Egypt Review Slideshow
advertisement

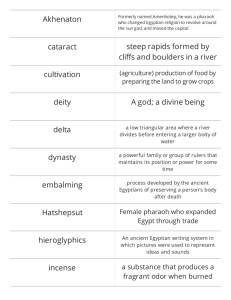
Egypt Locations E. White Nile F. Blue Nile 2. Khartoum 4. Meroe 5. Napata 8. Elephantine Island C. Lake Nasser 1. Aswan 6. Thebes B. Red Sea D. Nile River 3. Memphis 10. Upper Egypt 9. Lower Egypt 7. Alexandria “The Gift of the Nile” key answers • 2. Four natural barriers that isolated ancient Egypt: • Mediterranean Sea to north • Mountains to the south • Deserts to the east and the west 3. Causes of the Nile floods: • Rainfall in central Africa (Lake Victoria) • Snow melt in the Ethiopian Highlands (Lake Tana) 6. Papyrus: • Long, thin reed of a plant • Used to make baskets, boats, sandals and paper 7. Parts of Egypt and locations: • Upper Egypt (in south): from 1st cataract to the delta • Lower Egypt (in north): from Memphis to Med. (the delta) “The Gift of the Nile” key answers • 9. What is dynasty… how many?: • Series of rulers from the same family • 30 different dynasties ruled over Egypt 10a. Old Kingdom: • Dates: 2750– 2260BCE – They build the pyramids 10b. Middle Kingdom: • Dates: 2061 – 1784BCE – Became stronger: achieved in literature, art, and architecture 10c. New Kingdom: • Dates: 1570 – 1070 BCE – Egypt becomes a world power; conquers other nations, builds empires “Life in Egypt” key answers • 1. Why the preparation for afterlife?: • Life would continues after death, needed to be ready • Without a body, person’s spirit couldn’t eat, drink, dance • If body decayed, spirit would die (their Ka) 2. Why were dead buried with objects?: • They needed these items in the afterlife • Would include; food, jewelry, clothes, drink, games, cats, dogs and slaves • Tomb walls were painted with scenes of the dead person’s life 3. “Weighing of the heart”: • Heart was center of intelligence and memory • Used this to weigh it against the “feather of truth” • If heart is lighter than the feather, than they were pure and could go to afterlife • If heart was heavier, they died a second death “Life in Egypt” key answers • 4. Rosetta Stone: • Black, stone tablet which had writing in three different forms • Tablet used to “decode” the hieroglyphics 5. Job of a scribe: • They had extensive training, if you became one, then you had higher social standing than others • If you worked for the pharaoh you could live in his palace 6. Difference between Egypt and Meso kings: • Egypt kings (pharaoh) were thought of as gods, walking amongst the people • In Mesopotamia the kings ruled on behalf of the gods; got assistance from the priests “The Ancient Egyptian Pharaohs” key answers • Key facts: – Capital city of Old Kingdom = Memphis – Middle Kingdom was also known as “Period of Reunification” – New Kingdom was also known as the “Golden Age” • Capital city of New Kingdom = Thebes • Pharaoh Khufu – Pyramid Builder – Controlled food supply, gov’t officials, oversaw harvest of grain – Built first and largest pyramid (at Giza) • His sons (Khafre and Menkare built the other two) “The Ancient Egyptian Pharaohs” key answers • Pharaoh Hatshepsut – Promoter of Trade – 1st woman pharaoh, ruled for 20 years – Sent trade expedition to Punt (modern-day Somalia, Eritrea & Djibouti) – Acquired: gold, ivory, leopard skins, ostrich eggs, feathers, incense, rare woods and monkeys – Had obelisks constructed so people remember her – New Kingdom pharaoh, so buried in side of cliff at Valley of Kings “The Ancient Egyptian Pharaohs” key answers “The Ancient Egyptian Pharaohs” key answers “The Ancient Egyptian Pharaohs” key answers • Pharaoh Thutmose III– Military Leader – – – – Expanded for 20 years Empire from Nubia all way to Euphrates River Nations sent Egypt gifts/tributes Free nations even sent stuff b/c feared Egypt • Pharaoh Ramses II– Military Leader & Master Builder – – – – Called Ramses the Great Ruled for more than 60 years Empire reached into Canaan and north to Asia Minor Built temple at Abu Simbel