Electron Configuration
advertisement

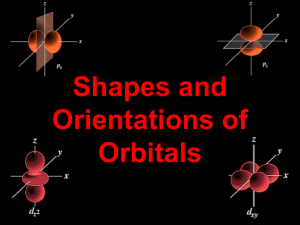
Chapter 5 Electrons in Atoms Anything in black letters = write it in your notes (‘knowts’) 5.1 – Revising the Atomic Model Rutherford’s Planetary Model of the Atom Electrons moving around a tiny nucleus Problems with Rutherford’s Model 1.Did not explain the chemical properties of the elements. 2.Did not explain atomic spectra (…later…) 3.e- would spiral into the nucleus, but they don’t The Bohr Model ~1913 Electrons are found only in specific locations (or energy levels) around the nucleus. To move from one energy level to another, an e- must gain or lose a quantum of energy. Niels Bohr The energy levels in atoms are unequally spaced, like the rungs in this unusual ladder. The higher energy levels are closer together. The Quantum Mechanical Model The modern description of e- in atoms. Similar to Bohr Model except the exact location of an electron is impossible to know Electrons are likely to be found in electron ‘clouds’ around the nucleus We will use the Bohr model in this class… Electron cloud Atomic orbital – Most probable place for e- to be. Orbitals can hold 2 e- maximum. The orbitals are named s, p, d & f S (1 type) p (3 types) d (5 types) There are 7 types of f orbitals Don’t worry about these shapes… Orbital Name s p d f Types of Maximum Electron Orbital Capacity x2 2 1 3 x2 6 x2 5 10 x2 7 14 Each orbital can hold 2 emaximum This chart is on page 132 Summary of Principal Energy Levels and Sublevels Energy Level Type of Orbitals in Energy Level Maximum Number of Electrons in Energy Level n=1 1s (1 orbital) 2 n=2 2s (1 orbital), 2p (3 orbitals) 8 n=3 3s (1 orbital), 3p (3 orbitals), 3d (5 orbitals) 18 n=4 4s (1 orbital), 4p (3 orbitals), 4d (5 orbitals), 4f (7 orbitals) 32 ASSIGN: Read 5.1 Lesson Check 5.1 (#1-7) page 132 5.2 – Electron Arrangement in Atoms Aufbau Principle – e- occupy the orbitals of lowest energy first. Pauli Exclusion Principle – Hund’s Rule – we will not cover Aufbau Diagram (p. 135) 6p 5d 6s 5p 4d 5s Increasing energy 4f 4p 3d 4s 3p 3s 2p 2s E- fill the lowest energy orbitals first Notice the 4s fills before the 3d 1s Another Aufbau Diagram (write this one down!) Orbital Maximum Number of e- Due to Orbitals s p 2 6 d f 10 14 Aufbauprinzip, (german) "building-up principle” Electron Configuration – shows how e- are arranged in an atom Example: Write the electron configuration for N How many e-? 7 Use Aufbau Diagram # of e- in orbitals 2 2 3 1s 2s 2p Your turn… Write the electron configuration for a) boron b) silicon c) sulfur Chapter 5 QUIZ!! LEFT RIGHT 1. What is the maximum number of electrons that can go into p orbital d orbital 2. What is the maximum number of electrons in the p orbitals d orbitals 3. Write the electron configuration for N Mg Mg K Cl C Can you see how the periodic table can be used as an Aufbau Diagram? ASSIGN: Read 5.2 Answer questions #8-14 page 136,137 5.3 – Atomic Emission Spectra and the Quantum Mechanical Model The Electromagnetic Spectrum (p. 139) Low energy ( = 700 nm) Frequency (s-1) 3 x 106 102 High energy ( = 380 nm) 3 x 1012 3 x 1022 10-8 10-14 A prism separates light into the colors it contains. White light produces a rainbow of colors. Screen Light bulb Slit Prism Light from a helium lamp produces discrete lines. Screen Slit Helium lamp Prism The lines that result are unique for each element and are called its atomic emission spectrum. Bohr’s Model explained the emission spectra When an atom absorbs energy an electron jumps to a higher energy level (excited state). The electron returns to the lower energy level, emitting a photon with a definite energy. The photon’s energy shows up as a line in the emission spectrum. Chapter 5 Quick Quiz 1. Explain the main difference between the Bohr Model and the Quantum Model of the atom. 2. An atomic orbital can hold a maximum of _____ electrons. 3. How many types of s, p, d, and f orbitals are there? s = ______, p = _______, d = ______, f = ______ 4. What is the maximum e- capacity of the s orbitals ____, p orbitals ____, d orbitals ____, f orbitals ____ 5. Write the electron configuration for the following elements. a) Helium (Z = 2) b) Strontium (Z = 38) c) Aluminum (Z = 13) d) Chlorine (Z=17) e) Silver (Z = 47) f) Arsenic (Z = 33) 5. Write the electron configuration for the following elements. a) Helium (Z = 2) b) Strontium (Z = 38) c) Aluminum (Z = 13) d) Chlorine (Z=17) e) Silver (Z = 47) f) Arsenic (Z = 33) Chapter 5 Things to Know… Rutherford Bohr Quantum Mechanical Models, Energy Levels, Atomic Orbitals (s, p, d, f) , Aufbau Principle & Diagram, Electron Configurations, Explanation of Atomic Emission Spectra Big Sale at the Nuclear Mall today! Make sure to get the closest parking stall. Nuclear Mall 1s 2p 2s 2p 3d 3p 3s 3p 3d 4d 4p 4s 4p 4d