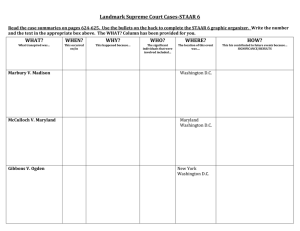
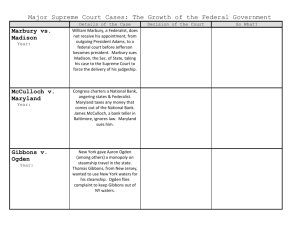
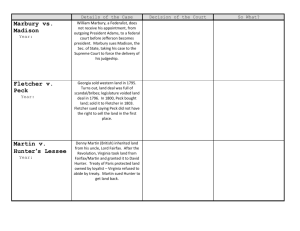
In a series of Marshall Court decisions from 1816
advertisement

In a series of Marshall Court decisions from 1816-1824, A) state charters were not recognized as legal contracts B) a strong federal government was promoted with a broad interpretation of national governmental powers C) Indian removal from the southeastern U.S. was approved D) a strict constructionist view of governmental authority was endorsed E) the relative position of state vs. national authority was not altered In the McCulloch v. Maryland case, the Supreme Court ruled that (A) a federal agency cannot be taxed by a state (B) Congress had the right to rule a law unconstitutional (C) charters were important contracts that states could not undo (D) the Bank of the U.S. charter was a legal document (E) Congress had the right to control interstate commerce Which of the following statements about the 1803 Marbury v. Madison case are accurate? I. It established the principle of judicial review, in which the Supreme Court can rule a law unconstitutional II. It involved federal judges appointed by John Adams prior to his leaving office in 1801 III. It overturned parts of the Judiciary Act of 1789 IV. It was a clear and complete victory for the Federalists, as it made for a more powerful Supreme Court V. It was a clear and complete victory for the DemocratRepublicans, as it denied Federalists control of federal judgeships A) I, II, III, and V only B) I, III, and IV only C) I, II, and III only D) I, II, and IV only E) all of the statements are accurate Which of the following Marshall Court decisions established the principles that state laws were invalid when in conflict with the Constitution and that contracts must be upheld? A) Marbury v. Madison B) Fletcher v. Peck C) Gibbons v. Ogden D) McCullough v. Maryland E) Fletcher v. Peck cases did John Marshall state "The power to tax is the power to destroy?" in an expansion of the implied powers of the federal government? A) Gibbons v. Ogden B) McCulloch v. Maryland C) Dartmouth College v. Woodward D) Martin v. Hunter's Lessee E) Cohens v. Virginia The 1954 Brown v. Topeka Board of Education decision resulted in which of the following? (A) the creation of white citizen councils throughout the deep South (B) the rapid desegregation of schools throughout the U.S. (C) the Montgomery bus boycott (D) the passage of the Civil Rights Act (E) the end of grandfather clauses and literary tests to prevent blacks from voting Which of the following decisions of the Marshall Court is improperly matched with its description? (A) Marbury v. Madison--established the principle of judicial review by overturning an act of Congress, the Judiciary Act of 1789 (B) McCullough v. Maryland--ruled that a state could not tax a federal agency, in this case the Bank of the U.S. (C) Gibbons v. Ogden--gave the federal government undisputed control over interstate commerce (D) Fletcher v. Peck--established the principle that state laws conflicting with the U.S. Constitution were invalid (E) Dartmouth College v. Woodward--states were no longer sovereign since they had signed the Constitution The McCulloch v. Maryland decision by the Marshall Court (A) was the first to rule a law of Congress unconstitutional (B) prevented the midnight judges from taking their positions (C) concerned the binding nature of contracts (D) ruled that a state could not tax a federal institution, in this case the Bank of the United States (E) concerned the rights of Indian tribes in conflict with those of a state's The 1954 Brown v. Topeka Board of Education decision (A) resulted in the immediate integration of schools throughout the South (B) supported the Plessy v. Ferguson doctrine of separate but equal (C) was met with support and enthusiasm throughout the Southern states (D) ruled that separate educational facilities are inherently unequal (E) immediately followed the Montgomery Bus Boycott The Supreme Court case of "Dartmouth College v. Woodward" had to do with a. the rights of freed slaves to attend public school b. state power and private contracts c. states' rights and slavery d. federal power and national banking e. local ordinances and voting rights In which of the following cases did the Court affirm the constitutionality of federal review of state court decisions? A) Gibbons v. Ogden B) Cohens v. Virginia C) Johnson v. McIntosh D) McCulloch v. Maryland The principle that guided John Marshall regarding constitutional questions was the doctrine of A. B. C. D. implied power. strict construction. cooperative federalism. loose construction. The Supreme Court made it clear that the power of judicial review applied to state as well as federal laws in the case of A B C D E Martin v. Hunter’s Lessee. Plessy v. Ferguson. Marbury v. Madison. Mapp v. Ohio. McCulloch v. Maryland. Which of the following are incorrectly matched? A. Dartmouth v. Woodward—prohibited states from altering contracts unilaterally. B. Martin v. Hunter's Lessee—power to review decisions by state courts. C. Gibbons v. Ogden—power to establish a national bank. D. Fletcher v. Peck—power to void state laws. IDENTIFY THE CASE