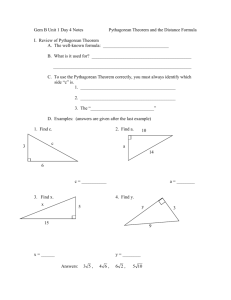
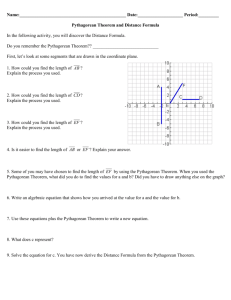
Topic/ Theme/ Duration Pythagorean Theorem
advertisement
Unit Plan Mathematics Unit: 7 Grade: 8 Solve one‐variable linear equations, including cases with infinitely many solutions or no solutions Solve problems involving volumes of cones, cylinders, and spheres together with previous geometry work, proportional reasoning and multi‐step problem solving in grade 7 Pythagorean Theorem Topic/ Theme/ 6 weeks Duration How do we solve for missing sides and angles of triangles? Essential Question(s) Find and understand square and cube roots Key Student the Pythagorean Theorem to find missing sides of right triangles Learning Objectives Use Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find distance on a coordinate plane Standard Explore special right triangles Skills 8.G.6( ). Explain a proof of the Pythagorean Theorem and its converse. Explain a proof of the Pythagorean Theorem and its converse. Tell whether a triangle is a right triangle Resources Supports CMP Looking for Pythagoras Above-grade level (challenging high performers): On grade level: Below grade level: ELL: SWD: Glencoe Chapter 5: Lesson 5, Inquiry Lab Common Core Mathematics CC 8-9, 3.2, 3,3 8.G.7( ). Apply the Pythagorean Theorem to determine unknown side lengths in right triangles in real-world and mathematical problems in two and three dimensions. Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find missing side lengths Apply the Pythagorean Big Ideas Math: 7.3, 7.5 CMP Looking for Pythagoras Glencoe Chapter 5: Lesson 6 Above-grade level (challenging high performers): On grade level: Below grade level: Theorem to real-world and word problems 8.G.8( ). Apply the Pythagorean Theorem to find the distance between two points in a coordinate system. Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find distance between points on a coordinate plane and in real world problems Common Core Mathematics 3.3 Big Ideas Math: 7.3, 7.5 CMP Looking for Pythagoras Glencoe Chapter 5: Lesson 7 Common Core Mathematics 3.4 8.NS.2: Use rational approximations of irrational numbers to compare the size of irrational numbers; locate then approximately on a number line diagram. Big Ideas Math: 7.3, 7.5 CMP Looking for Pythagoras ELL: SWD: Above-grade level (challenging high performers): On grade level: Below grade level: ELL: SWD: Glencoe Common Core Mathematics 3.4 8.EE.2: Use square root and cube root symbols to represent solutions to equations of the form x 2 = p and x3 = p, where p is a positive rational number. Evaluate square roots of small perfect squares and cube roots of small perfect cubes. Know that √2 is irrational. Big Ideas Math: 7.4 CMP Looking for Pythagoras Glencoe Common Core Mathematics 3.4 Vocabulary Sequence of Key Learning Activities Assessments Big Ideas Math: 7.1, 7.2, 7.3, 7.4, 7.5 right triangle, leg, hypotenuse, right angle, Pythagorean Theorem, square root, squared, formula, proof PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM Understand and apply the Pythagorean Theorem Develop strategies for finding the distance between two points on a coordinate grid Explain a proof of the Pythagorean Theorem Use the Pythagorean Theorem and its converse to solve a variety of problems Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the equation of a circle with its center located at the origin REAL NUMBERS Understand that the set of real numbers consists of rational and irrational numbers Interpret square roots and cube roots of numbers by making use of their related geometric representations Relate the area of a square to the side length of the square Estimate the values of square roots Estimate the values of cube roots Relate the volume of a cube to the edge length of the cube Compare numbers that can be represented as fractions (rational numbers) to numbers that cannot be represented as fractions (irrational numbers) and recognize that the set of real numbers consists of rational and irrational numbers Represent rational numbers as fractions and as terminating decimals or repeating decimals Recognize that irrational numbers cannot be represented as fractions and are nonterminating, nonrepeating decimals Recognize that the square root of a whole number that is not a square is irrational Locate irrational numbers on a number line Use and understand properties of rational and irrational numbers Note: Standards in bold are identified as major standards. Standards with checkmarks are standards recommended for greater emphasis GRADE 8 PERFORMANCE TASK: GEOMETRY Standards Solve real-life and mathematical problems involving angle measure, area, surface area, and volume. 7. G.4 Know the formulas for the area and circumference of a circle and use them to solve problems; give an informal derivation of the relationship between the circumference and area of a circle. 7.G.6 Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving area, volume and surface area of two- and three-dimensional objects composed of triangles, quadrilaterals, polygons, cubes, and right prisms. Understand and apply the Pythagorean Theorem. 8. G.3 Describe the effect of dilations, translations, rotations, and reflections on two-dimensional figures using coordinates. 