HUMAN RESOURCE PLANNING
advertisement

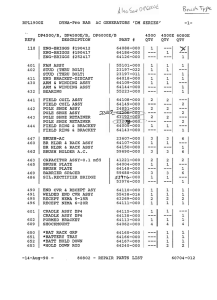
The Process of Human Resource Planning • Organizations need to do human resource planning so they can meet business objectives and gain a competitive advantage over competitors. – Human resource planning compares the present state of the organization with its goals for the future – Then identifies what changes it must make in its human resources to meet those goals Overview of the Human Resource Planning Process Human Resource Forecasting • HR Forecasting attempts There are three major to determine the supply steps to forecasting: and demand for various types of human resources, 1. Forecasting the demand for labor and to predict areas 2. Determining labor within the organization supply where there will be labor shortages or surpluses. 3. Determining labor surpluses and shortages HUMAN RESOURCE PLANNING FORECASTING HR REQUIREMENTS (DEMAND ANALYSIS) (Trying to predict future staffing needs) Managerial Estimates Sales Projections Simulations Vacancy Analysis (projected turnover) FORECASTING HR AVAILABILITY (SUPPLY ANALYSIS) (Predicting worker flows and availabilities) Succession or Replacement Charts Skills Inventories (use of HRIS) Labor Market Analysis Markov Analysis (Transition Matrix) Personnel Ratios Forecasting the Demand for Labor Trend Analysis • Constructing and applying statistical models that predict labor demand for the next year, given relatively objective statistics from the previous year. Leading Indicators • Objective measures that accurately predict future labor demand. CORRELATIONS/PROJECTIONS SIZE OF HOSPITAL 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 NUMBER OF NURSES 240 260 470 500 620 660 820 860 SIMULATION MODEL/REGRESSION FORECAST TARGET STORES STAFFING FORECAST MODEL Y = 8 + .0011(X1) + .00004(X2) + .02(X3) Y = Number of employees needed to staff the store X1 = Square feet of sales space X2 = Population of metropolitan area X3 = Projected annual disposable income in millions of dollars Y = 8 + .0011(50,000sq ft) + .00004(150,000popul) + .00000002($850 million) Y = 8 + 55 + 6 + 17 Y = 86 employees needed at this store VACANCY ANALYSIS Historic departures used to project turnover LEVEL # EMPL TURN % Expected Vacancies TOP MGMT 100 20 % 20 80 MID MGMT 200 24 % 48 152 LOW MGMT 600 22 % 132 468 SKILLED W 600 16% 96 504 ASSY WKRS 2000 12 % 240 1760 TOTALS 3500 536 2964 AVERAGE TURNOVER PERCENTAGE = 536 / 3500 = Expected to Remain .1531 Determining Labor Supply Predicting Worker Flows and Availabilities • Succession or Replacement Charts Who has been groomed/developed and is ready for promotion right NOW? • Human Resource Information Systems (HRIS) An employee database that can be searched when vacancies occur. • Transition Matrices (Markov Analysis) A chart that lists job categories held in one period and shows the proportion of employees in each of those job categories in a future period. It answers two questions: 1. “Where did people in each job category go?” 2. “Where did people now in each job category come from? • Personnel / Yield Ratios How much work will it take to recruit one new accountant? SUCCESSION PLANNING REPLACEMENT CHART FOR EXECUTIVE POSITIONS POSITION REPLACEMENT CARDS FOR EACH INDIVIDUAL POSITION ------------------------------------------------------------------------ POSITION WESTERN DIVISION SALES MANAGER DANIEL BEALER Western Division Sales Mgr POSSIBLE CANDIDATES