are the three small words A, AN, THE. Adjectives A and AN are called indefinite articles because they refer to any member of a general group. The indefinite article A is used before words with a consonant sound EXAMPLE: A girl The indefinite article AN is used before words with a vowel sound. EXAMPLE: An elephant Adjectives THE is called the definite article because it refers to something or someone in particular. EXAMPLE The dog ran outside. Verbs A word that is used to express action or a state of being Verbs Show action Can be physical or mental action Examples: – Juanita mailed the package. – I believe you. Verbs Show a state of being All forms of the verb BE are verbs that show a state of being Example: – He is happy. – I am disappointed. BE Verbs Being Am Is Are Was Were be Linking Verbs A verb that connects the subject to a word or word group that identifies or describes the subject. Example: – The answer is correct. – The winners are happy. Common Linking Verbs Be am Being are Were shall be Has been have been Shall have been will have been Should be Should have been Would have been Could have been is was will be had been can be could be would be Other Linking Verbs Appear Become Feel Grow Look Remain Seem Smell Sound Stay Taste turn Verb Phrases Verb phrases consist of one main verb and one or more helping verbs. Helping verbs are also called auxillary verbs. Helping verbs help the main verb express action or a state of being. Example: – The dog is leaving with my homework. Verb Phrases More examples: – She had always been thinking of her future. – Has my sister played her new CD for you? – She should not have borrowed that necklace. Adverbs Modifies a verb, an adjective, or another adverb. Adverbs Tell – WHERE – WHEN – HOW – TO WHAT EXTENT (how long or how much) Adverbs Just as an adjective makes a noun or pronoun more definite, an adverb makes the meaning of a verb, an adjective, or another adverb more definite. Common Adverbs There Up Here Down Tomorrow Weekly Later early More Common Adverbs Quickly Softly Carefully Beautifully Completely Hardly Slightly Partly Adverbs Modify ADJECTIVES Example: – Beth did an exceptionally fine job. – Slightly cooler temperatures are forecast. – Mr. Lomazzi is an especially talented chef. ADVERBS modify verbs Adverbs also modify (or describe) verbs. When they modify verbs, they tell HOW, WHERE, WHEN, TO WHAT EXTENT. EXAMPLES: She quickly agreed. He hardly moved. We lived there. Adverbs Modify other ADVERBS Examples: – Calvin was almost never there. – We’ll meet shortly afterward. – She slept too late. Prepositions Show the relationship of a noun or a pronoun to another word – Example: UNDER my bed Common Prepositions Think about any place a mouse can go. ON OVER NEAR THROUGH ABOVE BELOW IN AROUND Refer to page 400 for more examples. Object of the Preposition This is the noun that the preposition relates another word to The object of the preposition is always a noun. The object of the preposition always follows the preposition. – EXAMPLE: There is a mouse NEAR my bed. Conjunctions Words that join words or word groups Common Conjunctions And But Or Nor So For Yet These are called coordinating conjunctions Common Conjunctions Both…and Either…or Whether…or Not only…but also Neither…nor These are called correlative conjunctions. Examples of Conjunctions You AND I are friends. Both Jim and Roberto were outstanding athletes.