File
advertisement

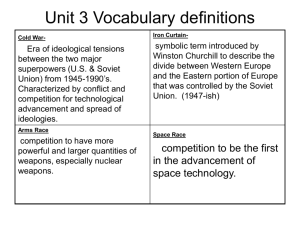
American History Unit 9 The Cold War Soviet Economy • Communism – An economic system where the ownership of factories and businesses is shared comunally and controlled centrally by the government. – The idea is to eliminate the rich and poor classes to make all equal – It generally starts in extremely poor countries with many farmers U.S. Economy • Capitalism – An economic system where the ownership of factories and businesses is private. – Profit is possible • GI Bill – Allowed more people to attend college • Rising middle class – More college graduates lead to an expansion of the middle class • Suburban sprawl – More people could afford homes and new houses were built outside of cities • The U.S. bragged about its economic success during the Cold War Nuclear Obsession • People were fascinated with the Atomic Bomb • Hydrogen Bomb – The U.S. tested even more powerful nuclear weapons on an island called the bikini Atoll • Both the U.S. and the Soviets ammased many nuclear weapons – Both sides said theirs were for defense – but each side saw the other’s as a threatening offensive build up Roots of the Cold War • U.S. opposed the Russian revolution in 1919 • U.S. was “slow” to open the Western Front during WW II • U.S. boasted of powerful weapons at the Potsdam conference • Europe was divided into spheres – Stalin viewed it as a defensive “Buffer zone” – U.S. viewed it as aggressive expansion 1940s • Iron Curtain speech – Delivered by Winston Churchill – March 5, 1946 at Westminster College in Fulton, MO – "From Stettin in the Baltic to Trieste in the Adriatic, an iron curtain has descended across the Continent." – Considered first “blow” of the cold war • Truman – Re-elected in 1948 – First cold war president • Truman doctrine – March 12, 1947 – idea that the United States would provide political, military and economic assistance to all democratic nations under threat from external or internal authoritarian forces 1940s • Containment 1947 – U.S. policy of preventing the spread of communism to other countries – Intervened in revolutions to prevent expansion – Idea George F. Kennan – Officially U.S. policy because of NSC 68 in 1950 1940s • Marshall plan 1948 – the United States gave $13 billion (approximately $160 billion in current dollar value) in economic support to help rebuild European economies after the end of World War II. – Idea was to prevent poverty to prevent fertile communist conditions – Also maintained sound economies to provide markets for U.S. goods • NATO – Founded in 1949 – Alliance of non-communist countries formed to combat the spread of communism and defend against a possible communist attack 1940s • East/West Germany – After WW II, Germany was divided by the allied countries – France, Britain and the U.S. split West Germany – Soviets controlled East Germany and they became communist • Berlin – Located inside of East Germany – Divided among the three powers as well • Stalin – Wanted Germany weak and divided – Decided to close off west berlin from the rest of East Germany – Used a blockade (not a wall yet) – Blockade April1948 -May 1949 (eventually reopened) – U.S. Airlifted supplies into west Germany to get around the blockades 1940s • Mao Tse-Tung (Zedong) – Leader of Communist forces in China – Wins revolution and drives U.S. backed forces out of China (Chiang Kai Shek) • Taiwan – Non-communist Chinese fled to the island of Formosa – Now known as Taiwan 1940s • Red scare – Initially fear of soviet espionage – Grew into a panic of all things “left” • HUAC – – – – Committee in the House of Representatives House unamerican Activities Committee Investigate suspected subversives Investigated the Movie industry in 1947 • Hollywood Ten – Beginning of the “witch hunt” aspect of the red scare – Hearings with hollywood actors and directors – Ten were blacklisted and not allowed to work in Hollywood • Alger Hiss – State Department Official – Accused by Whittaker Chambers in 1948 of being a Communist (not a spy) – HUAC investigated – Richard Nixon headed the investigation – Began paranoia of