Ch 9 ppnt
advertisement

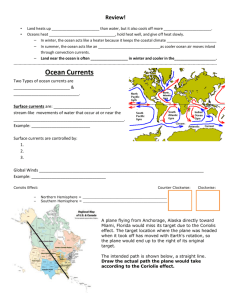
How does the Coriolis effect influence the wind? How do you think this would affect currents in the ocean? Journal 2: WED 1/11 What role do currents play in transporting heat? How do currents affect climate? WEBSITE FOR WEBQUEST: http://www.oar.noaa.gov/k12/html/elnino2.html Highways in the Sea Causes of Currents What forces are responsible for currents? Wind: transfers energy through friction on surface; causes currents and waves Sea level: steeper slope=greater pressure gradient=drives a larger, faster current Water density: greater density in one area causes pressure gradient to drive a current below the surface What influences the direction and nature of these currents? - Ocean boundaries force currents in various directions; - Trade winds and the westerlies account for most of the wind’s energy that drives currents Gyres What is a gyre? Combo of the westerlies pushing water eastward, the trade winds pushing it westward, and the Coriolis effect resulting in the circular flow in each ocean basin 5 major gyres What is an eddie? Friction against water’s surface that causes swirling currents Important because they can profoundly affect local temperatures and water conditions. Commercial fishing vessels use eddies to locate fish Can also influence the speed of a ship Can affect local climates by redistributing heat Western Boundary Currents & Eastern Boundary Currents How do Western Boundary Currents differ from Eastern Boundary Currents? - Eastern Currents: carry cool water towards equator; tend to be wide and shallow; not common to have eddies spin off these currents - Western Currents: much stronger; western intensification: Coriolis effect is a major contributor; there is weak flow of water toward the equator; flow of western boundary currents balances this slow drift; Trade winds also contribute to the strong western currents Upwelling vs. Downwelling Wind-driven currents that flow vertically Upwelling: upward vertical current that brings deep water to the surface Downwelling: downward vertical current that pushes surface water deep into the ocean What kind of biological effect does this have? -nutrients to shallow waters and to deeper waters -weather patterns El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO) Buildup of warm water in the Central and Eastern Equatorial Pacific Tremendously affects world weather patterns El Niño = warm surface current in equatorial eastern Pacific that occurs periodically around Christmastime Southern Oscillation = change in atmospheric pressure over Pacific Ocean accompanying El Niño ENSO describes a combined oceanic-atmospheric disturbance Normal Conditions in the PO El Nino Conditions El Nino Effect on weather, marine habitats, and human activity Most severe events of ENSO caused flooding, tornados, drought; 23,000 deaths and $33 billion in damages Ruins kelp beds by warming the water b/c kelp only thrives in moderate to cold waters This also affects local fish populations and other marine ecosystems La Nina Powerful upwellings bring deep cooler waters to the surface This colder than normal condition is called La Nina (opposite of El Nino) Scientists still trying to determine what exactly causes these warm and cold phases Ocean Conveyor Belt The interconnected flow of currents that redistribute heat Earth’s “air conditioner” Moderates the world’s climate Ocean Conveyor Belt Animation: http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire/content/chp58/5 802003.html Examples of Instruments/Methods that scientists use to study currents 1. Drogue: float that determines the drift of currents 2. Argo Float: float that transmits data to satellites 3. Various Flow Meters: measure and record current speed and direction (Eulerian study method) 4. Doppler Acoustic Current Meter: determines current direction and speed 5. Flotsam method: accidental opportunities to study currents; ships losing cargo that wash up on beaches and can improve computer models of currents CFA: SO3b: Explain the influence of the Coriolis effect on winds, ocean currents, and on weather and climate. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. What is the difference between an upwelling and downwelling? How does El Nino (ENSO) effect the Earth’s climate and weather? What is an eddie? How does it effect Earth’s climate? What forces are responsible for currents? Explain. What is the Ocean Conveyor Belt? Use a Venn Diagram to differentiate between western boundary and eastern boundary currents.