File apunit14outlineguide
advertisement

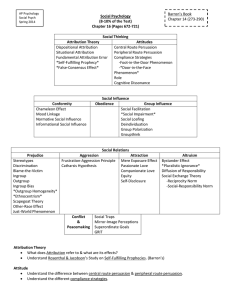
Unit 14: Social Psychology Outline Guide Social Psychologists Attributing Behavior to Persons or to Situations Attribution Theory Example Fundamental Attribution Error Study How might disposition vary? Effects of Attribution Marriage Politics Work Attitudes & Actions Attitudes Affect Actions Central Route Persuasion Peripheral Route Persuasion External Situation Actions Affect Attitudes Foot-in-the-Door Phenomenon Example Role-Playing Affects Attitudes Role Zimbardo’s Prison Experiment 1 Cognitive Dissonance Theory Example Social Influence Conformity & Obedience Chameleon Effect Mood Linkage Bad side of suggestibility Group Pressure & Conformity Conformity Soloman Asch Conditions that Strengthen Conformity (7) Reasons for Conforming Normative Social Influence Informational Social Influence Baron Study Obedience Stanley Milgram Obedience was highest when (4): Lessons from Conformity/Obedience Studies (3) 2 Group Influence Individual Behavior in Presence of Others Social Facilitation Example Easy vs. Difficult tasks Crowding Social Loafing Example Why? (2) Deindividuation Example Effects of Group Interaction Group Polarization Example Benefits Negatives Role of the Internet Groupthink Example What feeds groupthink? Cultural Influence Culture 3 How has culture changed our lives? Variation Across Cultures Norms Personal Space Who likes more/less? Expressiveness Pace of Life Variation Over Time Positives Negatives Power of Individuals Social Control Personal Control Minority Influence (3) Social Relations Prejudice Mixture of: Prejudice vs. Discrimination How Prejudiced are People? Overt vs. Subtle Modern Prejudice 4 Examples of overt prejudice Role of Gender (negative and positive) Social Roots of Prejudice Social Inequalities “Haves” justification Role of Stereotypes Blame-the-Victim Dynamic Us (Ingroup) & Them (Outgroup) Social Identities Similar Outgroups Ingroup Bias Emotional Roots of Prejudice Fear Anger Scapegoat Theory Role of feelings of insecurity Cognitive Roots of Prejudice Categorization Outgroup homogeneity Other-race Effect Exposure Vivid Cases Study 5 Just-World Phenomenon Role of Hindsight Bias Aggression Biology Genetic Influences Neural Influences Biochemical Influences High Testosterone Correlates with: Two-way influence Alcohol Psychological & Social-Cultural Factors Aversive Events Frustration-Aggression Principle Example Other aversive stimuli Social & Cultural Influences Learning principles Ostracism Ancestry Absent Fathers Parent-training suggests Observing Models 6 Study example Social Scripts Study example Video Games Study example Problem with Catharsis Hypothesis Attraction Psychology of Attraction Proximity Mere Exposure Effect Evolution Physical Attractiveness How do we see physically attractive people? Unrelated to self-esteem (2): Culture Averageness Similarity Dissimilarity Reward Theory of Attraction Romantic Love Passionate Love Role of physical arousal 7 Companionate Love Adaptive Equity Self-disclosure Study example Altruism Bystander Intervention We will help under these conditions (3): Role of the Presence of Others Diffusion of Responsibility Study example Gender difference Bystander Effect Norms for Helping Social Exchange Theory Example Intrinsic motivation Reciprocity Norm Social-Responsibility Norm Conflict and Peacemaking Conflict Social Traps 8 Threats to communal well-being Efforts to promote mutual betterment (3): Enemy Perceptions Mirror-Image Perceptions Example Self-Fulfilling Prophecies Example Contact University College London experiment Resegregation Cooperation Superordinate Goals Study example Fearsome external threat Communication Mediators Conciliation GRIT How does it work? Personal conflict example 9