The urinary system
advertisement
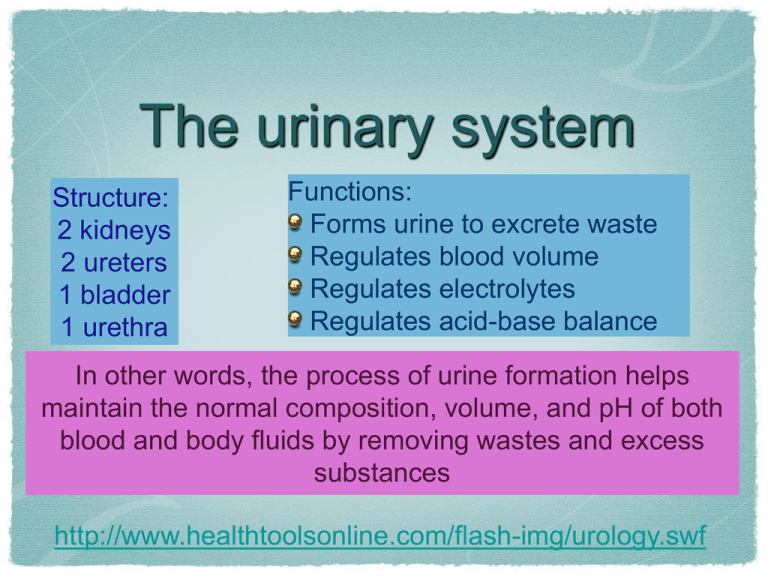
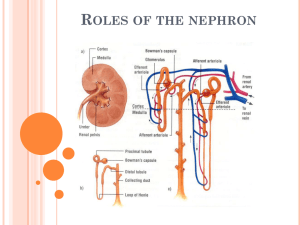
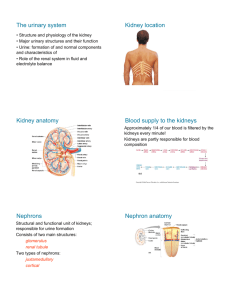
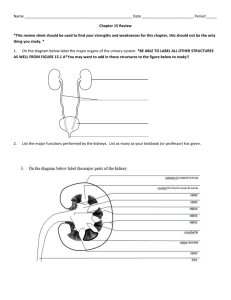
The urinary system Structure: 2 kidneys 2 ureters 1 bladder 1 urethra Functions: Forms urine to excrete waste Regulates blood volume Regulates electrolytes Regulates acid-base balance In other words, the process of urine formation helps maintain the normal composition, volume, and pH of both blood and body fluids by removing wastes and excess substances http://www.healthtoolsonline.com/flash-img/urology.swf IVP - Intravenous Pyelogram Three Processes Occur Filtration Reabsorption Secretion Functionally, cortical and juxtamedullary nephrons have distinct roles. Cortical nephrons (85% of all nephrons in humans) mainly perform excretory and regulatory functions, while juxtamedullary nephrons (15% of nephrons in humans) concentrate and dilute urine Why the difference in cortical and juxtamedullary nephrons? In the descending limb (of the loop), water moves freely but salt cannot. Longer descending limbs make the filtrate more hypertonic than shorter limbs In the ascending loop, salt is actively pumped out (no water exchanges) which makes the filtrate hypotonic http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SoilI_J0Vq0&f eature=related shows the medulla and cortex and explains pyramids, calyces. 1.4 min http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8TXXIJGz4F4&feat ure=related diagram and explanation of nephron, show cortex, medulla, and the two types of nephrons, collecting ducts 1.35 min http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6Wc4f2KnbYo&featu re=related shows kidney cortex, medulla, nephron function, chemistry, urine formation 8.5 min http://faculty.southwest.tn.edu/rburkett/A&P2%20urinary_system .htm nice site with lots of pictures including scanning electron micrographs http://video.google.com/videosearch?q=cystoscopy&site search=# shows cystoscopy and biopsies. 4 min - watch 1 min then go to about 3.5 for bx 150-180 liters filtered 99% reabsorped 1% becomes urine Oh No! Not Hormones Again!!! ADH - Antidiuretic Hormone increases reabsorption of water from filtrate back to blood PTH - Parathyroid Hormone increases reabsorption of calcium from filtrate back to blood and excretes phosphate into filtrate Aldosterone increases reabsorption of sodium from filtrate back to blood and excretion of patassium into filtrate. Water follows sodium. ANP - Atrial Natriuretic Peptide decreases reabsorption of sodium, which remains in the filtrate. More sodium & water are eliminated in urine (Table 18-1, page 428 and Fig 18-5, page 429, Scanlon text) Other Kidney Functions: Secretion of renin Production of erythropoietin Activation of vitamin D When BP goes down, kidneys secrete renin and BP goes up The small print: Renin converts angiotensin (from lungs and blood vessels) to angiotensin II. Angiotensin II causes blood vessels to constrict and stimulates aldosterone (from adrenal glands) Other Kidney Functions: Secretion of renin Production of erythropoietin Activation of vitamin D When blood oxygen goes down, kidneys produce erythropoietin and RBC