Chapter 13 The Costs of Production
advertisement

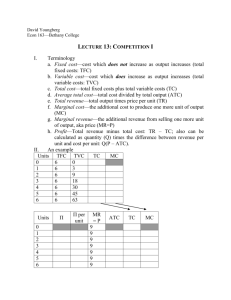
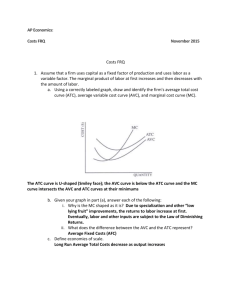
Economists assume goal of firms is to maximize profit Profit = Total Revenue – Total Cost In other words: Amount firm receives for sale of output minus amount that the firm pays to buy inputs Review – What is TR? Firm’s costs of production include all opportunity cost of producing output Explicit costs: require an outlay of $ Implicit costs: don’t require an outlay of $ Economic Profit: Total Revenue – Opportunity Costs of production (implicit & explicit) Accounting Profit: Total Revenue – Explicit Costs only Accounting Profit is greater than Economic Profit Production Function: Relationship between quantity of inputs and quantity of output Marginal Product: increase in the quantity of output obtained by an additional unit of input - How much more can we produce by hiring one more worker? As more workers are hired, each additional worker contributes less to the production As the quantity produced rises, the total cost curve becomes steeper Total cost is divided into fixed & variable costs Fixed costs: do not vary with quantity of output produced (incurred even if the firm produces nothing) Variable costs: Change as the firm alters the quantity of output produced Average Total Cost: Total Cost divided by quantity of output Average Total Cost = Average Fixed Cost + Average Variable Cost Marginal Cost = Increase in total cost by increasing production by one unit of output Putting 4 curves on costs vs. output graph Marginal cost rises with quantity of output because of diminishing marginal product When quantity produced is high – marginal product is low & marginal cost is high U-Shaped because AFC declines as output expands and AVC typically increases as output expands; AFC is high when output levels are low. Bottom of U-shape is quantity that minimizes average total cost, which is called the efficient scale of the firm When marginal cost is less than ATC, ATC is falling. When MC is greater than ATC, ATC is rising Analogy of your GPA 3 important properties: 1. MC eventually rises with quantity of output 2. ATC curve is U-shaped 3. MC curve crosses ATC curve at minimum of ATC These curves include implicit & explicit costs Some costs are fixed in the short run, but ALL costs are variable in the long run The long run ATC curve lies along the lowest points of the short run ATC curve because it has more flexibility to deal with changes in production in long run Still a U-shape but much flatter Economies of scale: long-run ATC falls as quantity of output increases (specialization) Diseconomies of scale: long-run ATC rises as quantity of output increases (coordination problems) Constant returns to scale: long-run ATC stays the same as quantity of output changes