Unit 4
advertisement
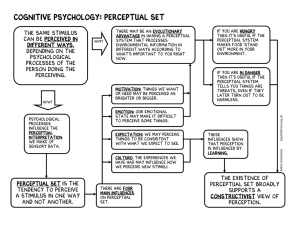
Unit 4: Sensation & Perception • • • • • • Definitions Sensory Systems Vision Hearing The Other Senses Perception STIMULUS A form of energy in the environment which can elicit a response. SENSE A particular physiological pathway for responding to a specific kind of stimulus energy. SENSATION The process by which stimulus energies are detected and encoded. TRANSDUCTION The breaking down of stimulus energies into neural impulses. What's out there (stimuli) is far removed from what we sense and perceive! The Senses • • • • • Vision Audition Gustation Olfaction Touch Some other senses: • • • Equilibrium-balance Kinesthesis-limb position & movement “Internal” Sense Vision • • Physiology of the Eye How We See Color Vision- Receptors Receptors in the Human Eye Cones Rods Number 6 million 120 million Location in retina Center Periphery Sensitivity in dim light Low High Color sensitive? Yes No How we see color Trichromatic (three color) Theory – Young and Helmholtz – three different retinal color receptors red green blue How we see color Opponent-Process Theory- opposing retinal processes enable color vision “ON” “OFF” red green green red blue yellow yellow blue black white white black Color-Deficient Vision People who suffer red-green blindness have trouble perceiving the number within the design Audition Physiology of the Ear The Other Senses Gustation Four basic taste sensations: SWEET, SOUR, SALTY, BITTER The Other Senses Olfaction Physiology Smell Seven Basic Smells? Floral Minty Musky Pungent Putrid Ethereal Camphoraceous The Other Senses Touch • • • Four basic touch sensations: PAIN, PRESSURE, WARM, COLD Pressure sensitivity and the two-point discrimination PERCEPTION The mental process by which sensations are organized and interpreted. Nature Theories The Gestalt Psychologists • • • Our perceptual abilities are inborn! Gestalt means-the whole is greater (different) than the sum of its parts. Gestalt principles of perceptual organization Proximity A perceptual tendency to group together visual & auditory events that are near each other. Similarity A perceptual tendency to group together similar elements. Continuity A perceptual tendency to group stimuli into smooth, continuous patterns. Closure A perceptual tendency to fill in gaps thus enabling one to perceive disconnected parts as a whole object. Figure-Ground The organization of the visual field into objects that stand out from their surroundings. Nature Theories Depth Perception • • Our ability to see depth or see in three dimensions. Eleanor Gibson & the visual cliff Depth Perception Binocular & Monocular Cues • • Retinal Disparity Convergence • • • • • Relative Size Overlap/Interposition Texture Gradient Relative Motion Linear Perspective Nurture Theories Our abilities to perceive are learned through experience! Nurture Theories Perceptual Constancy • Perception that objects have a constant size, shape and color regardless of sensory changes. Nurture Theories Perceptual Set • • • A mental predisposition that influences what we perceive. WHAT INFLUENCES OUR PERCEPTUAL SET? Immediate context, culture, etc.