production goes up The small print: Erythropoietin causes bone marrow to produce more red blood cells which can carry more oxygen Other Kidney Functions: Secretion of renin Production of erythropoietin Activation of vitamin D The kidneys activate vitamin D which increases absorption of calcium and phosphate The small print: Vitamin D is converted to an active form called calcitriol (D2) which causes the small intestines to take up more calcium from our food Finally, elimination! (sometimes called the home stretch) Rugae Detrusor muscles Internal and external sphincters Page 432 of Scanlon text urination Urination is a spinal cord reflex over which voluntary control may be exerted The bladder stretches as it fills. The detrusor muscles are sensitive to the stretching At about 300 ml, a message is sent to the spinal cord A parasympathetic nerve impulse is sent back to the detrusor muscles to contract * * remember The internal urethral sphincter relaxes parasympathetic nerve pathways? If urination is desired or required, the external urethral sphincter is voluntarily relaxed and the bladder empties So what is this stuff called urine? Review and Study Guide Be able to spell and define terms related to the urinary system Be able to label a diagram/picture of the kidney, the nephron, the urinary system, and the bladder as shown on these PPT slides Be able to clearly answer review questions on page 437 of your Scanlon text, specifically numbers 1, 3, 4, 7, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15 Be able to fully explain filtration, reabsorption and secretion Be able to discuss 4 mechanisms of tubular reabsorption (425 & 427) Let’s Review 1. name the three tubes that make up the urinary system 2. where are the kidneys located? 3. what is the functioning unit of the kidney 4. what is the name of the blood vessel the bring blood into the kidney? 5. what is the name of the cluster of blood vessels going into Bowman’s capsule? 6. which arteriole enters Bowman’s capsule? 7. Which exits? 8. what is the name of the convoluted tubule between Bowman’s capsule and the loop? 9. What is the name of the loop? 10. what is the name of the twisted tubule after the loop? 11. what is the name of the structure that all the nephrons drain into? 1. can you name the blood vessels from the abdominal aorta to the vena cava? 2. must be present for filtration to take place? 3. what happens in the loop of the cortical nephron? 4. what happens in the loop of the juxtamedullary nephron? 5. how much filtrate do we process each day? 6. how much urine do we secrete each day? 7. what is the first stimulus for urination? 8. list the structures from the glomerulus to the collecting duct 9. list the structures from the collecting duct to the urethra 10. what is meant by tubular threshold? 11. can you give an example of threshold? 12. what substances are secreted from the tubules? 13. name one hormone that influences reabsorption of water 1. Name another hormone that influences the reabsorption of water 2. summarize the process of urine formation 3. what does renin do? 4. does the kidney have to do with vitamin D? 5. what is erythropoietin and what does it cause? 6. What is urine made of mostly?