AS EASY AS PCR PRACTICAL ACTIVITY
advertisement

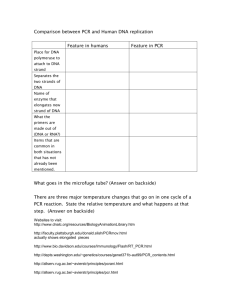
AS EASY AS PCR PRACTICAL ACTIVITY Introduction Genes are composed of DNA. The DNA sequence of a particular gene can vary because mutation generates a large number of different alleles within a species. However, DNA sequences are inherited. Our parents pass on the DNA sequences to us that they inherited from their parents. Therefore, by analysing the sequence of nucleotides in the DNA of different individuals, we can assess their degree of relationship. While we have considered this at the family level, it is also true at the level of different races within a species or when making comparisons between species. In order to perform such analysis it is important to be able to isolate large amounts of DNA for the same gene from different individuals. In 1983, Professor Kary Mullis reported the development of a new technique called the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR). Having carefully considered the normal process of DNA replication that occurs in cells, Mullis was able to mimic the process under controlled conditions. Rather than the DNA molecule going through a single round of DNA replication, in PCR it goes through many cycles of replication, yielding a vast number of identical copies. PCR has revolutionised molecular biology. It allows us to address many problems that could not be solved with other methods. In recognition of his groundbreaking research, Kary Mullis was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1993. Purpose To observe a simulation of the PCR process. To identify the key events in the process and how they relate to normal DNA replication. To consider three applications of PCR. A Simulation of the PCR reaction 1 Click on http://www.dnalc.org/ddnalc/resources/pcr.html to locate the DNA Learning Center at the Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory. Click on the button to the left of the word “Amplification” to commence the simulation. The successive steps of the PCR process can be followed by clicking the buttons under the diagrams of the DNA molecules. Follow the simulation through five cycles of DNA replication. Describe the events that happen at: A 94-96o C B 50-65o C C 72o C 2 Why is it necessary for the DNA to be denatured at the start of each cycle? 3 ‘The specific DNA sequence that will be amplified in PCR is determined by the primers used’. Explain the meaning of this statement. 4 What special property does Taq polymerase have that the DNA polymerase isolated from a mammalian cell would not have? Why is this important? 5 What would be the sequence of the two primers that you would use to amplify the following DNA sequence? (Your primers should both be 20 nucleotides in length.) 5’GCATCGATTGACTAGATGCATCAGCACGATGCATCTAGACTAGCA TCTCGCGCATA-3’ 3’CGTAGCTAACTGATCTACGTAGTCGTGCTACGTAGATCTGATCGTA GAGCGCGTAT-5’ The number of DNA molecules synthesised during PCR After viewing the five cycle results, click on the button labeled ‘Graph’. The graph can also be reached from the main menu page by clicking the button labeled ‘Amplification Graph’. This program allows you to plot a graph of the number of DNA copies synthesised (vertical axis) in a given number of cycles of replication in PCR (horizontal axis). Click on the ‘Next Cycle’ button at the bottom right. A chart at the top left corner of the graph shows that after one cycle there are two DNA copies. Click on the ‘Next Cycle’ button. Each time you click this button, the total number of DNA molecules produced after the given number of cycles of PCR will be shown on the chart and plotted on the graph. 6 How many DNA copies are produces after 28 cycles of PCR? 7 How many DNA copies would be produced after 32 cycles of PCR? 8 The chart shows a number of ‘target copies’ of DNA produced. This number is slightly smaller than the total number of DNA copies produced. What is meant by the term ‘target copies’? You may need to examine the PCR simulation again to answer this question. B Identifying family members DNA analysis was used to identify the recovered skeletons of the Romanov family, the last Tsar of Russia (Nicholas), his wife (Alexandra) and three of their children. This exercise will allow you to analyse some additional data. PCR was used to amplify mitochondrial DNA, which was then sequenced. This was performed for each of the skeletons recovered and for known relatives of the Romanov family. You can follow this exercise online and answer the questions that are included. Click on www.dnalc.org/bioforms/guide.pl?b_id=1&p_id=1 to locate the DNA learning center at the Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory. Click on ‘Solving the Mystery of the Romanovs’. Answer the questions included in this exercise. C The relationship between races Individuals of the same race have DNA sequences that are more similar to each other than they are to the DNA sequences from individuals of other races. Therefore, DNA sequences can be used to determine how closely different races are related to each other. Indeed, PCR allows us to examine how closely races that lived in the past resemble those that populate the earth today. Consider the story of the Ice Maiden. In 1995, high in the Andes Mountains the frozen body of a young Incan girl was discovered. The girl had been ritually sacrificed 500 years ago – buried alive wrapped in fine textiles and surrounded by gold statues and bags of corn. DNA analysis was used to compare the DNA sequence of the Ice Maiden with those of current races living in Central and South America. You can find this described at http://www.nationalgeographic.com/features/97/andes/ 9 Where was the Ice Maiden discovered? 10 Mitochondrial DNA was chosen for analysis. Why? 11 12 From which tissue was DNA extracted? Which current race is most closely related to the Ice Maiden? Conclusion 16 Write a paragraph outlining the importance of PCR in solving problems in biology and medicine.