File - Mr Addington
advertisement

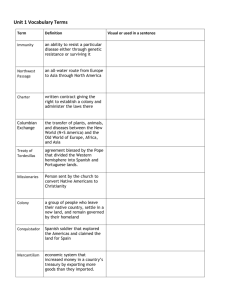
WHY DID EUROPEANS GO EXPLORING? Making Contact Contact Continues Why did the “Age of Exploration” Occur? • • • • End of the “Dark Ages” Renaissance Printing Press Gun powder What was the motivation of the individual explorer, conquistador, monarch? • • • • • Materialism, personal wealth Glory, personal fame Religion, conversion of the “heathens” to Christianity Nationalism, promoting the wealth and power of the nation Scientific Curiosity • Leads to fierce competition among leading European nation-states What made the “Age of Exploration” Possible? • Major innovations allow for more adventurous exploring • Technology - Sextant • Used for measuring accurate distances • Economics - Joint-Stock Companies • Early versions of corporations COLUMBIAN EXCHANGE The Exchange The Columbian Exchange How did the European Colonization affect Native Culture? • Settlement patterns • Political • Introduction of horses, cows, and oxen allow for greater movement among indigenous societies • Social • Intermarriage (more on that later) • Religious conversion • Diminishing language, customs, religions • 90% death rate in some areas • Disease (swine flu, small pox, whooping cough, chicken pox) • War • Economic • Forced labor • Loss of Land • New loyalty to Spanish Crown (see Las Casas) • Indigenous society authority largely disregarded • Loss of Liberty How did Native American Culture affect Old World civilizations? Food • Corn • Tomatoes • Peppers • Chocolate • Pineapples • Sweet Potatoes • Potatoes *** • Health, • Nutrition • Economic All of this spurs rapid population growth in Europe, pushing more individuals into the marketplace! Medicine • Vitamins • Anesthetics for Surgery and Dentistry • Cocaine and derivatives • Muscle relaxants • Curare • Expectorants for cold remedies • Guafenisen • Poison treatment • Ipecac • Malaria • “Fever Bark” - Quinine • Analgesics • Aspirin How did Native American Culture affect Old World civilizations? • Money Three times the gold and silver in Europe Inflation More money in more hands … … More People wanting more goods … … More People making more goods … … Industrial Revolution Shifts Europe from feudalism to capitalism! How did Native American Culture affect Old World civilizations? • Shift to capitalism and more open markets hence opportunities for wealth building leads to the “First Great Divergence” • This theory suggests that all old world regions (European, Asian, Russian, Middle Eastern, etc.) were on a relatively level playing field • Opening of exchange with the Western Hemisphere allows for the first real jump of one of the regions, Europe, and allowing for a massive acceleration of one group overs • Also known as the European Miracle • Within Europe, the competition nations push outward toward Empire Building LABOR IN THE NEW WORLD Ruling Colonial Territory • Why spend so much time talking about Spanish conquistadors/explorers? • Audiencias had authority under the general Counsel of the India, all under the Spanish royal authority • Audencias had legislative, executive, and judicial functions to try and bring the conquistadors under Spanish royal authority • Viceroyalty of Spain, a Spanish colonial administrative court, names this territory New Spain • Viceroyalty of Peru, also a Spanish administrative body, runs most of South America Encomienda System • Roots in the feudal system of Europe, conqueror wins territory and tax paying tributes in exchange for defense • Encomiendas were formal tracts of land paid to Spanish citizens and the Repartmento system was the process of assigning native labor to each encomiendor • Natives were to provide goods, metals, money, and labor • Spanish were to provide protection, Christian religion, defense of the area, taxes to the Crown • Most Encomiendas had a church and organized the surrounding land into parishes • Native population declines so drastically that Native labor is replaced by African labor • Intended to be for conversion to Catholism (and were only supposed to be in charge until natives became Catholics), but later economically exploited • Spanish Crown encouraged intermarrying, as a means to assimilation • Crown will try to intervene, partially because of the urging of Las Casas http://historicaltextarchive.com/sections.php?action=read&artid=633 Controversy of Treatment: Valladolid Debate • August 1550, 5 day debate in Valladolid, Spain • De Las Casas, arguing Amerindians were free and Catholic doctrine argued for equal treatment, and scholar Juan Gines de Sepulveda, arguing that Catholic doctrine supported punishing natives for ‘committing crimes against nature’ and slavery was appropriate • Official Council of the Indies never declared winner. However, both men claimed victory “New Laws” of 1542 • New Laws of the Indies for the Good Treatment and Preservation of • • • • • the Indians passed in 1542 Intended to drastically limit the power of the Encomendors Laws said: no enslavement of Indians, formally stated Indians were free persons, encomiendors could no longer