Chapter 6 - schultz915
advertisement

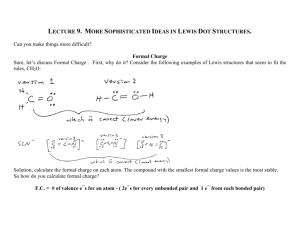
CHAPTER 8 SEC 8.4 Chemical Bonds CH 8 SEC 8.4 DETERMINATION OF BOND TYPE? Bond type: difference in electronegativity? Ionic : 3.3 – 1.7 range of diff. EN Polar covalent : .3 – 1.7 Nonpolar covalent: 0 - .3 Ch 6 table 6.2 for EN values for all atoms p.151 red book in class What type of bonding would be expected between the following pairs of elements? a) Cl and K Ans. Ionic (EN diff = 3.0 - .8 = 2.2) b) O and H Ans. 3.5 – 2.1 = 1.4 polar covalent c) O and O Ans. 3.5 – 3.5 = 0 nonpolar covalent CW: FILL IN THE FOLLOWING CHART WITH A PARTNER – ONE PAPER, TWO NAMES, EVERY OTHER LINE SWITCH WHO WRITES ANSWER. WAIT TO TURN IN…SHARING AT END bonding between: EN diff.: Bond type: More EN atom: 1. Na and Br 2. Ti and O 3. N and N 4. C and O 5. Ba and O 6. P and O 7. Ca and Cl 8. Be and F 9. S and Cl 10. N and O INTERMOLECULAR FORCES Forces of attraction between molecules (weaker than either ionic or covalent bonds) van der Waals forces are the weakest attractions between molecules (two types: dispersion forces & dipole interactions) Hydrogen bonding – “Not a true bond” The intermolecular force in which a hydrogen atom that is bonded to a highly electronegative atom is attracted to an unshared pair of electrons of an electronegative atom in a nearby molecule. Ex/ water molecules: dipole-interactions: Forces of attraction between polar molecules. Ex/ammonia London Dispersion forces: forces of attraction between nonpolar atoms or molecules that are created by temporary dipoles. ex/ Noble gases STRONGEST TO WEAKEST 1. Metallic bonding 2. Covalent bonding 3. Ionic bonding 4. hydrogen bonding (force of attraction, not a bond) 5. dipole-interactions (force of attraction btw polar molecules) 6. London dispersion (force of attraction btw nonpolar atoms – noble gases) CH 8 REVIEW 1. The following molecules contain polar bonds. The only nonpolar molecule is: HCl, H2O, CO2, NH3 2. A polar molecule contains ______________. 3. What is the Lewis structure of HCl? 4. The following molecules contain polar bonds. The only polar molecule is: CCl4, CO2, NH3, CH4 5. Atoms are __________ when they are combined. 6. In a molecule of fluorine, the two shared electrons give each fluorine atom _____ electrons in their outer energy level. 7. In which of the following is NOT a nonpolar covalent bond? HCl, O2, Cl2, H2 8. In metals, the valence electrons ________________________. 9. In drawing Lewis structure, the central atom is the ______________________________. 10. In drawing a Lewis structure, each nonmetal atom except H should be surrounded by _____ electrons. 11. What is the correct Lewis structure for CCl4 ? 12. As independent particles, atoms are ______. 13. VSEPR theory is a model for predicting_________________. 14. If the atoms that share electrons have an unequal attraction for the electrons the bond is called _______________. 15. The chemical formula for water is H2O. What type of formula is that? 16. The mixing of two or more atomic orbitals of similar energies on the same atom to produce new orbitals of equal energies is called ________. 17. The shiny appearance of metals is due to ________________. 18. The elements of the ______ group satisfy the octet rule without forming compounds. 19. According to VSEPR theory what is the shape of ammonia, NH3 ? 20. Use VSEPR theory to predict the shape of HCl? 21.The electrons involved in the formation of a chemical bond are called __________________. 22. In the crystal lattice of an ionic compound, each cation is surrounded by _______________. 23. Malleability and ductility are properties of ________ bonds. 24. Shifting layers in an ionic compound causes it to ___________________. 25. A chemical bond results from the mutual attraction of the nuclei of atoms and _________. 26. A covalent bond results when ________ are shared. 27. The B-F bond in BF3 (electronegativity for B is 2.0 and F is 4.0) is _________________. 28. A neutral group of atoms held together by covalent bonds is a __________________. 29. Which of the following is NOT an example of a molecular formula? B, O2, Cl2, H2, H2O 30. How many double bonds are in the Lewis structure for HF, hydrogen fluoride? 31. How many extra electrons are in the Lewis structure of the sulfate ion, SO42- ? 32. A chemical bond that results from the electrostatic attraction between cations and anions is called a(n)____________________. 33. An octet is equal to ______ electrons. The End ☻