government based subversives 1950s • Korean War – 1950-1953 – Communist North, Kim Il Sung – Non-Communist South, Syngman Rhee – North invaded South – United Nations intervened on behalf of the South – Ended up in a stalemate with Korea seperated along the 38th parallel 1950s • Eisenhower – Elected in 1952 and 1956 – Former allied leader in Europe – Built nuclear arsenal as a defense against the Soviets – Coined the Domino Theory • If one country fell to communism that others would follow • We must intervene to prevent spreading 1950s • Warsaw Pact – Formed by Soviet Leader Nikita Khrushchev in 1955 – Defense treaty among 8 communist states in central and eastern Europe – Counterbalance to NATO • Vietnam War – French colony that revolted for its independence – Dien Bien Phu - the decisive battle for independence – Vietnam was divided into North and South with Ho Chi Minh leading the Communist North 1950s • Rosenberg trial 1951 – 1946 Congress mandated death for convicted Atomic spies – Julius and Ethel Rosenberg were convicted and executed for giving secrets to the Soviets • Joe McCarthy – Republican Senator from Wisconsin from 1947-1957 – Served on SISS – He claimed that large numbers of communists and soviet spies were working in the U.S. government – He was the most visible face of the “witch hunts” of the Red Scare – He gained widespread fame and credibility until he attacked the army as full of spies – He was censured by the Senate in 1954 1960s • U2 incident 1960 – An American Spy Plane (U2) was shot down over Soviet Air Space – The plane was flown by a CIA pilot – The U.S. tried to voer up the planes purpose but was forced to admit its attempts at espionage by the Soviets – This lead to further deterioration of U.S.-Soviet relations • John F. Kennedy – Democrat elected president in 1960 – Delivered a speech in Berlin after the Wall was erected in 1961 – Took a tough stance against Khrushchev and the Soviets 1960s • Fidel Castro – Communist leader of Cuba from 1959 to 2008 • Bay of Pigs Invasion – Failed CIA invasion of Cuba to overthrow Castro in 1961 – The failed invasion strengthened the position of Castro's dictatorship and strengthened ties with the USSR. – This led eventually Cuban Missile Crisis • Cuban Missile Crisis – Soviets placed Nuclear Missiles in Cuba in response to U.S. missiles being in Turkey and Italy – This lead to a tense standoff between the U.S. and the Soviets with many worrying that full scale war would erupt – Eventually both sides backed down and the missiles were removed from Cuba 1960s • Tet Offensive – Vietnam War continued – 1968 North Vietnam launched massive attacks on the U.S. forces and the South Vietnamese • SALT I – Strategic Arms Limitations Treaty – Signed between the U.S. and soviets in 1969 – Reduced number of Nuclear weapons that each had 1970s • Nixon – – – – Republican President elected in 1968 First U.S. president to visit Red China First U.S. president to visit the Soviet Union Ended the Vietnam War under his presidency • Détente – General term for the “thawing out” period of the cold war – Generally associated with Presidents Nixon and Ford 1980s • Ronald Reagan – Republican President elected in 1980 and 1984 – Planned the Strategic Defense Initiative (Star Wars) • Defensive satelite system to prevent Nuclear Attack 1980s • 1980 Moscow Olympics – Boycotted by President Carter • 1984 Los Angeles Olympics – Boycotted by Soviet union and Communist Bloc Countries • Mikhail Gorbachev – Soviet Leader from 1985 to 1991 – Brought a new ways of thinking to Soviet leadership – Institutes perestroika and glasnost 1980s • Fall of the berlin wall – Revolutions swept through Eastern Bloc countries as communism began to fall – the East German government announced on 9 November 1989 that movement between nations would be allowed – Many people rushed to visit west Germany and began to break down the wall 1990s • START I – Signed by George H.W. Bush and Mikhail Gorbachev – 31 July 1991 and entered into force on 5 December 1994 – Greatly reduced Nuclear weapons – Essentially the end to cold war • Soviet Union Broke up in 1991