How to Organize Elements… Periodic Table Designs
advertisement

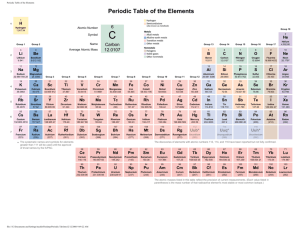
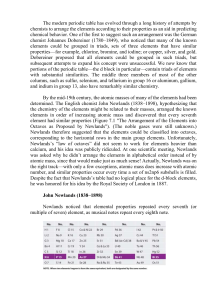
How to Organize Elements… Periodic Table Designs How to Organize… Baseball Cards: year, team, player, card number, value ($). Elements: when they weremass, discovered, family, reactivity, alphabetically, value, density, state or of liquid matter,ormetal solid gas vs. non-metal, atomic mass, atomic number. Which way is CORRECT to organize the elements? Is it possible to organize the elements correctly in more than one way? Interactive Periodic Table e Ir O N Mn 77 1 8 7 25 The Human Element H H He 1 2 1 2 3 Li Be B C N O F Ne 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Al Si P S Cl Ar 13 14 15 16 17 18 Na Mg 11 4 K 19 5 7 Ca Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Br Kr 23 24 35 36 I Xe 53 54 20 21 22 Rb Sr Y Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd In 39 40 41 42 49 Hf Ta W 72 73 74 37 6 12 38 Cs Ba 55 56 Fr Ra 87 88 * W 25 43 26 44 Re Os 75 76 27 28 29 47 30 45 46 Ir Pt Au Hg Tl 77 78 81 79 48 31 80 32 33 34 Sn Sb Te 50 51 Pb Bi 82 83 52 Po At Rn 84 85 86 Rf Db Sg Bh Hs Mt 104 105 106 107 108 109 La Ce Pr Nd Pm Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu 57 58 59 Ac Th Pa 89 90 91 60 U 92 61 62 63 64 65 66 Np Pu Am Cm Bk Cf 93 94 95 96 97 98 67 68 69 70 71 Es Fm Md No Lr 99 100 101 102 103 Aliens Activity Nautilus shell has a repeating pattern. Look carefully at the drawings of the ‘aliens’. Organize all the aliens into a meaningful pattern. Aliens Lab Cards Periodic Table Alkali earth metals H 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8A He Alkali metals 1A Transition metals 3A 4A 5A 6A 7A B C N O F 1 2A Boron group Li Be Nonmetals 3 4 Na Mg 11 12 K Ca 19 20 21 22 Rb Sr Y Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd In 37 38 39 40 41 42 49 Cs Ba Hf Ta W 55 56 72 73 74 Fr Ra 87 88 Noble gases 5 Al 8B 3B 4B 5B 6B 7B 1B 2B Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn 23 24 25 26 43 27 44 Re Os 75 76 28 29 30 47 13 45 46 48 Ir Pt Au Hg Tl 77 78 81 79 80 7 8 9 10 Si P S Cl Ar 14 15 16 17 18 As Se Br Kr 33 32 Sn Sb 50 51 Pb Bi 82 83 34 35 36 Te I Xe 52 53 54 At Rn 85 86 Po 84 Rf Db Sg Bh Hs Mt 104 105 106 107 108 109 Lanthanoid Series 6 C Br Liquid H La Ce Pr Nd Pm Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu 57 Solid 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 Actinoid Series 7 Ac Th Pa U Np Pu Am Cm Bk Cf Es Fm Md No Lr Gas 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 Ne 6 Ga Ge 31 2 100 101 102 103 Dutch Periodic Table 117 116 115 114 113 112 111 110 109 108 107 106 Strong, Journal of Chemical Education, Sept. 1989, page 743 118 Stowe’s Periodic Table Benfey’s Periodic Table Döbereiner’s Triads Johann Döbereiner ~1817 Name Atomic Mass Name Atomic Mass Name Atomic Mass Calcium Barium 40 137 Chlorine Iodine 35.5 127 Sulfur Tellurium 32 127.5 Average 88.5 Average 81.3 Average 79.8 Strontium 87.6 Bromine 79.9 Selenium 79.2 Döbereiner discovered groups of three related elements which he termed a triad. Smoot, Price, Smith, Chemistry A Modern Course 1987, page 161 Newlands Law of Octaves John Newlands ~1863 Newlands Law of Octaves 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Li Na K Be Mg B Al C Si N P O S F Cl Smoot, Price, Smith, Chemistry A Modern Course 1987, page 161 Development of Periodic Table J.W. Döbereiner (1829) Law of Triads Elements could be classified into groups of three, or triads. Trends in physical properties such as density, melting point, and atomic mass were observed. J.A.R. Newlands (1864) Law of Octaves Arranged the 62 known elements into groups of seven according to increasing atomic mass. He proposed that an eighth element would then repeat the properties of the first element in the previous group. Lothar Meyer (1830 – 1895) Invented periodic table independently of Mendeleev his work was not published until 1870 - one year after Mendeleev's