SHARON GREEN GEORGE WEI HARRY SHOW TRAVIS WOOD CURRENT POSITION Western Oregon Sales Manager N. California Sales Manager Idaho/Utah Sales Manager Seattle Area Sales Manager Outstanding Ready Now PRESENT PERFORMANCE PROMOTION POTENTIAL Outstanding Outstanding Satisfactory Satisfactory Ready Now Needs Training Needs Training Questionable ------------------------------------------------------------------------- HUMAN RESOURCE INFORMATION SYSTEMS (HRIS) PERSONAL DATA Age, Gender, Dependents, Marital status, etc EDUCATION & SKILLS Degrees earned, Licenses, Certifications Languages spoken, Specialty skills Ability/knowledge to operate specific machines/equipment/software JOB HISTORY Job Titles held, Location in Company, Time in each position, etc. Performance appraisals, Promotions received, Training & Development MEMBERSHIPS & ACHIEVEMENTS Professional Associations, Recognition and Notable accomplishments PREFERENCES & INTERESTS Career goals, Types of positions sought Geographic preferences CAPACITY FOR GROWTH Potential for advancement, upward mobility and growth in the company Transition Matrix Example for an Auto Parts Manufacturer MARKOV ANALYSIS (STATISTICAL REPLACEMENT ANALYSIS) TO: A TRANSITION MATRIX FROM: TOP MID TOP .80 .02 MID .10 .76 .04 .06 .78 .01 .15 .01 .84 .15 LOW SKILL ASSY LOW SKILLED ASSY EXIT .18 .10 .05 .88 .07 ------------------------------------------ MARKOV ANALYSIS – 2 (Captures effects of internal transfers) (Start = 3500) FROM/ TO: TOP 100 MID 200 LOW 600 TOP .80 .10 A TRANSITION MATRIX MID LOW SKILLED ASSY .02 EXIT .18 .76 .04 .06 .78 .01 .15 .01 .84 .15 SKILL 600 .10 ASSY 2000 .05 .88 .07 --------------------------------------------------------- END YR WITH: 100 NEED RECRUITS ? NEED LAYOFFS ? 0 KEEP STABLE 100 190 482 10 118 610 240* (10)* 200 600 1760 600 [358 left] 368 tot (10) tot 2000 = 3500 Tot MARKOV ANALYSIS – 3 (Anticipates Changes in Employment Levels) Employment needs are changing. We need a 10% increase in skilled workers (660), and a 15% decrease in assembly workers (1700) by year’s end. ------------------------------------------------------(Start = 3500) A TRANSITION MATRIX FROM/ TO: TOP MID LOW SKILLED ASSY EXIT TOP 100 .80 .02 .18 MID 200 .10 .76 .04 .10 LOW 600 .06 .78 .01 .15 SKILL 600 .01 .84 .15 ASSY 2000 .05 .88 .07 --------------------------------------------------------END YR WITH: 100 NEED RECRUITS ? NEED LAYOFFS ? 0 NEW LEVELS 100 190 482 610 10 118 50* 1760 [358 left] (60)* 200 600 600 1700 = 3260 tot Determining Labor Surplus or Shortage • Based on the forecasts for labor demand and supply, the planner can compare the figures to determine whether there will be a shortage or surplus of labor for each job category. • Determining expected shortages and surpluses allows the organization to plan how to address these challenges. PERSONNEL / YIELD RATIOS Past experience has developed these yield ratios for recruiting a Cost Accountant: FOR EVERY 12 APPLICATIONS RECEIVED, ONLY 1 LOOKS PROMISING ENOUGH TO INVITE FOR AN INTERVIEW OF EVERY 5 PERSONS INTERVIEWED, ONLY 1 IS ACTUALLY OFFERED A POSITION IN THE ORGANIZATION OF EVERY 3 JOB OFFERS MADE, ONLY 2 ACCEPT THE POSITION OF EVERY 10 NEW WORKERS WHO BEGIN THE TRAINING PROGRAM, ONLY 9 SUCCESSFULLY COMPLETE THE PROGRAM THUS: 100 APPLICATIONS MUST BE RECEIVED, so that 8.33 JOB INTERVIEWS CAN BE HELD, so that 1.67 JOB OFFERS CAN BE MADE, and 1.11 PEOPLE MUST BE TRAINED, so that we get ONE NEW COST ACCOUNTANT!!!