require tributes, if Indians worked, they needed to be paid, encomienda grants could not be passed down upon death, Indians shouldn’t work in mines unless ‘absolutely necessary’ When the Viceroy of Peru tried to enforce, the Encomendors rebelled and killed Viceroy chair, so the Viceroy of New Spain decided not to enforce them All of these laws were eventually revoked by 1545. Mixed historical reviews on their effectiveness depending on the position. Did allow for the release of many Indian slaves, but the Spanish still needed labor. Dominicans will continue pushing for reforms. Mission System • The mission system will eventually replace the encomiendas (late 1700s) • Started by mostly Franciscans and Jesuits, Spain had 3 goals: • Education (literacy) • Gain tax base • Conversion to Christianity • These missions will continue, particularly in places like California, until its annexation into the US • Missions would baptize natives first, then force them to attend daily religious services and labor Spanish/Portuguese search for labor • Need for labor - support plantation-based agriculture and extract precious metals and other resources • Dramatic forced labor of indigenous societies, accompanied by a tremendous reduction in population leads to a hunt for new labor (see Las Casas) • As minerals were extracted and land producing fewer natural resources, Spanish colonists transitioned into sugar production, leading to a massive plantation system in the new world (see Columbian Exchange article) A New Issue? • The Colombian Exchange also introduced the slave trade which would be central to the development of economic structures, social hierarchies, and human relations for … Extraction of Africans • Spanish and Portuguese traders reached West Africa and partnered with some African groups to exploit local resources and recruit slave labor for the Americas • Example: Portuguese King Manuel I (who will marry Isabella and Ferdinand’s daughter, responsible for Vasco de Gama and discovery of Brazil) and Congo King Affonoso entered symbiotic relationship. • Congo sells lower class African citizens to King Manuel as prisoners of war for shipment as slaves • Evidence of letters where they address one another as ‘brothers’ and would send one another extravagant gifts. • Eventually Affonoso tried to break ties, but too late • Similar agreements in Nigeria and Ghana http://hnn.us/article/41431 http://www.bbc.co.uk/history/british/abolition/africa_article_01.shtml#four Spanish Caste System 3 present ‘races’ in North America: Spanish, Amerindian, African 1. Peninsulares – Born in Spain, living in the Americas 2. Criollos – pure Spanish blood, born in the Americas 3. Mestizos – mixed race of Native American and Spanish, born in the Americas, Bearing Spanish names, they became the backbone of the Spanish empire in the Americas. Mestizos made up the majority of conscripts in the army; they became artisans, traders, and local officials. 4. Mulattos – typically classified as the first generation of Spanish and African mix 5. Indios – Native Americans 6. Africans/Negros – most first generation in the Americans were slaves, but there were many free-black communities, who because of their close social ties to slavery, were in this caste level, as well 7. Zambo – Amerindian and Negro mix http://nativeheritageproject.com/2013/06/15/las-castas-spanish-racial-classifications / Casts System aka Spanish Caste System 3 present ‘races’ in North America: Spanish, Amerindian, African 1. Peninsulares – Born in Spain, living in the Americas 2. Criollos – pure Spanish blood, born in the Americas 3. Mestizos – mixed race of Native American and Spanish, born in the Americas, Bearing Spanish names, they became the backbone of the Spanish empire in the Americas. Mestizos made up the majority of conscripts in the army; they became artisans, traders, and local officials. 4. Mulattos – typically classified as the first generation of Spanish and African mix 5. Indios – Native Americans 6. Africans/Negros – most first generation in the Americans were slaves, but there were many free-black communities, who because of their close social ties to slavery, were in this caste level, as well 7. Zambo – Amerindian and Negro mix http://nativeheritageproject.com/2013/06/15/las-castas-spanish-racial-classifications / • Sambo, 1770 • Little Black Sambo - 1899 Amerindians and Africans struggle for autonomy • In spite of slavery, Africans’ cultural and linguistic adaptations to the Western Hemisphere resulted in varying degrees of cultural preservation and autonomy • Examples: (think Salem Witch Trials influence) • Syncretic Religions formed • Santeria – Yoruba and Catholicism • Louisiana Voodoo • Language • Formation of pidgin languages • Runaway slaves would often form maroon communities, particularly in the Caribbean, armed groups often run to smaller islands or eventually conquered • Some major rebellion stories such as the Amistad (1840) Additional Things To Know • Ferdinand & Isabella • Coronado • Cortes • Moctezuma • Incas • Aztecs • Treaty of Tordesilla • Bartolome de Las Casas