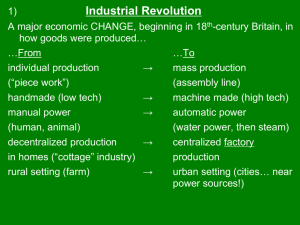
ap 15 ppt review
advertisement

• . In preindustrial Europe, the economy of a household that developed on farms, in artisans’ workshops, and in small merchants’ shops, and was known as the • Domestic economy • Private economy • Merchant economy • Household economy • Family economy • . In preindustrial Europe, the economy of a household that developed on farms, in artisans’ workshops, and in small merchants’ shops, and was known as the • Domestic economy • Private economy • Merchant economy • Household economy • Family economy • The enclosure movement is best assessed by which of the following statements? • A peasant movement demanding special courts for nobles who were accused of fur collar crime • A set of naval maneuvers perfected by Sir Francis Drake • A set of military fortifications separating Alsace Lorraine from Germanic lands • A set of rules governing trade between the Germanic states involved in the Zollverien • The slow movement away from the open field system as the nobility fenced in their land and moved the peasants off of it. • The enclosure movment is best assessed by which of the following statements? • A peasant movement demanding special courts for nobles who were accused of fur collar crime • A set of naval maneuvers perfected by Sir Francis Drake • A set of military fortifications separating Alsace Lorraine from Germanic lands • A set of rules governing trade between the Germanic states involved in the Zollverien • The slow movement away from the open field system as the nobility fenced in their land and moved the peasants off of it. • All of the following were causes of explosive growth in the population of Europe during the 18h century EXCEPT • Disappearance of the plague • Improvement in sanitation • Better nutrition • Fewer deaths • Immigration from North America • All of the following were causes of explosive growth in the population of Euroipe during the 18h century EXCEPT • Disappearance of the plague • Improvement in sanitation • Better nutrition • Fewer deaths • Immigration from North America • The system of cottage manufacture (or the "putting-out" system) originated, in part, as a way for entrepreneurs to avoid: • (A) capitalism • (B) guild regulations • (C) church tithes • (D) child labor laws • (E) mercantilistic export restrictions • The system of cottage manufacture (or the "putting-out" system) originated, in part, as a way for entrepreneurs to avoid: • (A) capitalism • (B) guild regulations • (C) church tithes • (D) child labor laws • (E) mercantilistic export restrictions • The enclosure movement in eighteenth-century England did which of the following? • (A) Provided cheap housing for the rural poor. • (B) Secured the nation's coastal defenses. • (C) Initiated a program of church-building throughout the country. • (D) Encouraged the development of market oriented agricultural production. • (E) Barred Roman Catholic heirs from the throne • The enclosure movement in eighteenth-century England did which of the following? • (A) Provided cheap housing for the rural poor. • (B) Secured the nation's coastal defenses. • (C) Initiated a program of church-building throughout the country. • (D) Encouraged the development of market oriented agricultural production. • (E) Barred Roman Catholic heirs from the throne • Which of the following best describes the enclosure movement? • (A) A system of high tariffs erected by Philip II of Spain • (B) A military maneuver developed by Henry V of England • (C) The fencing of common farmland in England for private use • (D) A network of improved roads and bridges • (E) The erection of a fortified line between France and Germany • Which of the following best describes the enclosure movement? • (A) A system of high tariffs erected by Philip II of Spain • (B) A military maneuver developed by Henry V of England • (C) The fencing of common farmland in England for private use • (D) A network of improved roads and bridges • (E) The erection of a fortified line between France and Germany • The enclosure movement in Britain was most directly a result of • The development of the manorial system • The failure of merchantislism • The collectivization of agriculture • The development of the Bessemer process • The development of market-oriented agriculture • The enclosure movement in Britain was most directly a result of • The development of the manorial system • The failure of merchantislism • The collectivization of agriculture • The development of the Bessemer process • The development of market-oriented agriculture • The cottage industry or putting-out system that had dramatic effect on European economic and social life in the 18th century primarily produced • Steel • Iron • Cotton • Guns • Textiles • The cottage industry or putting-out system that had dramatic effect on European economic and social life in the 18th century primarily produced • Steel • Iron • Cotton • Guns • Textiles • • • • • • The putting out system Created the urban craft industry Reduced rural poverty Eliminated the need for merchant capitalists Destroyed cottage industry Replaced factory manufacturing • • • • • • The putting out system Created the urban craft industry Reduced rural poverty Eliminated the need for merchant capitalists Destroyed cottage industry Replaced factory manufacturing • The process in which children in their young teens would leave their nuclear family, learn a trade, and eventually marry and form their own independent household is known as • Alienation • Neolocalism • Taille • Hobereaux • Corvees • The process in which children in their young teens would leave their nuclear family, learn a trade, and eventually marry and form their own independent household is known as • Alienation • Neolocalism • Taille • Hobereaux • Corvees • In pre-industrial Europe, the dominant concern of married women was • Childrearing • Producing enough farm goods to ensure an adequate food supply • Childbearing • Improving the social status of their husbands • Domestic duties such as cooking, cleaning and sowing • In pre-industrial Europe, the dominant concern of married women was • Childrearing • Producing enough farm goods to ensure an adequate food supply • Childbearing • Improving the social status of their husbands • Domestic duties such as cooking, cleaning and sowing • The Industrial Revolution was partially responsible for all of the following developments in Great Britain EXCEPT • • (A) an increase in the mobility of the work force • (B) the improvement of the transportation network • (C) increased emigration to the colonies • (D) a large increase in annual national income • (E) an increase in the number of small landowners • The Industrial Revolution was partially responsible for all of the following developments in Great Britain EXCEPT • • (A) an increase in the mobility of the work force • (B) the improvement of the transportation network • (C) increased emigration to the colonies • (D) a large increase in annual national income • (E) an increase in the number of small landowners • Important prerequisites for Great Britain’s industrialization in the mid-eighteenth century included which of the following? • • (A) Innovations in agricultural techniques and increases in food production • (B) Dramatic improvements in workers’ housing in the cities • (C) A rapid increase in the amount of gold imported from New World colonies • (D) Rapid growth of a national system of rail transport • (E) Strong monarchical leadership and a centralized government bureaucracy • Important prerequisites for Great Britain’s industrialization in the mid-eighteenth century included which of the following? • • (A) Innovations in agricultural techniques and increases in food production • (B) Dramatic improvements in workers’ housing in the cities • (C) A rapid increase in the amount of gold imported from New World colonies • (D) Rapid growth of a national system of rail transport • (E) Strong monarchical leadership and a centralized government bureaucracy • Throughout the Industrial Revolution, the country that held the lead in innovation and industrial production was • Russia • France • Germany • Great Britain • e. Holland • Throughout the Industrial Revolution, the country that held the lead in innovation and industrial production was • Russia • France • Germany • Great Britain • e. Holland • Improvements associated with the Agricultural Revolution of the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries began in • • (A) France and Spain • (B) the Low Countries and Britain • (C) Prussia and Saxony • (D) Poland • (E) Russia • Improvements associated with the Agricultural Revolution of the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries began in • • (A) France and Spain • (B) the Low Countries and Britain • (C) Prussia and Saxony • (D) Poland • (E) Russia • . The 18th century agricultural revolution included all of the following EXCEPT • Rotating crops with nitrogen-fixing plants and root plants • Enclosure of common land • Better animal breeding practices • New crops, such as potatoes and turnips • The use of chemical fertilizers • . The 18th century agricultural revolution included all of the following EXCEPT • Rotating crops with nitrogen-fixing plants and root plants • Enclosure of common land • Better animal breeding practices • New crops, such as potatoes and turnips • The use of chemical fertilizers • The agricultural changes which took place in England during the 1600s contributed to England’s later industrial development by • A. strengthening the importance of the family farm. • B. breaking large estates into smaller farms. • C. encouraging city dwellers to return to farming. • D. producing more food with fewer workers. • The agricultural changes which took place in England during the 1600s contributed to England’s later industrial development by • A. strengthening the importance of the family farm. • B. breaking large estates into smaller farms. • C. encouraging city dwellers to return to farming. • D. producing more food with fewer workers. • The agricultural revolution of the late 17th and 18th centuries came about because of all of the following EXCEPT • Crop rotation • The Enclosure Movement • Establishment of the open field system • Establishment of capitalist farming • Disappearance of common land • The agricultural revolution of the late 17th and 18th centuries came about because of all of the following EXCEPT • Crop rotation • The Enclosure Movement • Establishment of the open field system • Establishment of capitalist farming • Disappearance of common land • Which of the following factors in the breaking of the traditional population cycle in 18th century Europe? • the Black Death • the Hundred Years War • the development of heavy industry • the development of rural manufacturing • the advent of steam power • Which of the following factors in the breaking of the traditional population cycle in 18th century Europe? • the Black Death • the Hundred Years War • the development of heavy industry • the development of rural manufacturing • the advent of steam power • .Between 1700 and 1800, Europe’s population rose from 100-120 million people to • Almost 750 million • About 310 million • About 520 million • Almost 190 million • Almost 150 million • .Between 1700 and 1800, Europe’s population rose from 100-120 million people to • Almost 750 million • About 310 million • About 520 million • Almost 190 million • Almost 150 million • Introduced from the New World, this new product allowed a more certain food supply in Europe and enabled more children to survive to adulthood and rear children of their own • Squash • Maize • Potato • Wheat • Corn • Introduced from the New World, this new product allowed a more certain food supply in Europe and enabled more children to survive to adulthood and rear children of their own • Squash • Maize • Potato • Wheat • Corn • What industry pioneered the