Social Psychology Outline
advertisement
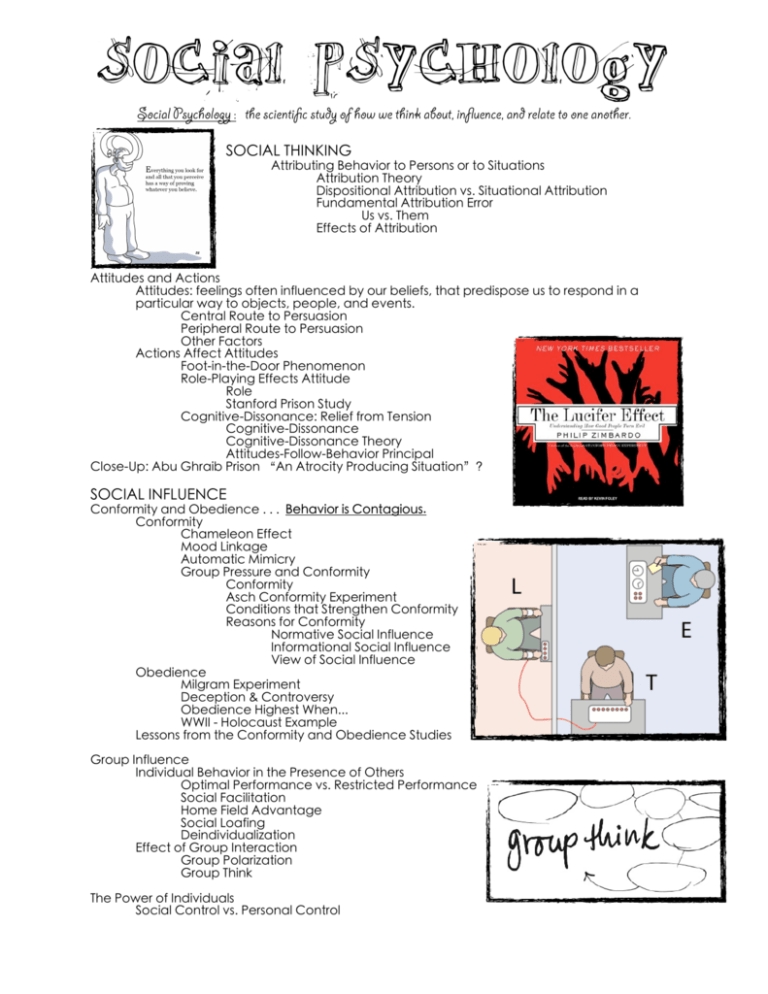
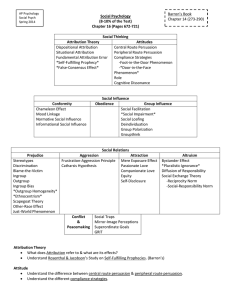
Social PSYCHOLOGY Social Psychology : the scientific study of how we think about, influence, and relate to one another. SOCIAL THINKING Attributing Behavior to Persons or to Situations Attribution Theory Dispositional Attribution vs. Situational Attribution Fundamental Attribution Error Us vs. Them Effects of Attribution Attitudes and Actions Attitudes: feelings often influenced by our beliefs, that predispose us to respond in a particular way to objects, people, and events. Central Route to Persuasion Peripheral Route to Persuasion Other Factors Actions Affect Attitudes Foot-in-the-Door Phenomenon Role-Playing Effects Attitude Role Stanford Prison Study Cognitive-Dissonance: Relief from Tension Cognitive-Dissonance Cognitive-Dissonance Theory Attitudes-Follow-Behavior Principal Close-Up: Abu Ghraib Prison “An Atrocity Producing Situation”? SOCIAL INFLUENCE Conformity and Obedience . . . Behavior is Contagious. Conformity Chameleon Effect Mood Linkage Automatic Mimicry Group Pressure and Conformity Conformity Asch Conformity Experiment Conditions that Strengthen Conformity Reasons for Conformity Normative Social Influence Informational Social Influence View of Social Influence Obedience Milgram Experiment Deception & Controversy Obedience Highest When... WWII - Holocaust Example Lessons from the Conformity and Obedience Studies Group Influence Individual Behavior in the Presence of Others Optimal Performance vs. Restricted Performance Social Facilitation Home Field Advantage Social Loafing Deindividualization Effect of Group Interaction Group Polarization Group Think The Power of Individuals Social Control vs. Personal Control Social PSYCHOLOGY Minority Influence SOCIAL RELATIONS Prejudice Prejudice, Stereotype, Discrimination How Prejudiced are People? Overt vs. Subtle Prejudice Close-Up: Automatic Prejudice Implicit Racial Associations Unconscious Patronization Race-Influenced Perceptions Seeing Black Reflexive Bodily Responses Social Roots of Prejudice Social Inequalities Us and Them: Ingroup and Outgroup Ingroup Bias Emotional Roots of Prejudice Scapegoat Theory Cognitive Roots of Prejudice Categorization Other-Race Effect vs Own-Race Bias Vivid Cases The Just-World Phenomenon Just-World Phenomenon Aggression The Biology of Aggression Genetic Influences Neural Influences Biochemical Influences Psychological and Social-Cultural Factors in Aggression Aversive Events Frustration-Aggression Principle Fight or Flight Reaction Social and Cultural Influences Ostracism Cultural Impact Aggression-Replacement Program Observing Models of Aggression X-Rated Films and Aggression Rape Myth Zillman Studies Acquiring Social Scripts VIdeo Game Violence Close-Up: Parallels Between Smoking Effects and Media Violence Effects Attraction Psychology of Attraction Proximity Mere Exposure Effect Physical Attractiveness Similarity Close-Up: Online Matchmaking and Speed Dating Romantic Love Passionate Love Compassionate Love Equity Self-Disclosure Social PSYCHOLOGY Altruism Bystander Intervention Diffusion of Responsibility Bystander Effect Best Odds for Help Norms for Helping Utilitarianism Social Exchange Theory Reciprocity Norm Social-Responsibility Norm Conflict and Peacemaking Conflict Social Traps Conditions Where Most Likely to Cooperate Enemy Perceptions Mirror-Image Perceptions Contact Cooperation Superordinate Goals Communication Conciliation GRIT ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: Unit 15 – Social Psych • How are individuals affected by groups? • How do people explain (or attribute) the behavior of others? What impact does this have on individuals and society as a whole? • Under what conditions do people obey, conform, make friendships, find love, and help others? • How do attitudes and actions influence individual and group behavior? • How do psychologists define culture? What influence does culture have on individuals and groups?