SW Asian Government Study Guide: Systems & Countries
advertisement

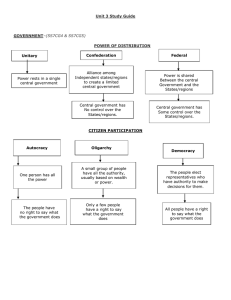
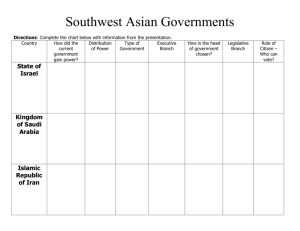
Study Guide for SW Asian Government 1. In a Unitary government system, most of the power is in the hands of the a. Individual voters b. king and advisors c. local government d. central government 2. Which country is an example of a unitary government? a. Israel b. Lebanon c. Saudi Arabia d. the United States 3. In a confederate government system, most of the power is in the hands of the a. Legislature b. individual voters c. local governments d. central government 4. What is a weakness of a confederation government system? a. A confederation is very expensive b. Confederations are too large to rule effectively c. A confederation does not share power with its members d. The central government has only as much power as the local governments are willing to give. 5. Which SW Asian country is an example of a federal system of government? a. Iran b. Israel c. Kuwait d. Saudi Arabia 6. Who makes most of the important governmental decisions in an autocracy? a. The ruler b. the people c. the courts d. the elected legislature 7. Which SW Asian country is an autocracy a. Iraq b. Israel c. Turkey d. Saudi Arabia 8. Who makes most of the important governmental decisions in an oligarchy? a. The king b. the people c. the legislature d. small group of powerful leaders 9. Why do the individual voters have more power in a democracy than they do in an autocracy or an oligarchy? a. Kings are always cruel rulers b. The voters get to choose the people who make the laws. c. All of the power stays in the hands of the local governments. d. Voters in democratic countries always choose qualified leaders. 10. Which SW Asian country has a democratic system of government? a. Iran b. Israel c. Kuwait d. Saudi Arabia 11. Which best describes the government of Saudi Arabia a. Oligarchy b. monarchy c. democracy d. dictatorship 12. Which branch of government is responsible for making and carrying out the laws in a parliamentary system of government? a. Judicial b. executive c. legislative d. the monarch 13. The leader of a parliamentary system is often called the a. King b. president c. governor d. prime minister 14. The leader of a parliamentary system is chosen by a. The king or monarch b. Popular vote of the people c. National courts d. The political party with the most representation in the legislature 15. In a presidential system of government, how is a president chosen? a. National courts b. Majority vote of the legislature c. Separate from the one that choses the legislature d. By the political party with the most representation in the legislature 16. What is the role of the president regarding the laws passed by the legislature? a. Enforces the laws b. Change laws he does not like c. Sends laws to the state for approval d. Laws don’t have to go to the president for approval 17. The Israel parliament is called the a. Senate b. Knesset c. Congress d. House of Representatives 18. Who is allowed to vote in Israeli elections? a. Citizens over 16 b. Citizens over 18 c. Men who are Israeli citizens d. People born in the state of Israel 19. Saudi Arabia is ruled by a a. King b. representative government c. president d. group of religious leaders 20. How long does a monarch rule? a. One term b. ten years c. until he dies 21. What role do the people play in a government that is a monarchy such as Saudi Arabia? a. They vote the rulers out of office b. Approve the laws c. Little influence, the ruler makes the decisions d. Guaranteed rights by a written constitution 22. What is the definition of a theocracy? a. Government that sees god as the supreme ruler b. Government that allows people to choose its leaders c. Religious law and civil law are separate d. Only religious leaders are allowed to vote 23. Why is Iran called a theocratic republic a. Iran’s religious leaders make all the laws b. Religious leaders decide who can vote c. The people have no say in choosing their government leaders d. Iran’s government is led by an elected parliament and religious leaders 24. Why does Iran’s government have an impact on countries all around the world a. They are a theocracy b. They are a member of OPEC with lots of oil wealth c. They have an Ayatollah d. They have Shariah law