Industrial Revolution? • Housing • Transportation • Textiles • Luxury goods • What industry pioneered the Industrial Revolution? • Housing • Transportation • Textiles • Luxury goods • Factory production of purely cotton fabric was made possible by the invention of the • Putting out system • Flying shuttle • Spinning jenny • Water frame • Factory production of purely cotton fabric was made possible by the invention of the • Putting out system • Flying shuttle • Spinning jenny • Water frame • • • • • • The Industrial revolution came first to Britain Spain France Germany Denmark • • • • • • The Industrial revolution came first to Britain Spain France Germany Denmark • In England, the first country to industrialize , the first industry to implement machinery was • Mining • Textiles • Iron production • Ship building • Railroads • In England, the first country to industrialize , the first industry to implement machinery was • Mining • Textiles • Iron production • Ship building • Railroads • The early Industrial Revolution was detrimental to skilled craftsmen primarily because • Wages went down drastically • They were forced to move to the big cities • The guilds disappeared • The new jobs were for unskilled labor • All of the above • The early Industrial Revolution was detrimental to skilled craftsmen primarily because • Wages went down drastically • They were forced to move to the big cities • The guilds disappeared • The new jobs were for unskilled labor • All of the above • An important social aspect of the early part of the Industrial Revolution in England was the • urbanization of factory workers. • acceptance of rebellious religious groups. • removal of the class system. • development of government-funded housing and medical care programs • An important social aspect of the early part of the Industrial Revolution in England was the • urbanization of factory workers. • acceptance of rebellious religious groups. • removal of the class system. • development of government-funded housing and medical care programs • Which was a geographic advantage for England in the Industrial Revolution? • Coastal mountains. • Moderate climate. • Natural harbors. • Nutrient-rich soil. • Which was a geographic advantage for England in the Industrial Revolution? • Coastal mountains. • Moderate climate. • Natural harbors. • Nutrient-rich soil. • All are important reasons for the Industrial Revolution beginning in England EXCEPT • Agricultural imporvements • Increased demand for manufacture goods • Adequate transportation • Sufficient oil reserves • A banking system • All are important reasons for the Industrial Revolution beginning in England EXCEPT • Agricultural imporvements • Increased demand for manufacture goods • Adequate transportation • Sufficient oil reserves • A banking system • How did the steam engine affect industrial growth? • Goods could be transported to new markets. • It offered a more efficient source of power. • Rail transport came to replace sea transport. • It reduced pollution from oil and coal. • How did the steam engine affect industrial growth? • Goods could be transported to new markets. • It offered a more efficient source of power. • Rail transport came to replace sea transport. • It reduced pollution from oil and coal. • What was the main reason the population of England nearly tripled between 1750 and 1850? • Agricultural improvements. • Better sanitation. • Increased immigration. • The smallpox vaccine • What was the main reason the population of England nearly tripled between 1750 and 1850? • Agricultural improvements. • Better sanitation. • Increased immigration. • The smallpox vaccine • Which of the following was a result of the development of rural manufacturing in the 18th century? • The spread of capital throughout the population • A decrease in total agricultural output • The enclosure movement • Urbanization • The formation of a working class • Which of the following was a result of the development of rural manufacturing in the 18th century? • The spread of capital throughout the population • A decrease in total agricultural output • The enclosure movement • Urbanization • The formation of a working class • Which of the following explains the rapid development of technology in the textile industry in the 18th century • A shortage of labor • The inter-connected nature of technical innovation • The triumph of reason over superstition • The cotton boom • The invention of the steam engine • Which of the following explains the rapid development of technology in the textile industry in the 18th century • A shortage of labor • The inter-connected nature of technical innovation • The triumph of reason over superstition • The cotton boom • The invention of the steam engine • Which of the following might be explained as a result of the introduction of steam power? • The creation of the factory system • The invention of the automobile • Decreased demand for coal • An increased demand for coal • The collapse of the shipping industry • Which of the following might be explained as a result of the introduction of steam power? • The creation of the factory system • The invention of the automobile • Decreased demand for coal • An increased demand for coal • The collapse of the shipping industry • The incentive for the development of large factories associated with England’s early Industrial Revolution was primarily connected with which of the following? • The establishment of railroads • The discovery of new methods of iron production • The increasing demand for weaponry due to imperial warfare • The mechanization of the spinning process in the textile industry • The expansion of the canal system • The incentive for the development of large factories associated with England’s early Industrial Revolution was primarily connected with which of the following? • The establishment of railroads • The discovery of new methods of iron production • The increasing demand for weaponry due to imperial