File
advertisement

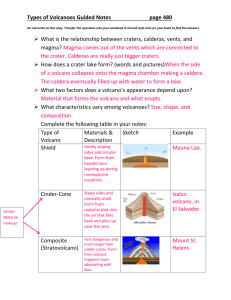
Types of Volcanoes Guided Notes page 480 Do not write on this copy. Transfer the questions into your notebook in Cornell style and use your book to find the answers. What is the relationship between craters, calderas, vents, and magma? Craters are the depressions in the tops of volcanoes, and they are connected to the magma reserves underground by vents. Calderas are what form when land collapses into a magma chamber. How does a crater lake form? (words and pictures) The magma chamber under a volcano collapses, leaving a large depression or bowl on the Earth’s surface. When this bowl fills with water it makes a crater lake. What two factors does a volcano’s appearance depend upon? The type of material the volcano is formed out of and the type of eruptions that occur. Types of Volcanoes Guided Notes page 480 Do not write on this copy. Transfer the questions into your notebook in Cornell style and use your book to find the answers. What characteristics vary among volcanoes? Shape, size, and composition. Complete the following table in your notes: Type of Materials Sketch Volcano & Descriptio n Shield Formed when layers of balsastic lava pile on top of one another. They have wide, gently sloped sides. Cinder-Cone Formed when materials ejected high into the sky from volcanoes return to the Exampl e Mauna Loa in Hawaii Izalco volcano in El Salvado r Types of Volcanoes Guided Notes page 480 Do not write on this copy. Transfer the questions into your notebook in Cornell style and use your book to find the answers. surface and pile up. They have steep sides and are usually small. Composite (Stratovolcan o) Formed when layers of volcanic fragments alternate with lava. They are extremely large and explosive. Mt. St. Helens How do the volcanoes compare in terms of size and slope? Composite are the largest followed by shield cone and then cinder cone. Composite and cinder cone both have concave slopes and shield cone has straight slopes. What factors cause differences in size and slope? Different materials that make up the volcano, the vegetation on the slope, the climate, and the eruption history Types of Volcanoes Guided Notes page 480 Do not write on this copy. Transfer the questions into your notebook in Cornell style and use your book to find the answers. What is tephra? Tephra is rock thrown into the air by volcanic eruptions What is a pyroclastic flow? Rapidly moving volcanic material including gas, ash and tephra. Where are most volcanoes found? Most of them are found at plate boundaries. Use the maps provided to show: (1) the Circum Pacific Belt and the Mediterranean Belt where convergent volcanism occur and (2) the Hawaiian Emperor Volcanic Chain. How do hotspots form? They are formed when mantle comes close to the surface What do hotspots tell us about tectonic plates? They tell us plate direction and motion Circum Pacific and Mediterranean Volcanic Belt Hawaiian Emperor Volcanic Chain