8. G.7. Apply the Pythagorean Theorem to determine unknown side lengths in right triangles in real-world and mathematical problems in two and three dimensions. 8. G.8 Apply the Pythagorean Theorem to find the distance between two points in a coordinate system. Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving volume of cylinders, cones, and spheres. 8. G.9 Know the formulas for the volumes of cones, cylinders, and spheres and use them to solve real-world and mathematical problems. Skills Plot points on a coordinate plane Substitute into the Pythagorean Theorem and solve the equation to find the missing side of a right triangle. Answer word problems using the Pythagorean Theorem by drawing a diagram. Apply formulae for perimeter, area and volume. 5 Fencing and Grassing Your Property You want to put a fence around your large yard. There are two companies that you have found to do the work. They have each given you a quote for how much the work will cost. Of course, you want to find out which company will be the cheapest. The boundary of your yard is determined by five trees. The lines connecting them form the edge of your property. Shown below are the descriptions for the positions of the trees relative to your house. Tree A B C D E Position (relative to your house) 100 ft east 40 ft east, 80 ft south 40 ft west, 120 ft south 90 ft west, 60 ft north 20ft east, 110ft north PART 1: On graph paper, mark the position of each of the trees on your land. Let each block of the graph paper represent a 10-foot by 10-foot square. Using a straightedge, connect Tree A to Tree B, Tree B to Tree C, Tree C to Tree D, and so on. PART 2: a) Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the length of each side of your property. Round each answer to the nearest hundredth, if necessary. b) Determine the perimeter of your property. c) Company 1 says that they will complete the job for $12 per foot of fencing. Company 2 says that they will charge you $250 for the first 100 feet of fencing and $13 for each additional foot. Determine the cost of fencing for both companies. d) Figure out which company will complete the job for the least amount of money PART 3: a) A circular swimming pool with a radius of 20 ft is positioned with a center at 40 ft west and 30 ft north. Mark the position of the pool on your graph. The depth of the swimming pool is 5ft. Calculate the volume of water needed to fill the pool. b) A barn is being built with corners at (30 ft north, 30 ft east); (70 ft east, 30 ft north); (30 ft east, 20 ft south); (70 ft east, 20 ft south). Mark this barn on your graph. c) The rest of the property is to be grassed at a cost of 20 cents per square foot. You have given the contract for the grassing to the company who was cheapest in Step 5. They will give you a discount of 8% on the cost of grassing. Calculate the cost of the grassing. 6 Name: ________________________________ Date: ______________ Part 1: Graph of Your Property Lines Plot the points that represent the trees that mark the edges of your property. Use the locations given on the previous page. To make things easier, use the origin (0, 0) as the position of your house. Remember that each grid represents 10 feet. Finally, connect the points using a straightedge. 7 Name: ________________________________ Date: ______________ Part 2: a) & b) Break your property into smaller parts and use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the length of each side. Remember that each grid line on your graph represents 10 feet. Also remember to round to the nearest hundredth if necessary. Show your work below. Work for the distance from Tree A to Tree B Work for the distance from Tree B to Tree C Distance: ____________ ft Distance: ____________ ft Work for the distance from Tree C to Tree D Work for the distance from Tree D to Tree E Distance: ____________ ft Distance: ____________ ft Work for the distance from Tree E to Tree A Work for the Perimeter of Your Property Distance: ____________ ft Perimeter: ____________ ft c) Company 1 charges $12 per foot of fence. Find the cost if Company 1 completes the job. Show work! Cost: $ ___________ Company 2 charges $250 for the first 100 feet of fence and $13 for each additional foot. Find the cost if Company 2 completes the job. Show work! Cost: $ ___________ d) Both companies must charge a 6% sales tax. Determine which company will be the cheapest. Then, find the cost including tax. Round to the nearest cent. Show work! Company _________ Cost: $ ___________ 8 Part 3a) Calculate the area and volume of the swimming pool (to 1 decimal place). Don’t forget to add the correct units. Area: ________________ Volume: ______________ c) Calculate the area of the grassed area by first calculating the area of the entire property and then subtracting the area of the pool and the barn. Show your working. Calculate the cost of the grassing at $2 per square foot: Cost: $____________ Calculate the discount given: Discount: $___________ Calculate the final cost of the grassing: Cost: $__________ 9 Part 4: If your property was dilated by a factor of ½, what effect will this have on the perimeter? How could you prove your answer is correct? Use the Graph below to help. 10