warfare • The mechanization of the spinning process in the textile industry • The expansion of the canal system • Which of the following was most central to the development of the early Industrial Revolution? • The replacement of iron by steel • The shift from human and animal power to mechanical power • The substitution of unionized for independent labor • The decline of individual enterprise in favor of cooperative efforts • The shift from coal to oil-fired forges • Which of the following was most central to the development of the early Industrial Revolution? • The replacement of iron by steel • The shift from human and animal power to mechanical power • The substitution of unionized for independent labor • The decline of individual enterprise in favor of cooperative efforts • The shift from coal to oil-fired forges • In the years between 1600 and 1750, the cities that grew most vigorously were • Free and coastal cities • Capitals and ports • Military forts and capitals • Industrial and ecclesiastical cities • Ports and cities bordering the national line • In the years between 1600 and 1750, the cities that grew most vigorously were • Free and coastal cities • Capitals and ports • Military forts and capitals • Industrial and ecclesiastical cities • Ports and cities bordering the national line • From the Middle Ages through the end of the 18th century, medical manuals advised people to • Wash only parts of their bodies that were covered by clothes • Bathe once a year • bathe every day • wash only the parts of their bodies that could be seen in public • bathe once a week • From the Middle Ages through the end of the 18th century, medical manuals advised people to • Wash only parts of their bodies that were covered by clothes • Bathe once a year • bathe every day • wash only the parts of their bodies that could be seen in public • bathe once a week • The largest single group in 18th century cities was/were • shop keepers, artisans and wage earners • the unemployed • merchants • clergy • the middle class • The largest single group in 18th century cities was/were • shop keepers, artisans and wage earners • the unemployed • merchants • clergy • the middle class • All of the following are true of the steam engine EXCEPT • It enabled industrialization to grow and expand into different areas of production • Its use spread slowly because James Watt retained exclusive patent rights until 1800 • It provided the first steady and virtually unlimited source of inanimate power • It differed from other contemporary engines in that it was powered by burning coal • It was invented by James Watt • All of the following are true of the steam engine EXCEPT • It enabled industrialization to grow and expand into different areas of production • Its use spread slowly because James Watt retained exclusive patent rights until 1800 • It provided the first steady and virtually unlimited source of inanimate power • It differed from other contemporary engines in that it was powered by burning coal • It was invented by James Watt • All of the following conditions led to Great Britain’s preeminence as a industrial leader in the 18th century except • A thriving newspaper industry regularly publicized consumer goods • The economy benefited from consumer demand from the North American colonies • The country’s social structure encourage lower classes to imitate the lifestyles of their social superiors • It lack of free trade kept supply low, which in turn increased consumer demand • The bustling city of London exposed large number of people to the latest in fashions and style • All of the following conditions led to Great Britain’s preeminence as a industrial leader in the 18th century except • A thriving newspaper industry regularly publicized consumer goods • The economy benefited from consumer demand from the North American colonies • The country’s social structure encourage lower classes to imitate the lifestyles of their social superiors • It lack of free trade kept supply low, which in turn increased consumer demand • The bustling city of London exposed large number of people to the latest in fashions and style • The Game Laws exemplified what aspect of 18th century social life in Britain • A governmental willingness to overlook gambling • A nascent environmentalism • Preferential treatment for aristocrats • Fair policies for British landowners and city – dwellers alike • Restrictive policies on aristocratic privilege • The Game Laws exemplified what aspect of 18th century social life in Britain • A governmental willingness to overlook gambling • A nascent environmentalism • Preferential treatment for aristocrats • Fair policies for British landowners and city – dwellers alike • Restrictive policies on aristocratic privilege • Which of the following was a major social effect of the early Industrial Revolution? • • New rhythms of work and leisure • Increase of the average age at first marriage • Rapid improvement in workers’ wages • Decline of children’s employment opportunities • Extensive government efforts to provide public housing • Which of the following was a major social effect of the early Industrial Revolution? • • New rhythms of work and leisure • Increase of the average age at first marriage • Rapid improvement in workers’ wages • Decline of children’s employment opportunities • Extensive government efforts to provide public housing • Thomas Newcomen’s pumping machine, invented in the early 1700s, was considered a radical innovation because • It generated electricity • It was powered by electricity • It was powered by steam • It used fine-kilned brick as a heat insulator • It was the world first prepared motion machine • Thomas Newcomen’s pumping machine, invented in the early 1700s, was considered a radical innovation because • It generated electricity • It was powered by electricity • It was powered by steam • It used fine-kilned brick as a heat insulator • It was the world first prepared motion machine