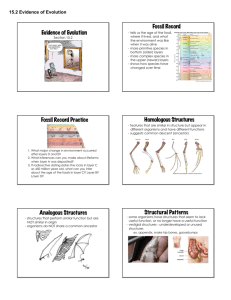
Vestigial Structures
advertisement

DO NOW 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What is fitness? If an organism does not have high fitness what will happen to it? What will happen to its species? In natural selection, what decides the best traits to “keep” What are changes in genetic info called? What is a fossil? EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION Objectives: Understand homologous structures Be able to give an example of a vestigial structure Know that molecules can also be vestigial Vocabulary Homologous structures Analogous structures Vestigial structure Homologous Protein Homologous Genes Evidence for Evolution • By Darwin’s time, scientists had noted that all vertebrate limbs had the same basic bone structure. Common Descent Common descent – all organisms on this planet come from a single common ancestor This was from Monday’s vocabulary Comparing Anatomy and Embryology – The front limbs of amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals contain the same basic bones. Homologous • Darwin proposed that animals with similar structures evolved from a common ancestor with a basic version of that structure. • homologous structures - Structures that are shared by related species and that have been inherited from a common ancestor Homologous Structures Analogous Structures Analogous structures – structures that share a common function, but not structure Vestigial Structures Vestigial Structures – structures that have lost much or all of their original function Vestigial structures/ vestigial genes are some of the strongest evidence for evolution Brainstorm! Vestigial Structures Dolphins have hip bones that do nothing, heck they aren’t even attached anymore! Vestigial Structures Vestigial Structures Refresher Proteins are made of amino acids The instructions for making proteins comes from DNA The flow of information in a cell (any cell) is DNA -> RNA -> Protein Question: If the DNA is changed what happens to the protein? Vestigial Genes In our Genome (our DNA) we have the genes that code for things our ancestors had, but we no longer need. These genes have been sitting in our DNA for millions of years Every once in a while, these genes are expressed. Because they have been dormant for so long they often do not work very well. Atavisms Atavisms also are called "throwbacks" and can be found in modern horses and their relatives despite millions of years of evolutionary separation from their fossil horse ancestors. Atavisms Atavisms are caused because we still have the DNA from our ancient ancestors. Chicken With Teeth Homologous Molecules Homologous proteins – proteins that share extensive structural and chemical properties. That means that they do the same job and look similar. Homologous Genes Homologous genes – are genes that perform the same task These are NO DIFFERENT that homologous alleles Homologous Genes Embryology DNA these letters also spell DAN Everything we are is just an expression of DNA Your eye for example, is at its core nothing more than thousands of T’s G’s C’s and A’s. If one of those T’s G’s C’s or A’s is changed then it is possible that the structure of the eye will change as well. Every time your cells go through mitosis mistakes are made in the DNA Over time these mistake add up We can actually tell how closely related to species are by looking only at these mistakes Exit Ticket 1. 2. What is the difference between a homologous structure and an analogous structure? Give an example of a vestigial structure.