C5: Ionic and Molecular Compounds
advertisement

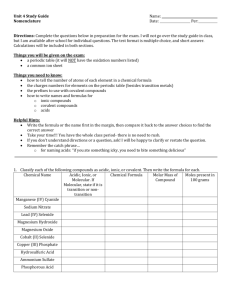
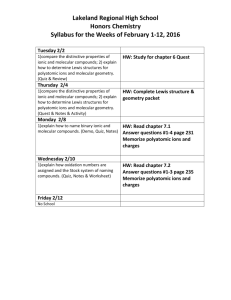
C5: Ionic and Molecular Compounds C5 Vocabulary terms to define: Allotrope Hygroscopic Anhydrous Inorganic compound Binary compound Molecular element Deliquescent Molecular substance Distillation Organic compound Formula unit Oxidation number Hydrate Polyatomic ion Hydrocarbon C5 Vocabulary Quiz Definitions: Word Bank: 1. A compound that only contains two elements. 2. The charge on the ion. 3. An ion group that has two or more different elements. Ie: SO4-2, aka sulfate. 4. A substance that absorbs enough water to become a liquid solution. 5. A compound with all the water removed. 6. A compound held together by a covalent bond 7. A transfer of electrons resulting in a this type of bond. 8. Molecules of the same element with different structure. Ionic bond Molecular substance Oxidation number Formula unit Distillation Allotrope Anhydrous Binary compound Polyatomic ion Hygroscopic 5.1: Ionic Compounds • Review of common properties: • • • • • Transfer of electrons to make ions Electrostatic attraction (opposite charges attract) Brittle Conduct electricity when dissolved in water or molten Strong Bond – High melting points Binary Ionic Compounds • Binary = A compound that contains only two elements. • Examples – KI = potassium iodide – NaCl = sodium chloride Naming Binary Ionic Compounds • Steps: – 1. Write the name of the positively charged ion. • Usually a metal. Example: Na = Sodium – 2. Add the name of the negatively charged ion. • Usually a nonmetal. Example: Chlorine – 3. Change the ending to –ide • Example: Chlorine becomes Chloride Practice Naming Binary Compounds Use your periodic table to name the following: 1.KI 2.KCl 3. CaS 4.NaBr 5.BaO Predicting Charge on Ions Using Charges to write formulas • Oxidation number = charge on ion. • Charges must cancel (equal and opposite for compounds to form) Practice: • • • • 1. lithium oxide 2. calcium bromide 3. sodium oxide 4. aluminum sulfide Polyatomic ions Poly = “many” Polyatomic ion = an ion that has two or more different elements. Writing a formula containing a polyatomic ion • Write the formula for lithium carbonate 1. Find group and charge of lithium using periodic table. 2. Look at polyatomic table and find carbonate. 3. Write the symbols for lithium and carbonate. 4. Determine the correct ratios to cancel charges 5. Check your work Examples and practice • • • • • Sodium phosphate Magnesium hydroxide Ammonium phosphate Potassium dichromate Aluminum sulfate Compounds with Transition metals • C3 we learned Transition metals are not as predictable as representative elements (main group) • Sometimes Transition metals can have more than one charge depending on reaction conditions • We identify the specific charge using Roman Numerals! Examples • Iron(III) sulfate = Fe2(SO4)3 • Copper(II) oxide = CuO Practice • Write the formula for the following: – Copper(I) sulfite – Tin(IV) fluoride – Gold(III) cyanide • Write the names for the following: – Pb(NO3)2 – Mn2O3 – HgF2 Hydrates and Anhydrous Compounds C5-2: Molecular Substances • Substances held together by covalent bonds – Covalent = electrons are shared • Examples of molecular substances: – plastics – Fats, oils etc… – Rubber – Diamond and quartz Properties of molecular substances • Varied properties…soft, elastic, to hard. • Distillation = a method of separating substances in a mixture by evaporation of a liquid and condensing the vapor. Molecular Elements • Meet Mr. BrINClHOF • Diatomics – Br2, I2, N2, Cl2, H2, O2, F2 Allotropes • Molecules of a single element that differ in structure. • Example: Naming Molecular Compounds • Name first element (farthest left element on periodic table). Use a prefix if there is more than one. • Name the second element and use a prefix to denote the number of elements in compound. Change the ending to –ide. Prefixes • • • • • • • • Mono = 1 Di = 2 Tri = 3 Tetra = 4 Penta = 5 Hexa = 6 Hepta = 7 Octa = 9 Nona = 9 Deca = 10 Examples • • • • CO2 = carbon dioxide CO = carbon monoxide N2O3 = dinitrogen trioxide CS2 = carbon disulfide Practice • Name the following molecular substances: – S2Cl2 – SO3 – P4O10 • Write the formula for the following molecular substances: – Carbon tetrachloride – Iodine heptafluoride – Sulfur dioxide C5-1 Summary • Binary ionic compounds: naming and writing formulas • Position on periodic table determines charge • Polyatomic ions – use the table • Transition metals use Roman Numerals • Hydrates v. anhydrous C5-2 Summary • Molecular substances: naming and writing formulas • Seven diatomics: BrINClHOF • Allotropes