Urinary System
advertisement

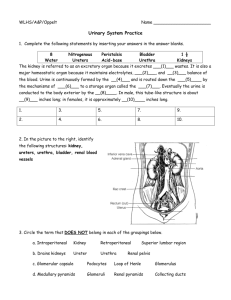
Ch 17 Main function: Filter blood and remove salts and nitrogenous waste. Maintains normal water and electrolyte concentration. Regulates pH and volume of body fluids. Controls red blood cell production and blood pressure. Kidneys (2) – Remove substances from blood, form urine, and regulate RBC production. Ureters (2) – Transport urine from kidneys to bladder. Urinary bladder – Stores urine Urethra – Conducts urine outside the body Location – either side of the vertebral column on posterior wall of the abdominal cavity High – T12-L3ish Left is slightly higher than right. Attached to inferior vena cava and abdominal aorta. Hilum Renal sinus – filled with adipose tissue Renal pelvis – major/minor calyces Medulla Cortex – houses nephrons Maintain homeostasis • Removes wastes from blood and dilute with water and electrolytes to form urine. Secretes hormone erythropoietin – regulate RBC production Activates Vitamin D Maintains blood volume and pressure (enzyme: renin) abdominal aorta -> renal arteries -> (kidneys) interlobar arteries -> arcuate arteries -> interlobular arteries -> afferent arterioles-> (nephron glomerulus) -> efferent arteriole -> peritubular capillary system -> interlobular vein -> arcuate vein -> interlobar vein -> renal vein (exits kidney) -> inferior vena cava Each kidney has about 1 million nephrons. Two main parts: renal corpuscle and renal tubule. Corpuscle – Glomerulus – filters fluid (step 1 of urine production) Glomerular capsule – receives filtered fluid Tubule Proximal convoluted tubule Nephron loop – descending and ascending Distal convoluted tubule Collecting Duct Juxtaglomerular Apparatus – where ascending loop, afferent, and efferent vessels come together Involved in renin secretion. Urine formation happens through three processes: • Glomerular filtration • Tubular reabsorption • Tubular secretion Amount of urine = amt. filtered-amt. reabsorbed + amt. secreted Glomerular capillaries in glomerulus filter water and other dissolved substances to create glomerular filtrate. Glomerular filtrate moves to glomerular capsules. Pressure is created by hydrostatic pressure of blood. Pressure is decreased by osmotic pressure of plasma and hydrostatic pressure inside glomerular capsule. Net filtration pressure = blood’s H-S P – (plasma’s osmotic P + glom.caps’s H-S P) Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) – commonly used to measure kidney function. Affected by changes in diameter of afferent or efferent arterioles. Can also change due to kidney stones, enlarged prostate gland, etc. Filtration Rate Regulation • Most of the time, it’s constant. • Increases when body fluids are excessive • Decreases when body needs to conserve fluids Controlled by sympathetic nervous system reflexes. Can also be affected by renin counts. From renal tubule back to blood Changes concentrations in filtrate. Happens in proximal convoluted tubes using microvilli using carrier proteins. Substances reabsorbed: • Glucose, amino acids, sodium – active transport • Water – osmosis • Proteins – pinocytosis • Negative ions diffusion From blood back to distal convoluted tubule Substances secreted: • Hydrogen ions and organic compounds – active transport • Potassium ions – active and passive transport Can be changed by presence of hormones • Aldosterone – secreted by adrenal glands (located posteriorly to kidneys); stimulates reabsorption of sodium and secretion of potassium. • ADH – secreted by neurons in hypothalamus; responds to decrease in water concentration or blood volume; causes water to be reabsorbed; negative feedback system. Increased ADH=more water reabsorption Decreased ADH=less water reabsorption Urea – made by amino acid catabolism; reflects amount of protein in diet; 20% leaves/80% reabsorbed Uric acid – product of metabolism of nucleic acids; small amounts secreted into renal tubule and excreted in urine. Determined by the amount of water in diet and plasma. Changes with changes in diet and metabolic activity. Should not have • Glucose – sign of diabetes or large glucose intake. • Proteins – may be there after strenuous exercise • Ketones – after a prolonged fast • Blood – sign of disease or disorder From collecting tubes in renal medulla To ureter To urinary bladder To urethra Ureters - From renal pelvis to bottom of urinary bladder. Three layers • Mucous coat – inside • Muscular coat – middle (smooth muscle) • Fibrous coat – connective tissue Flap-like fold acts as valve allowing urine to enter bladder without backflow Urinary bladder – hollow, distendable, muscular organ Stores urine and forces into urethra Four layers • Mucous coat – inner layer (transitional epithelium) • Submucous coat • Muscular coat – smooth muscle fiber called detrusor muscle • Serous coat – outer layer Internal urethral sphincter • Sustained contraction keeps bladder from emptying • Detrusor muscle innervated with parasympathetic nerve fibers External urethral sphincter • Voluntary skeletal muscle Micturition – Urination Stimulated by distension of bladder triggering micturition reflex center • Controlled by pons and hypothalamus Urge felt at about 150 mL Powerful contractions felt at 300 mL Pain felt at about 600 mL Urethra – tube that conveys urine to outside Female – 4 cm Male – shared by urinary and reproductive system Kidneys Nephron Ureters Urinary bladder Urethra Renal vein Renal artery Distal convoluted tube Proximal convoluted tube loop Glomerular capsule Glomerulus Renal cortex Renal medullary