Chapter 7 - King William County Public Schools
advertisement

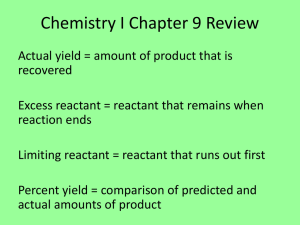
DE CHEMISTRY – King William High School 1 mole = 6.02 x 1023 particles EX: How many molecules of CO2 are in 1.75 moles? EX: How many moles of carbon are in 1.50 moles of C5H10O2? The amount of grams equal to one mole (decimal # from periodic table) EX: What is the molar mass of aluminum oxide? How many grams are in 0.500 moles of sodium chloride? Left of the arrow = reactants (what you start with) Right of the arrow = products (what you end up with…what you make) Must be balanced because of the Law of Conservation of Mass EX: Fe2S3 + HCL FeCl3 + H2S EX: Na3PO4 + MgCl2 Mg3(PO4)2 + NaCl Synthesis (or combination) one product Decomposition one reactant Single replacement one element + one compound on each side of the arrow Double replacement 2 compounds on each side of the arrow Combustion oxygen is a reactant Electrons are transferred from one substance to another OIL RIG EX: Cu (s) + O2 (g) CuO (s) How many moles of sulfur are needed to react with 1.42 moles of iron? Fe (s) + S (s) Fe2S3 (s) How many grams of carbon dioxide are produced when 54.6 g of acetylene is burned? C2H2 + O2 CO2 + H2O Exothermic – released of energy (energy is a product and DH is negative) Endothermic – energy is absorbed (energy is a reactant and DH is positive) How can you speed the rate of a reaction up??? Temperature (molecules move faster so there is a better chance that they collide and react) Concentration (more collisions because more molecules in a given space) Catalyst (lowers energy of activation)