Chapter 4
advertisement

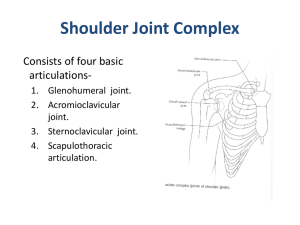
Chapter 6 Humerus & Shoulder Proximal Humerus • ____________ – Rounded portion. • _________________ – Inferior to head slightly constricted area • _________________ – Small process inferior to anatomic neck • _________________ – Large lateral process Proximal Humerus • ____________________ – Space between tubercles. • ___________________ – Tapered area inferior to head & tubercles • Body – Long portion of humerus Humerus Imaging Routine • • • • AP Lateral 40” SID 70 kVp AP Humerus • __________ hand so ___________ are parallel to cassette. • Include _______________ • Center at mid-shaft • Rotate _________ to long axis of humerus • Collimate to skin Lateral Humerus • __________ hand so ____________ are perpendicular to cassette • Include __________________ • Center to mid-shaft • Rotate collimator to long axis of humerus • Collimate to skin Questionable Fracture • _________________!!!!!!! • Erect Mediolateral • X-table Lateral • Transthoracic Erect Mediolateral • • • • • • Pt upright in ___________ Elbow ______________ Move arm posterior, away from the body Align __________________to the IR CR to mid shaft Shoulder may not be on the image X-table Lateral • Pt. Supine • ______________________with positioning sponge • Place ______________________and arm • CR to mid shaft • Shoulder may not be on the image Transthoracic Lateral Trauma • Position ____________with affected side closest to IR • Raise ________________ • Center to surgical neck of Humerus • Use a breathing technique Shoulder Girdle • __________________ – _____________connection to axial skeleton at sternum (Sternoclavicular joint) – ______________ connection by muscles off of scapula Scapula • Posterior aspect of shoulder girdle • ________________bone with: – 3 borders – 3 angles – 2 surfaces Scapula Borders • ________________ Border – Uppermost aspect • _________________Border – Border closest to Arm pit (Axilla) • _________________Border – Border closest to vertebral column Scapula Angles • ___________ Angle – Head of scapula forms glenoid fossa. • ___________ Angle – Lowest point on vertebral border. • ___________ Angle – Highest point on vertebral border. Scapula Surfaces • ___________ Surface – Anterior Surface • ___________Surface – Posterior Surface Scapula Anatomy Costal Surface • _______________Process – Projection off of superior border. • ______________ notch – Depression between superior border and coracoid. Scapular Anatomy Dorsal Surface • _____________ Spine – Elevated projection across posterior scapula • ______________ – Large projection off of spine • Supraspinous fossa – Depression superior to spine • Infraspinous fossa – Depression inferior to spine Shoulder Joint • Scapulohumeral • Spheroidal (Ball and Socket) • ___________________ – “Socket” where humeral head sits Shoulder Imaging • • • • • • • • Routine AP Internal Rotation AP External Rotation Scapular ‘Y’ Glenoid Fossa Axial Transthoracic Lateral (Trauma) 40” SID 75 kVp AP External Rotation • Erect or Supine • ____________ hand so ___________ are parallel to cassette • Center ________________process • Suspend respiration • Shows _____________in profile • __________rotate if fx or dislocation present AP Internal Rotation • Erect or Supine • __________ hand so _______________ are perpendicular to cassette • Center _______________process • Suspend respiration • Shows ________________in profile • _____________rotate if fx or dislocation is present Glenoid Fossa • Erect or Supine • Position into _________________with affected side toward IR. • Abduct arm slightly • Center at shoulder joint • Suspend respiration • Shows _________________ in profile without humerus obstructing Scapular ‘Y’ • Try to position erect • Position into _______________with affected side closest to IR. • Palpate _________________to determine true lateral • Slightly abduct arm • Center to joint space ________________ • Suspend respiration Axial Inferiosuperior • Supine • Place the cassette _____________ to the table against the __________________the neck. • ______________, with external rotation. • Direct the CR through _______________ • Suspend respiration • Shows coracoid process, lesser tubercle, scapular spine, and humeral head glenoid fossa Transthoracic Lateral Trauma • Position ________________with affected side closest to IR • Raise ________________ • Center to surgical neck of Humerus • Use a breathing technique