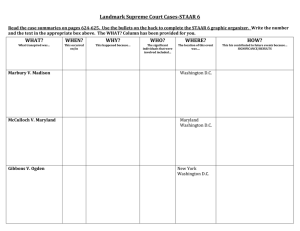
Details of the Case
advertisement

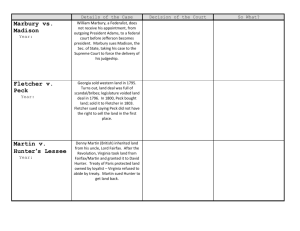
Major Supreme Court Cases: The Growth of the Federal Government Marbury vs. Madison Year: McCulloch v. Maryland Year: Gibbons v. Ogden Year: Details of the Case William Marbury, a Federalist, does not receive his appointment, from outgoing President Adams, to a federal court before Jefferson becomes president. Marbury sues Madison, the Sec. of State, taking his case to the Supreme Court to force the delivery of his judgeship. Congress charters a National Bank, angering states & Federalist. Maryland taxes any money that comes out of the National Bank. James McCulloch, a bank teller in Baltimore, ignores law. Maryland sues him. New York gave Aaron Ogden (among others) a monopoly on steamship travel in the state. Thomas Gibbons, from New Jersey, wanted to use New York waters for his steamship. Ogden files complaint to keep Gibbons out of NY waters. Decision of the Court So What? Major Supreme Court Cases: The Growth of the Federal Government Moral of today’s Lesson: The Constitution says ___________________________________________________________________________________________________. Marbury vs. Madison Year: (1803) Fletcher v. Peck Year: (1810) Martin v. Hunter’s Lessee Year: (1816) McCulloch v. Maryland Year: (1819) Cohens v. Virginia Year: (1821) Details of the Case Decision of the Court So What? William Marbury, a Federalist, does not receive his appointment to a federal court before Jefferson becomes president. He sues Madison, the Sec. of State, to force the delivery of his judgeship, taking his case directly to the Supreme Court. Partly in order to avoid showdown with Jefferson, court rules in favor of Madison, stating that Judiciary Act of 1789 was unconstitutional to start with, thus, Marbury took his case to the wrong place. He does not receive his appointment. Despite backing down to Jefferson, Court gains powerful tool – Judicial Review. Court now has authority to rule whether or not acts of the government are constitutional. Georgia sold western land in 1795. Turns out, land deal was full of scandal/bribes; legislative voided land deal in 1796. In 1800, Peck bought land; sold it to Fletcher in 1803. Fletcher sued saying Peck did not have the right to sell the land in the first place. Court held that since the estate had been legally "passed into the hands of a purchaser for a valuable consideration," the Georgia legislature could not take away the land or invalidate the contract. The Court held that laws annulling contracts or grants made by previous legislative acts were constitutionally impermissible – regardless of intention when passed. Denny Martin, British, inherited land from his uncle, Lord Fairfax. After Revolution, Virginia took land from Fairfax/Martin and granted it to David Hunter. Treaty of Paris protected land owned by loyalist – Virginia refused to abide by treaty. Martin sued Hunter to get land back. VA SC upheld the confiscation, not on the grounds that VA law was superior to US treaties, but because it argued that its own interpretation of the treaty revealed that the treaty did not, in fact, cover the dispute. The USSC disagreed, and remanded the case back to VA S.C., VA argued that the USSC did not have authority over cases originating in state court. The USSC reversed VA’s decision on appeal, ruling that questions of federal law were within its jurisdiction, and thereby establishing supremacy in matters of constitutional interpretation. 1st: protected contracts from state interference. 2nd: Court could overturn state laws that opposed specific provisions of the Constitution Contract Clause: Art I, sect 10, clause 1. It states: “ No State shall…pass any Bill of Attainder, ex post facto Law, or Law impairing the Obligation of Contracts… Court could accept appeals from state courts that involve federal laws or treaties. More importantly, it asserted the Supreme Court’s sovereignty over state courts, rejecting VA’s claim that they were equal sovereigns. Congress charters a National Bank, angering states & Federalist. Maryland taxes any money that comes out of the National Bank. James McCulloch, a bank teller in Baltimore, ignores law. Maryland sues him. Court ruled that Congress did have the authority to charter a bank – via their authority to collect taxes, borrow money, regulate commerce & raise army/navy (necessary and proper). Also, Fed Govt is supreme and states could not interfere; taxing the bank was interference. Established doctrine of implied powers, providing Congress with more flexibility to enact legislation. Reaffirmed supremacy of Federal government. Congress passed a law allowing lottery tickets sold in DC; Cohen brothers sell them in Virginia, breaking VA law. VA convicted brothers and stated that VA courts were the final arbiters of disputes between the states and the national government. Court upheld conviction of Cohen brothers. The larger issue: actually reviewing state court cases. The SC claimed full appellate jurisdiction over any case tried before a state court. VA decided that this was unacceptable & declared the decision the SC made null & void, even though it had upheld the previous conviction, Reasserted federal judicial authority over state courts. Supreme Court argued that when states ratified the Constitution, they gave up some sovereignty to federal courts. Major Supreme Court Cases: The Growth of the Federal Government because VA felt the ruling limited states' rights. Gibbons v. Ogden Year: (1824) New York gave Aaron Ogden (among others) a monopoly on steamship travel in the state. Thomas Gibbons, from New Jersey, wanted to use New York waters for his steamship. Ogden files complaint to keep Gibbons out of NY waters. The Court ruled the monopoly unconstitutional. Constitution grants Congress the power to regulate interstate commerce – along coast or on waterways between states. States could regulate trade within its own border. Gave Congress the right to regulate interstate commerce. Interstate commerce clause (along with Necessary & Proper Clause) major vehicle for expanding federal power.